
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Complications
- Does the Relationship of the Autonomic Symptoms Questionnaire COMPASS 31 with Cardiovascular Autonomic Tests Differ between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus?
- Ilenia D’Ippolito, Marika Menduni, Cinzia D’Amato, Aikaterini Andreadi, Davide Lauro, Vincenza Spallone
- Received August 28, 2023 Accepted November 22, 2023 Published online February 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0301 [Epub ahead of print]

- 617 View
- 44 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The aim was to investigate if autonomic symptoms questionnaire Composite Autonomic Symptom Score (COMPASS) 31 has different association with cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy (CAN) and diagnostic performance between type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
Seventy-nine participants with T1DM and 140 with T2DM completed COMPASS 31 before cardiovascular reflex tests (CARTs) for CAN, and assessment of symptoms, signs, vibration, and thermal perception thresholds for diabetic polyneuropathy (DPN) diagnosis.
Results
COMPASS 31 total weighted score (TWS) was similar in the two groups, but significantly associated with confirmed CAN only in T1DM (P=0.0056) and not T2DM group (P=0.1768) and correlated with CARTs score more strongly in T1DM (rho=0.356, P=0.0016) than in T2DM group (rho=0.084, P=0.3218) (P=0.016). Only in T1DM and not T2DM group, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) reached a fair diagnostic accuracy (>0.7) for confirmed CAN (0.73±0.07 vs. 0.61±0.08) and DPN (0.75±0.06 vs. 0.68±0.05), although without a significant difference. COMPASS 31 TWS (cut-off 16.44) reached acceptable diagnostic performance in T1DM, with sensitivity for confirmed CAN 81.2% and sensitivity and specificity for DPN 76.3% and 78%, compared to T2DM group (all <70%). AUC for DPN of orthostatic intolerance domain was higher in T1DM compared to T2DM group (0.73±0.05 vs. 0.58±0.04, P=0.027).
Conclusion
COMPASS 31 is more weakly related to CAN in T2DM than in T1DM, with a fair diagnostic accuracy for confirmed CAN only in T1DM. This difference supports a multifactorial origin of symptoms and should be considered when using COMPASS 31.
- Complications
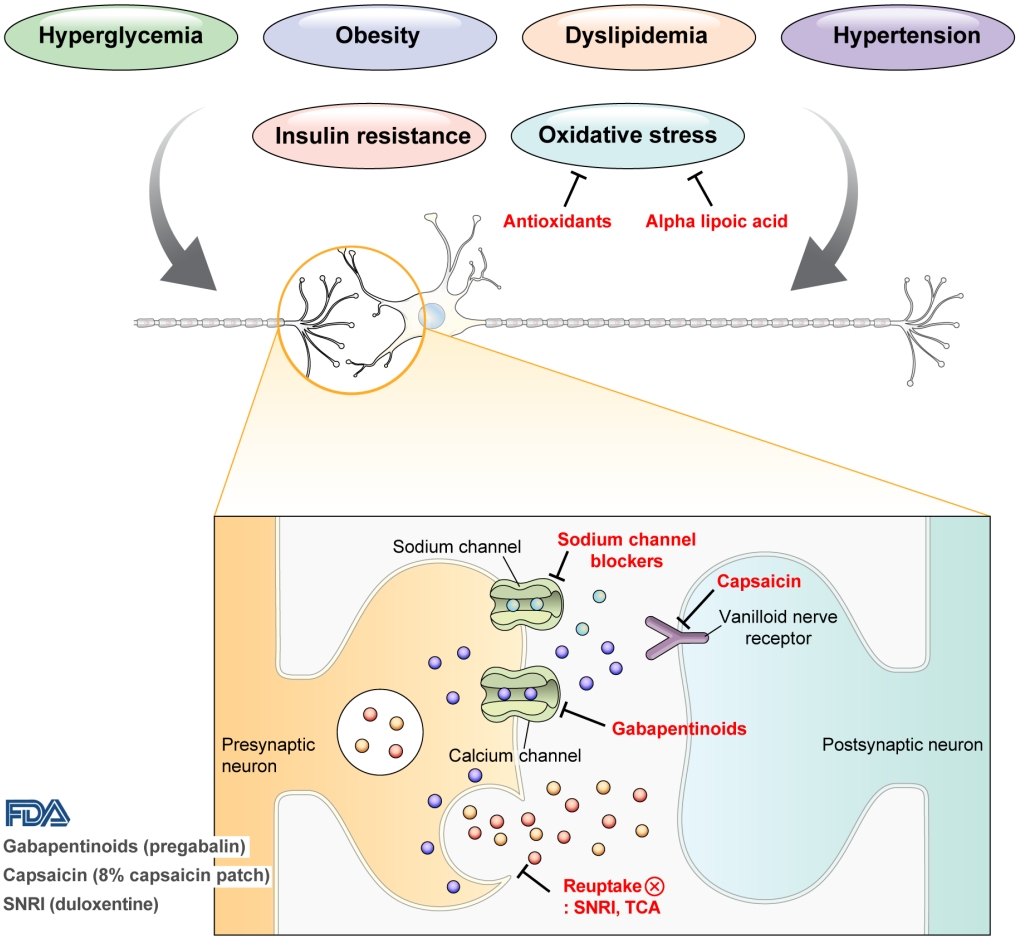
- Pharmacological and Nonpharmacological Treatments for Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
- Han Na Jang, Tae Jung Oh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):743-756. Published online September 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0018
- 3,988 View
- 552 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is one of the most prevalent chronic complications of diabetes. The lifetime prevalence of DPN is thought to be >50%, and 15%–25% of patients with diabetes experience neuropathic pain, referred to as “painful DPN.” Appropriate treatment of painful DPN is important because this pain contributes to a poor quality of life by causing sleep disturbance, anxiety, and depression. The basic principle for the management of painful DPN is to control hyperglycemia and other modifiable risk factors, but these may be insufficient for preventing or improving DPN. Because there is no promising diseasemodifying medication for DPN, the pain itself needs to be managed when treating painful DPN. Drugs for neuropathic pain, such as gabapentinoids, serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, alpha-lipoic acid, sodium channel blockers, and topical capsaicin, are used for the management of painful DPN. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved pregabalin, duloxetine, tapentadol, and the 8% capsaicin patch as drugs for the treatment of painful DPN. Recently, spinal cord stimulation using electrical stimulation is approved by the FDA for the treatment for painful DPN. This review describes the currently available pharmacological and nonpharmacological treatments for painful DPN.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- J-2156, a small molecule somatostatin type 4 receptor agonist, alleviated hindpaw hypersensitivity in the streptozotocin-induced rat model of painful diabetic neuropathy but with a 2-fold decrease in potency at an advanced stage in the model, mimicking mo
