
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Others
- Can Habitual Exercise Help Reduce Serum Concentrations of Lipophilic Chemical Mixtures? Association between Physical Activity and Persistent Organic Pollutants
- Yu-Mi Lee, Ji-Yeon Shin, Se-A Kim, David R. Jacobs, Duk-Hee Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):764-774. Published online May 11, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0158
- 5,410 View
- 87 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Low-dose persistent organic pollutants (POPs), especially organochlorine pesticides (OCPs), have emerged as a new risk factor of many chronic diseases. As serum concentrations of POPs in humans are mainly determined by both their release from adipose tissue to circulation and their elimination from circulation, management of these internal pathways may be important in controlling the serum concentrations of POPs. As habitual physical activity can increase the elimination of POPs from circulation, we evaluated whether chronic physical activity is related to low serum POP concentrations.
Methods A cross-sectional study of 1,850 healthy adults (age ≥20 years) without cardio-metabolic diseases who participated in the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999 to 2004 was conducted. Information on moderate or vigorous leisure-time physical activity was obtained based on questionnaires. Serum concentrations of OCPs and polychlorinated biphenyls were investigated as typical POPs.
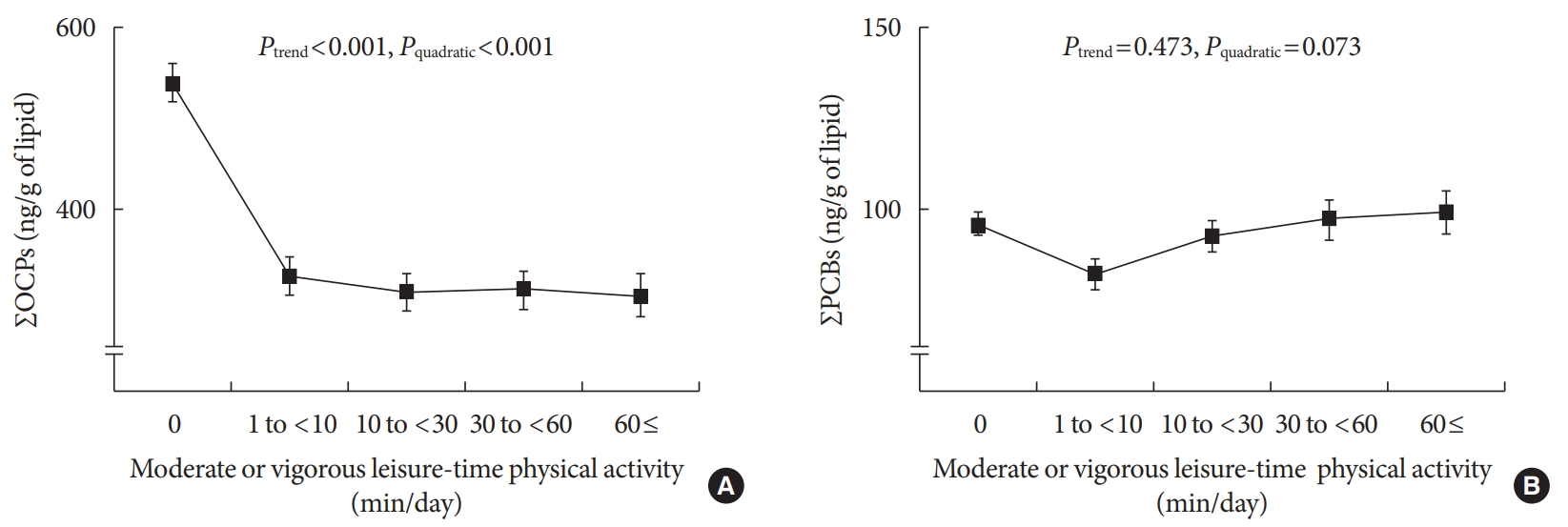
Results Serum concentrations of OCPs among physically active subjects were significantly lower than those among physically inactive subjects (312.8 ng/g lipid vs. 538.0 ng/g lipid,
P <0.001). This difference was maintained after adjustment for potential confounders. When analyses were restricted to physically active subjects, there were small decreases in the serum concentrations of OCPs with increasing duration of physical activity, showing a curvilinear relationship over the whole range of physical activity (P quadratic <0.001). In analyses stratified by age, sex, body mass index, and smoking status, a strong inverse association was similarly observed among all subgroups.Conclusion Physical activity may assist in decreasing serum concentrations of lipophilic chemical mixtures such as OCPs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is Physical Activity an Efficient Strategy to Control the Adverse Effects of Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Context of Obesity? A Narrative Review
Quentin A. Serrano, Sébastien Le Garf, Vincent Martin, Serge S. Colson, Nicolas Chevalier
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 883. CrossRef - Physical exercise and persistent organic pollutants
Chang Liu, Hui sheng Hou
Heliyon.2023; 9(9): e19661. CrossRef - Exposure to a low concentration of mixed organochlorine pesticides impairs glucose metabolism and mitochondrial function in L6 myotubes and zebrafish
Chul-Min Park, Ki-Tae Kim, Dong-Young Rhyu
Journal of Hazardous Materials.2021; 414: 125437. CrossRef - Can Environmental Pollutants Be a Factor Linking Obesity and COVID-19?