A. Kuo, M. Z. Imam, R. Li, L. Lin, A. Raboczyj, A. E. Bohmer, J. R. Nicholson, L. Corradini, M. T. Smith
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Chronic Wound–Related Pain Model
Kevin Woo
Clinics in Geriatric Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- J-2156, a small molecule somatostatin type 4 receptor agonist, alleviated hindpaw hypersensitivity in the streptozotocin-induced rat model of painful diabetic neuropathy but with a 2-fold decrease in potency at an advanced stage in the model, mimicking mo
- Complications
- Effect of the Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Autonomic Function in Subjects with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Carla Greco, Daniele Santi, Giulia Brigante, Chiara Pacchioni, Manuela Simoni
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):901-911. Published online April 12, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0314
- 4,486 View
- 266 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
In addition to the metabolic effects in diabetes, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists lead to a small but substantial increase in heart rate (HR). However, the GLP-1R actions on the autonomic nervous system (ANS) in diabetes remain debated. Therefore, this meta-analysis evaluates the effect of GLP-1R agonist on measures of ANS function in diabetes.
Methods
According to the Cochrane Collaboration and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement, we conducted a meta-analysis considering clinical trials in which the autonomic function was evaluated in diabetic subjects chronically treated with GLP-1R agonists. The outcomes were the change of ANS function measured by heart rate variability (HRV) and cardiac autonomic reflex tests (CARTs).
Results
In the studies enrolled, HR significantly increased after treatment (P<0.001), whereas low frequency/high frequency ratio did not differ (P=0.410); no changes in other measures of HRV were detected. Considering CARTs, only the 30:15 value derived from lying-to-standing test was significantly lower after treatment (P=0.002), but only two studies reported this measurement. No differences in other CARTs outcome were observed.
Conclusion
The meta-analysis confirms the HR increase but seems to exclude an alteration of the sympatho-vagal balance due to chronic treatment with GLP-1R agonists in diabetes, considering the available measures of ANS function. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Liraglutide does not increase heart rate of diabetic patients during acute myocardial infarction
Qianyi Li, Chunxuan Wu, Shiqun Sun, Lingchao Yang, Yanyan Li, Yixin Niu, Li Zhang, Wei Li, Ying Yu
Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hormonal Gut–Brain Signaling for the Treatment of Obesity
Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3384. CrossRef - Effects of new hypoglycemic drugs on cardiac remodeling: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Yi-lin Huang, Xiao-zhuo Xu, Jing Liu, Pin-yao Wang, Xue-li Wang, Hong-lin Feng, Cheng-jiang Liu, Xu Han
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity and hypertension: Obesity medicine association (OMA) clinical practice statement (CPS) 2023
Tiffany Lowe Clayton, Angela Fitch, Harold Edward Bays
Obesity Pillars.2023; 8: 100083. CrossRef - Incretins and microvascular complications of diabetes: neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy and microangiopathy
Jonathan Goldney, Jack A. Sargeant, Melanie J. Davies
Diabetologia.2023; 66(10): 1832. CrossRef - Diabetes-Induced Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy: Impact on Heart Function and Prognosis
Susumu Z. Sudo, Tadeu L. Montagnoli, Bruna de S. Rocha, Aimeé D. Santos, Mauro P. L. de Sá, Gisele Zapata-Sudo
Biomedicines.2022; 10(12): 3258. CrossRef
- Liraglutide does not increase heart rate of diabetic patients during acute myocardial infarction
- Complications
- Peripheral Neuropathy Phenotyping in Rat Models of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Evaluating Uptake of the Neurodiab Guidelines and Identifying Future Directions
- Md Jakir Hossain, Michael D. Kendig, Meg E. Letton, Margaret J. Morris, Ria Arnold
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):198-221. Published online March 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0347
- 5,217 View
- 225 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) affects over half of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients, with an urgent need for effective pharmacotherapies. While many rat and mouse models of T2DM exist, the phenotyping of DPN has been challenging with inconsistencies across laboratories. To better characterize DPN in rodents, a consensus guideline was published in 2014 to accelerate the translation of preclinical findings. Here we review DPN phenotyping in rat models of T2DM against the ‘Neurodiab’ criteria to identify uptake of the guidelines and discuss how DPN phenotypes differ between models and according to diabetes duration and sex. A search of PubMed, Scopus and Web of Science databases identified 125 studies, categorised as either diet and/or chemically induced models or transgenic/spontaneous models of T2DM. The use of diet and chemically induced T2DM models has exceeded that of transgenic models in recent years, and the introduction of the Neurodiab guidelines has not appreciably increased the number of studies assessing all key DPN endpoints. Combined high-fat diet and low dose streptozotocin rat models are the most frequently used and well characterised. Overall, we recommend adherence to Neurodiab guidelines for creating better animal models of DPN to accelerate translation and drug development.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- SIRT3 alleviates painful diabetic neuropathy by mediating the FoxO3a‐PINK1‐Parkin signaling pathway to activate mitophagy
Jing Yang, Zhuoying Yu, Ye Jiang, Zixian Zhang, Yue Tian, Jie Cai, Min Wei, Yanhan Lyu, Dongsheng Yang, Shixiong Shen, Guo‐Gang Xing, Min Li
CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Compound Qiying Granules alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathy by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis
Yan Hu, Chen Chen, Zhengting Liang, Tao Liu, Xiaoling Hu, Guanying Wang, Jinxia Hu, Xiaolin Xie, Zhiyan Liu
Molecular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - HCV affects KATP channels through GnT-IVa-mediated N-glycosylation of GLUT2 on the surface of pancreatic β-cells leading to impaired insulin secretion
Ben Niu, Lijing Ma, Lixuan Yao, Yating Zhang, Heng Su
Endocrine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Multimodal Comparison of Diabetic Neuropathy in Aged Streptozotocin-Treated Sprague–Dawley and Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats
Annalisa Canta, Valentina A. Carozzi, Alessia Chiorazzi, Cristina Meregalli, Norberto Oggioni, Virginia Rodriguez-Menendez, Barbara Sala, Roberto Cosimo Melcangi, Silvia Giatti, Raffaella Lombardi, Roberto Bianchi, Paola Marmiroli, Guido Cavaletti
Biomedicines.2022; 11(1): 20. CrossRef
- SIRT3 alleviates painful diabetic neuropathy by mediating the FoxO3a‐PINK1‐Parkin signaling pathway to activate mitophagy
- Complications
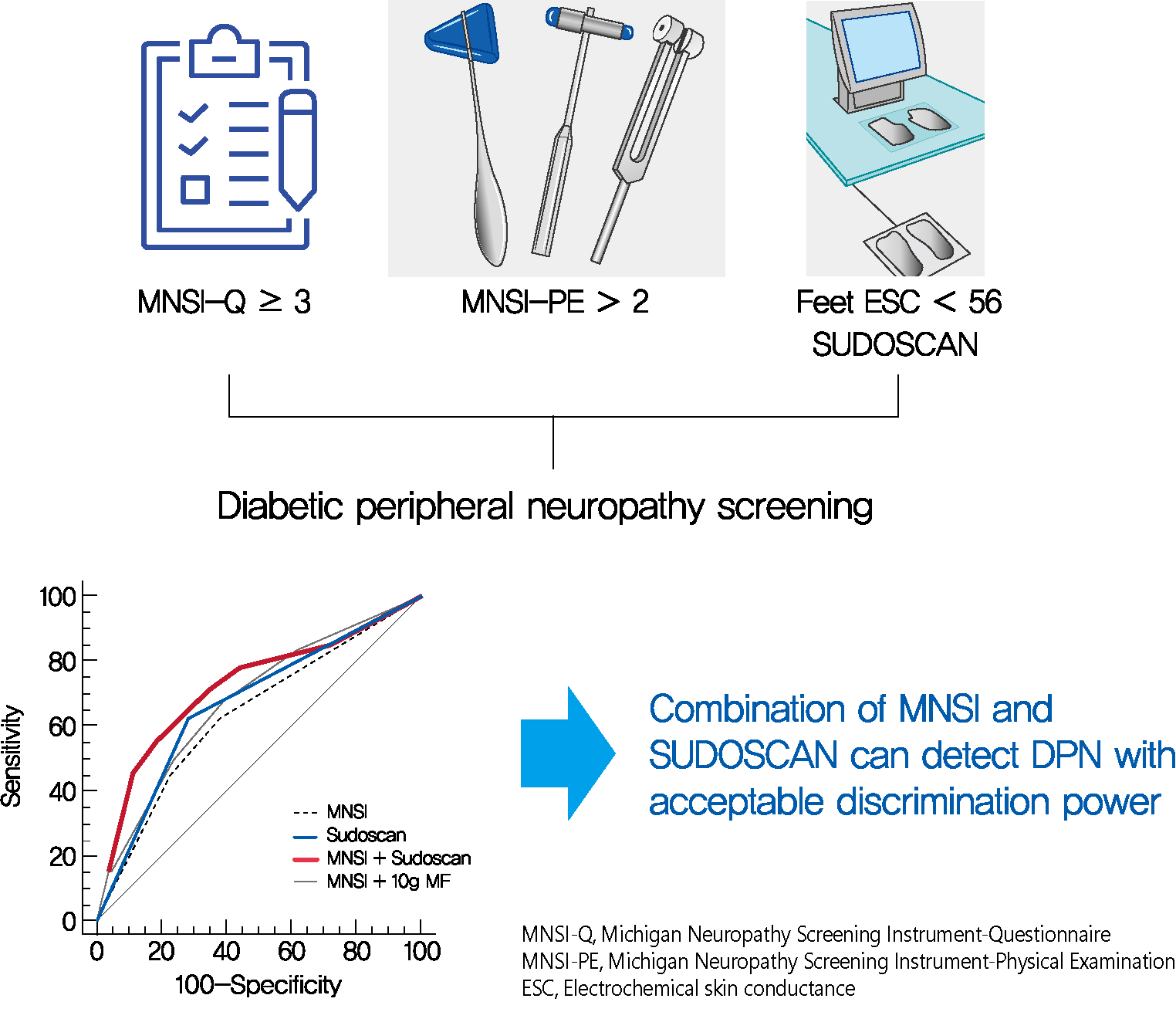
- SUDOSCAN in Combination with the Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument Is an Effective Tool for Screening Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
- Tae Jung Oh, Yoojung Song, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):319-326. Published online September 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0014
- 5,831 View
- 315 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Screening for diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is important to prevent severe foot complication, but the detection rate of DPN is unsatisfactory. We investigated whether SUDOSCAN combined with Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument (MNSI) could be an effective tool for screening for DPN in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in clinical practice.