Duk-Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Letter to the Editor: Effect of fatty fish or nut consumption on concentrations of persistent organic pollutants in overweight or obese men and women: A randomized controlled clinical trial
Yu-Mi Lee, Duk-Hee Lee
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2020; 30(5): 849. CrossRef - Can habitual exercise really increase serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants?
Yu-Mi Lee, Duk-Hee Lee
Environment International.2020; 140: 105615. CrossRef - Response to correspondence ENVINT_2020_552 “Can habitual exercise really increase serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants?”
Sidsel L. Domazet, Tina K. Jensen, Anders Grøntved
Environment International.2020; 140: 105616. CrossRef
- Is Physical Activity an Efficient Strategy to Control the Adverse Effects of Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Context of Obesity? A Narrative Review
- Others
- Mitochondrial Toxins and Healthy Lifestyle Meet at the Crossroad of Hormesis
- Yu-Mi Lee, Duk-Hee Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(5):568-577. Published online October 24, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0143
- 5,853 View
- 94 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Mitochondrial function is crucial for the maintenance of cellular homeostasis under physiological and stress conditions. Thus, chronic exposure to environmental chemicals that affect mitochondrial function can have harmful effects on humans. We argue that the concept of hormesis should be revisited to explain the non-linear responses to mitochondrial toxins at a low-dose range and develop practical methods to protect humans from the negative effects of mitochondrial toxins. Of the most concern to humans are lipophilic chemical mixtures and heavy metals, owing to their physical properties. Even though these chemicals tend to demonstrate no safe level in humans, a non-linear dose-response has been also observed. Stress response activation, i.e., hormesis, can explain this non-linearity. Recently, hormesis has reemerged as a unifying concept because diverse stressors can induce similar stress responses. Besides potentially harmful environmental chemicals, healthy lifestyle interventions such as exercise, calorie restriction (especially glucose), cognitive stimulation, and phytochemical intake also activate stress responses. This conceptual link can lead to the development of practical methods that counterbalance the harm of mitochondrial toxins. Unlike chemical hormesis with its safety issues, the activation of stress responses via lifestyle modification can be safely used to combat the negative effects of mitochondrial toxins.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) micro- and nanoplastic particles affect the mitochondrial efficiency of human brain vascular pericytes without inducing oxidative stress
Sean M. Gettings, William Timbury, Anna Dmochowska, Riddhi Sharma, Rebecca McGonigle, Lewis E. MacKenzie, Guillaume Miquelard-Garnier, Nora Bourbia
NanoImpact.2024; 34: 100508. CrossRef - Rules of Heliogeomagnetics Diversely Coordinating Biological Rhythms and Promoting Human Health
Kuniaki Otsuka, Germaine Cornelissen, Andi Weydahl, Denis Gubin, Larry A. Beaty, Masatoshi Murase
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(2): 951. CrossRef - Can lipophilic pollutants in adipose tissue explain weight change‐related risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus?
Duk‐Hee Lee, In‐Kyu Lee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(4): 528. CrossRef - Hormetic Effects of Cerium, Lanthanum and Their Combination at Sub-micromolar Concentrations in Sea Urchin Sperm
Giovanni Pagano, Antonios Apostolos Brouziotis, Daniel Lyons, Ivana Čarapar, Rahime Oral, Serkan Tez, Philippe J. Thomas, Franca Tommasi, Giovanni Libralato, Marco Guida, Marco Trifuoggi
Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Mitochondria: It is all about energy
Amaloha Casanova, Anne Wevers, Santiago Navarro-Ledesma, Leo Pruimboom
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Type 2 Diabetes Induced by Changes in Proteomic Profiling of Zebrafish Chronically Exposed to a Mixture of Organochlorine Pesticides at Low Concentrations
Yan Gao, Hyojin Lee, Sangkyu Lee, Ki-Tae Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(9): 4991. CrossRef - Effect of Low-Dose Persistent Organic Pollutants on Mitochondrial Function: Human and in Vitro Evidence
Se-A Kim, Hoyul Lee, Sung-Mi Park, Mi-Jin Kim, Yu-Mi Lee, Young-Ran Yoon, Hyun-Kyung Lee, Hyo-Bang Moon, In-Kyu Lee, Duk-Hee Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 592. CrossRef - Can Environmental Pollutants Be a Factor Linking Obesity and COVID-19?
Duk-Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Intensive weight loss and cognition: The dynamics of persistent organic pollutants in adipose tissue can explain the unexpected results from the Action for Health in Diabetes (Look AHEAD) study
Yu‐Mi Lee, Sun‐Hee Park, Duk‐Hee Lee
Alzheimer's & Dementia.2020; 16(4): 696. CrossRef - Lipophilic Environmental Chemical Mixtures Released During Weight‐Loss: The Need to Consider Dynamics
Duk‐Hee Lee, David R Jacobs, Lars Lind, P. Monica Lind
BioEssays.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Environmental toxicology and ecotoxicology: How clean is clean? Rethinking dose-response analysis
Evgenios Agathokleous, Edward J. Calabrese
Science of The Total Environment.2020; 746: 138769. CrossRef
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) micro- and nanoplastic particles affect the mitochondrial efficiency of human brain vascular pericytes without inducing oxidative stress

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