Methods
We analysed the data for 144 people with T2DM without other cause of neuropathy. The presence of DPN was confirmed according to the Toronto Consensus criteria. Electrochemical skin conductance (ESC) of the feet was assessed using SUDOSCAN. We compared the discrimination power of following methods, MNSI only vs. SUDOSCAN only vs. MNSI plus SUDOSCAN vs. MNSI plus 10-g monofilament test.
Results
Confirmed DPN was detected in 27.8% of the participants. The optimal cut-off value of feet ESC to distinguish DPN was 56 μS. We made the DPN screening scores using the corresponding odds ratios for MNSI-Questionnaire, MNSI-Physical Examination, SUDOSCAN, and 10-g monofilament test. For distinguishing the presence of DPN, the MNSI plus SUDOSCAN model showed higher areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) than MNSI only model (0.717 vs. 0.638, P=0.011), and SUDOSCAN only model or MNSI plus 10-g monofilament test showed comparable AUC with MNSI only model.
Conclusion
The screening model for DPN that includes both MNSI and SUDOSCAN can detect DPN with acceptable discrimination power and it may be useful in Korean patients with T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of sudomotor dysfunction with risk of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes
Ming Wang, Niuniu Chen, Yaxin Wang, Jiaying Ni, Jingyi Lu, Weijing Zhao, Yating Cui, Ronghui Du, Wei Zhu, Jian Zhou
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Vitamin D deficiency increases the risk of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in elderly type 2 diabetes mellitus patients by predominantly increasing large-fiber lesions
Sijia Fei, Jingwen Fan, Jiaming Cao, Huan Chen, Xiaoxia Wang, Qi Pan
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 209: 111585. CrossRef - Early detection of diabetic neuropathy based on health belief model: a scoping review
Okti Sri Purwanti, Nursalam Nursalam, Moses Glorino Rumambo Pandin
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Peripheral Neuropathy in Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Diagnostic Options
Raffaele Galiero, Alfredo Caturano, Erica Vetrano, Domenico Beccia, Chiara Brin, Maria Alfano, Jessica Di Salvo, Raffaella Epifani, Alessia Piacevole, Giuseppina Tagliaferri, Maria Rocco, Ilaria Iadicicco, Giovanni Docimo, Luca Rinaldi, Celestino Sardu, T
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3554. CrossRef - Screening for diabetic peripheral neuropathy in resource-limited settings
Ken Munene Nkonge, Dennis Karani Nkonge, Teresa Njeri Nkonge
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The value of electrochemical skin conductance measurement by Sudoscan® for assessing autonomic dysfunction in peripheral neuropathies beyond diabetes
Jean-Pascal Lefaucheur
Neurophysiologie Clinique.2023; 53(2): 102859. CrossRef - Electrochemical skin conductances values and clinical factors affecting sudomotor dysfunction in patients with prediabetes, type 1 diabetes, and type 2 diabetes: A single center experience
Bedia Fulya Calikoglu, Selda Celik, Cemile Idiz, Elif Bagdemir, Halim Issever, Jean-Henri Calvet, Ilhan Satman
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(5): 499. CrossRef - Autonomic Nerve Function Tests in Patients with Diabetes
Heung Yong Jin, Tae Sun Park
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(2): 71. CrossRef - Validation of the Body Scan®, a new device to detect small fiber neuropathy by assessment of the sudomotor function: agreement with the Sudoscan®
Jean-Pierre Riveline, Roberto Mallone, Clarisse Tiercelin, Fetta Yaker, Laure Alexandre-Heymann, Lysa Khelifaoui, Florence Travert, Claire Fertichon, Jean-Baptiste Julla, Tiphaine Vidal-Trecan, Louis Potier, Jean-Francois Gautier, Etienne Larger, Jean-Pas
Frontiers in Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Electrochemical Skin Conductance by Sudoscan in Non-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
Liang-Te Chiu, Yu-Li Lin, Chih-Hsien Wang, Chii-Min Hwu, Hung-Hsiang Liou, Bang-Gee Hsu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(1): 187. CrossRef - The Presence of Clonal Hematopoiesis Is Negatively Associated with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes
Tae Jung Oh, Han Song, Youngil Koh, Sung Hee Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 243. CrossRef - Case report: Significant relief of linezolid-induced peripheral neuropathy in a pre-XDR-TB case after acupuncture treatment
Yuping Mo, Zhu Zhu, Jie Tan, Zhilin Liang, Jiahui Wu, Xingcheng Chen, Ming Hu, Peize Zhang, Guofang Deng, Liang Fu
Frontiers in Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Detection of sudomotor alterations evaluated by Sudoscan in patients with recently diagnosed type 2 diabetes
Ana Cristina García-Ulloa, Paloma Almeda-Valdes, Teresa Enedina Cuatecontzi-Xochitiotzi, Jorge Alberto Ramírez-García, Michelle Díaz-Pineda, Fernanda Garnica-Carrillo, Alejandra González-Duarte, K M Venkat Narayan, Carlos Alberto Aguilar-Salinas, Sergio H
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(6): e003005. CrossRef
- Association of sudomotor dysfunction with risk of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Complications
- Influence of Glucose Fluctuation on Peripheral Nerve Damage in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Yu Ji Kim, Na Young Lee, Kyung Ae Lee, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):117-128. Published online September 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0275

- 5,223 View
- 179 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
It is unclear whether glycemic variability (GV) is a risk factor for diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), and whether control of GV is beneficial for DPN. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of GV on peripheral nerve damage by inducing glucose fluctuation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
Methods
Rats were divided into four groups: normal (normal glucose group [NOR]), diabetes without treatment (sustained severe hyperglycemia group; diabetes mellitus [DM]), diabetes+once daily insulin glargine (stable hyperglycemia group; DM+LAN), and diabetes+once daily insulin glargine with twice daily insulin glulisine (unstable glucose fluctuation group; DM+Lantus [LAN]+Apidra [API]). We measured anti-oxidant enzyme levels and behavioral responses against tactile, thermal, and pressure stimuli in the plasma of rats. We also performed a quantitative comparison of cutaneous and sciatic nerves according to glucose fluctuation.
Results
At week 24, intraepidermal nerve fiber density was less reduced in the insulin-administered groups compared to the DM group (P<0.05); however, a significant difference was not observed between the DM+LAN and DM+LAN+API groups irrespective of glucose fluctuation (P>0.05; 16.2±1.6, 12.4±2.0, 14.3±0.9, and 13.9±0.6 for NOR, DM, DM+LAN, and DM+LAN+API, respectively). The DM group exhibited significantly decreased glutathione levels compared to the insulin-administered groups (2.64±0.10 μmol/mL, DM+LAN; 1.93±0.0 μmol/mL, DM+LAN+API vs. 1.25±0.04 μmol/mL, DM; P<0.05).
Conclusion
Our study suggests that glucose control itself is more important than glucose fluctuation in the prevention of peripheral nerve damage, and intra-day glucose fluctuation has a limited effect on the progression of peripheral neuropathy in rats with diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glucose Fluctuation Inhibits Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Hippocampal Tissues and Exacerbates Cognitive Impairment in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
Haiyan Chi, Yujing Sun, Peng Lin, Junyu Zhou, Jinbiao Zhang, Yachao Yang, Yun Qiao, Deshan Liu, Eusebio Chiefari
Journal of Diabetes Research.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Artesunate Inhibits Apoptosis and Promotes Survival in Schwann Cells via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Axis in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Xin Zhang, Zhifang Liang, Ying Zhou, Fang Wang, Shan Wei, Bing Tan, Yujie Guo
Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin.2023; 46(6): 764. CrossRef - The Potential of Glucose Treatment to Reduce Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Apoptosis of Inflamed Neural Cells In Vitro
Juin-Hong Cherng, Shu-Jen Chang, Hsin-Da Tsai, Chung-Fang Chun, Gang-Yi Fan, Kenneth Dean Reeves, King Hei Stanley Lam, Yung-Tsan Wu
Biomedicines.2023; 11(7): 1837. CrossRef - Relationship between acute glucose variability and cognitive decline in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Haiyan Chi, Min Song, Jinbiao Zhang, Junyu Zhou, Deshan Liu, Victor Manuel Mendoza-Nuñez
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(9): e0289782. CrossRef
- Glucose Fluctuation Inhibits Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Hippocampal Tissues and Exacerbates Cognitive Impairment in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Complications
- Study on Risk Factors of Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Establishment of Prediction Model
- Birong Wu, Zheyun Niu, Fan Hu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):526-538. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0100

- 7,243 View
- 310 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is one of the most serious complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). DPN increases the risk of ulcers, foot infections, and noninvasive amputations, ultimately leading to long-term disability.
Methods
Seven hundred patients with T2DM were investigated from 2013 to 2017 in the Sanlin community by obtaining basic data from the electronic medical record system (EMRS). From September 2018 to July 2019, 681 patients (19 missing) were investigated using a questionnaire, physical examination, biochemical index test, and follow-up Toronto clinical scoring system (TCSS) test. Patients with a TCSS score ≥6 points were diagnosed with DPN. After removing missing values, 612 patients were divided into groups in a 3:1 ratio for external validation. Using different Lasso analyses (misclassification error, mean squared error, –2log-likelihood, and area under curve) and a logistic regression analysis of the training set, models A, B, C, and D were established. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, calibration plot, dynamic component analysis (DCA) measurements, net classification improvement (NRI) and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) were used to validate discrimination and clinical practicality of the model.
Results
Through data analysis, model A (containing four factors), model B (containing five factors), model C (containing seven factors), and model D (containing seven factors) were built. After calibration, ROC curve, DCA, NRI and IDI, models C and D exhibited better accuracy and greater predictive power.
Conclusion
Four prediction models were established to assist with the early screening of DPN in patients with T2DM. The influencing factors in model C and D are more important factors for patients with T2DM diagnosed with DPN. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetes Mellitusu Olan Bireylerde Periferal Nöropati ve Hemşirelik Bakımı
Semanur BİLGİÇ, Burcu BAYRAK KAHRAMAN
Akdeniz Hemşirelik Dergisi.2024; 2(3): 113. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Subclinical Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Li Gao, Jiexing Qin, Ying Chen, Wenqun Jiang, Desheng Zhu, Xiajun Zhou, Jie Ding, Huiying Qiu, Yan Zhou, Qing Dong, Yangtai Guan
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2024; Volume 17: 417. CrossRef - Predictive model and risk analysis for peripheral vascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients using machine learning and shapley additive explanation
Lianhua Liu, Bo Bi, Li Cao, Mei Gui, Feng Ju
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Multi‐feature, Chinese–Western medicine‐integrated prediction model for diabetic peripheral neuropathy based on machine learning and SHAP
Aijuan Jiang, Jiajie Li, Lujie Wang, Wenshu Zha, Yixuan Lin, Jindong Zhao, Zhaohui Fang, Guoming Shen
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical significance of vascular endothelial growth factor and endothelin-1 in serum levels as novel indicators for predicting the progression of diabetic nephropathy
Wei Chu, Lin-Lin Ma, Bin-Xian Li, Ming-Cheng Li
European Journal of Inflammation.2023; 21: 1721727X2311515. CrossRef - Common and contrast determinants of peripheral artery disease and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in North Central Nigeria
Felicia Ehusani Anumah, Yakubu Lawal, Rifkatu Mshelia-Reng, Special Odiase Omonua, Kenechukwu Odumodu, Ramatu Shuaibu, Ukamaka Dorothy Itanyi, Amina Ibrahim Abubakar, Hadijat Oluseyi kolade-Yunusa, Zumnan Songden David, Babajide Ogunlana, Andrew Clarke, O
The Foot.2023; 55: 101987. CrossRef - ApoA-I and Diabetes
Thomas W. King, Blake J. Cochran, Kerry-Anne Rye
Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology.2023; 43(8): 1362. CrossRef - Study on risk factors of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and establishment of a prediction model by machine learning
Xiaoyang Lian, Juanzhi Qi, Mengqian Yuan, Xiaojie Li, Ming Wang, Gang Li, Tao Yang, Jingchen Zhong
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Establishment and health management application of a prediction model for high-risk complication combination of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on data mining
Xin Luo, Jijia Sun, Hong Pan, Dian Zhou, Ping Huang, Jingjing Tang, Rong Shi, Hong Ye, Ying Zhao, An Zhang, Yee Gary Ang
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(8): e0289749. CrossRef - Development and validation of risk prediction model for diabetic neuropathy among diabetes mellitus patients at selected referral hospitals, in Amhara regional state Northwest Ethiopia, 2005–2021
Negalgn Byadgie Gelaw, Achenef Asmamaw Muche, Adugnaw Zeleke Alem, Nebiyu Bekele Gebi, Yazachew Moges Chekol, Tigabu Kidie Tesfie, Tsion Mulat Tebeje, Jacopo Sabbatinelli
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(8): e0276472. CrossRef - Machine Learning Models for Blood Glucose Level Prediction in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Kui Liu, Linyi Li, Yifei Ma, Jun Jiang, Zhenhua Liu, Zichen Ye, Shuang Liu, Chen Pu, Changsheng Chen, Yi Wan
JMIR Medical Informatics.2023; 11: e47833. CrossRef - Establishment of models to predict factors influencing periodontitis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hong-Miao Xu, Xuan-Jiang Shen, Jia Liu
World Journal of Diabetes.2023; 14(12): 1793. CrossRef - Impact of Nutraceuticals on Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Induced Micro- and Macrovasculopathies
Philanathi Mabena, Thandi M. D. Fasemore, Pilani Nkomozepi
Applied Sciences.2023; 14(1): 64. CrossRef - Prediction Model for the Risk of HIV Infection among MSM in China: Validation and Stability
Yinqiao Dong, Shangbin Liu, Danni Xia, Chen Xu, Xiaoyue Yu, Hui Chen, Rongxi Wang, Yujie Liu, Jingwen Dong, Fan Hu, Yong Cai, Ying Wang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(2): 1010. CrossRef - Management of Type II Diabetes Mellitus using Adult Autologous Adipose derived stem cells with Platelets Rich Plasma (PRP)
Shahzad Anwar, Ayesha Nawaz, Zaigham Abbas
Pakistan BioMedical Journal.2022; : 270. CrossRef - A Nomogram for Predicting the Possibility of Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Wanli Zhang, Lingli Chen
Brain Sciences.2022; 12(10): 1328. CrossRef
- Diabetes Mellitusu Olan Bireylerde Periferal Nöropati ve Hemşirelik Bakımı
- Complications
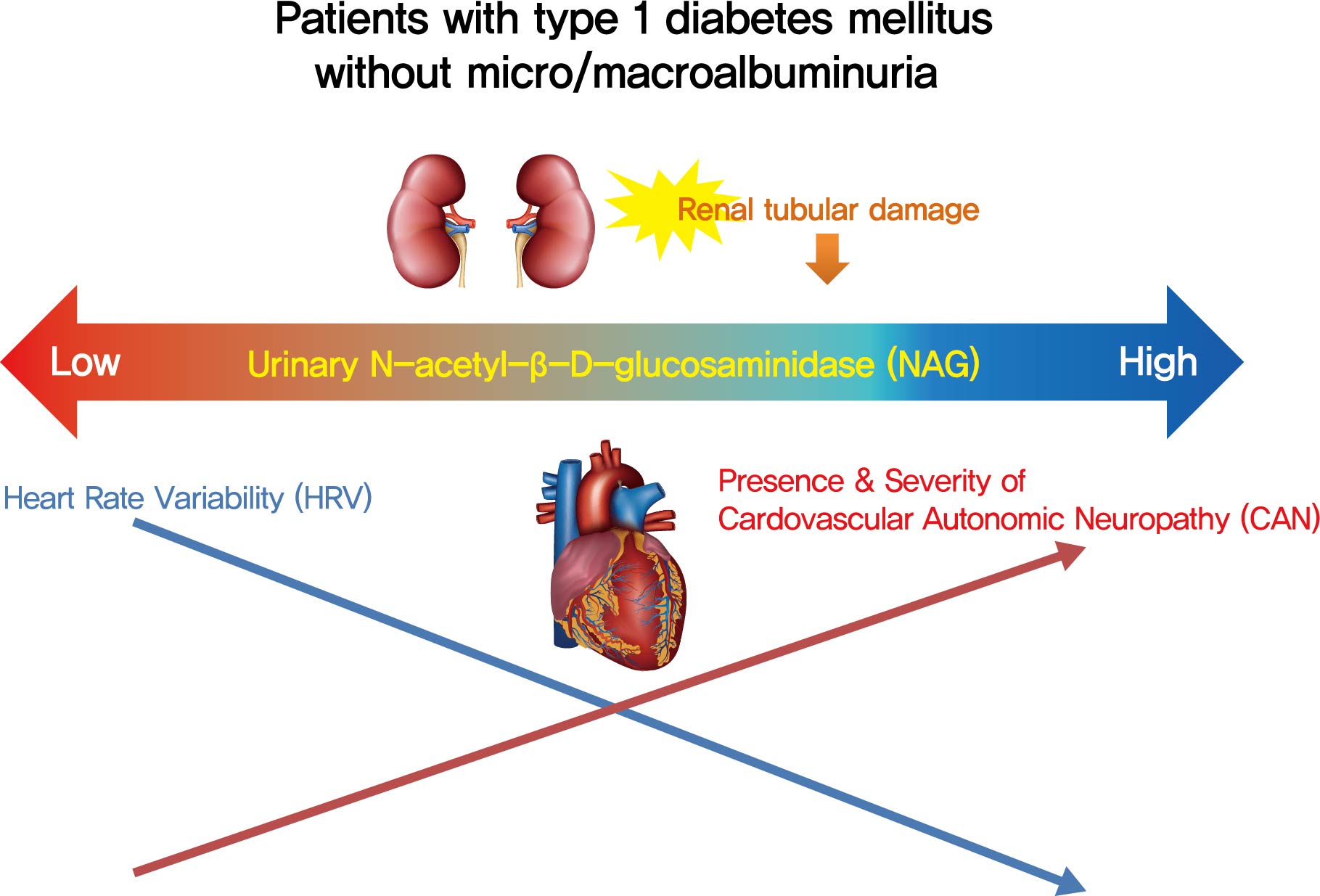
- Association of Urinary N-Acetyl-β-D-Glucosaminidase with Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus without Nephropathy
- Min Sun Choi, Ji Eun Jun, Sung Woon Park, Jee Hee Yoo, Jiyeon Ahn, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Moon-Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):349-357. Published online February 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0211
- 5,641 View
- 121 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy (CAN) is a common microvascular complication of diabetes and related to albuminuria in diabetic nephropathy (DN). Urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (uNAG) is a renal tubular injury marker which has been reported as an early marker of DN even in patients with normoalbuminuria. This study evaluated whether uNAG is associated with the presence and severity of CAN in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) without nephropathy.
Methods
This cross-sectional study comprised 247 subjects with T1DM without chronic kidney disease and albuminuria who had results for both uNAG and autonomic function tests within 3 months. The presence of CAN was assessed by age-dependent reference values for four autonomic function tests. Total CAN score was assessed as the sum of the partial points of five cardiovascular reflex tests and was used to estimatethe severity of CAN. The correlations between uNAG and heart rate variability (HRV) parameters were analyzed.
Results
The association between log-uNAG and presence of CAN was significant in a multivariate logistic regression model (adjusted odds ratio, 2.39; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.08 to 5.28; P=0.031). Total CAN score was positively associated with loguNAG (β=0.261, P=0.026) in the multivariate linear regression model. Log-uNAG was inversely correlated with frequency-domain and time-domain indices of HRV.
Conclusion
This study verified the association of uNAG with presence and severity of CAN and changes in HRV in T1DM patients without nephropathy. The potential role of uNAG should be further assessed for high-risk patients for CAN in T1DM patients without nephropathy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Determination of Diabetes-associated Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Risk Factors among Insulin and Non-insulin Dependent Diabetics
Ibrahim Abdulsada, Zain Alabdeen Obaid, Farah Almerza, Mays Alwaeli, Anmar Al-Elayawi, Taha Al-Dayyeni, Harir Al-Tuhafy
The Journal of Medical Research.2023; 9(6): 141. CrossRef - Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef
- Determination of Diabetes-associated Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Risk Factors among Insulin and Non-insulin Dependent Diabetics
- Complications
- Status of Diabetic Neuropathy in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort Analysis (2006 to 2015)
- Seong-Su Moon, Chong Hwa Kim, Seon Mee Kang, Eun Sook Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Jae-Seung Yun, Ho Chan Cho, Dae Jung Kim, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):115-119. Published online December 18, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0120

- 7,045 View
- 275 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - This report presents the status of diabetic neuropathy (DN) in Korea as determined using a National Health Insurance ServiceNational Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC). Annual prevalences of DN were estimated by age and gender using descriptive statistics. Pharmacological treatments for DN were also analyzed. The annual prevalence of DN increased from 24.9% in 2006 to 26.6% in 2007, and thereafter, gradually subsided to 20.8% in 2015. In most cases, pharmacological treatments involved a single drug, which accounted for 91.6% of total prescriptions in 2015. The most commonly used drugs (in decreasing order) were thioctic acid, an anti-convulsive agent, or a tricyclic antidepressant. In conclusion, the prevalence of DN decreased over the 10-year study period. Thioctic acid monotherapy was usually prescribed for DN. To reduce the socio-economic burden of DN, more attention should be paid to the diagnosis of this condition and to the appropriate management of patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of cardiovascular events according to the tricyclic antidepressant dosage in patients with chronic pain: a retrospective cohort study
Hyunji Koo, Seung Hun You, Sewon Park, Kyeong Hye Jeong, Nakyung Jeon, Sun-Young Jung
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 79(1): 159. CrossRef - How does diabetic peripheral neuropathy impact patients' burden of illness and the economy? A retrospective study in Beijing, China
Qi Pan, Sijia Fei, Lina Zhang, Huan Chen, Jingyi Luo, Weihao Wang, Fei Xiao, Lixin Guo
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Chronic disease management program applied to type 2 diabetes patients and prevention of diabetic complications: a retrospective cohort study using nationwide data
Min Kyung Hyun, Jang Won Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pharmacological and Nonpharmacological Treatments for Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Han Na Jang, Tae Jung Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 743. CrossRef - Are herbal medicines alone or in combination for diabetic peripheral neuropathy more effective than methylcobalamin alone? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Chang-Woo Lee, Joon-Soo Jin, Seungwon Kwon, Chul Jin, Seung-Yeon Cho, Seong-Uk Park, Woo-Sang Jung, Sang-Kwan Moon, Jung-Mi Park, Chang-Nam Ko, Ki-Ho Cho
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2022; 49: 101657. CrossRef - Pathogenesis and Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Seon Mee Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(4): 222. CrossRef - Status of Diabetic Neuropathy in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort Analysis (2006 to 2015) (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:115-9)
Seong-Su Moon, Chong Hwa Kim, Seon Mee Kang, Eun Sook Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Jae-Seung Yun, Ho Chan Cho, Dae Jung Kim, Tae Sun Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 459. CrossRef - Status of Diabetic Neuropathy in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort Analysis (2006 to 2015) (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:115-9)
Tímea Csákvári, Diána Elmer, Lilla Horváth, Imre Boncz
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 454. CrossRef - Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
Ja Young Jeon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 613. CrossRef - Diffculties and ways to overcome them in selection of therapy for pain syndromes in patients with diabetes mellitus
K. A. Makhinov, P. R. Kamchatnov
Medical alphabet.2021; (22): 25. CrossRef
- Risk of cardiovascular events according to the tricyclic antidepressant dosage in patients with chronic pain: a retrospective cohort study
- Complications
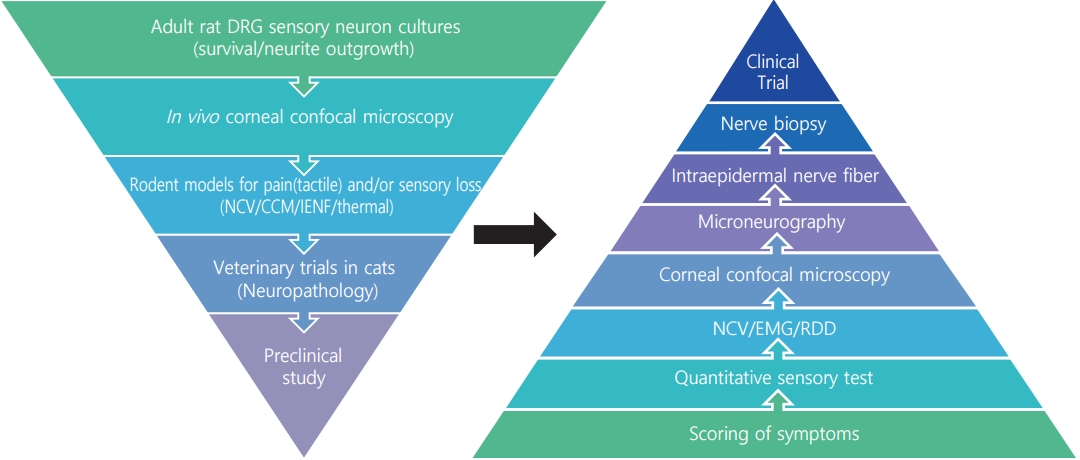
- Lost in Translation? Measuring Diabetic Neuropathy in Humans and Animals
- Heung Yong Jin, Seong-Su Moon, Nigel A. Calcutt
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):27-42. Published online December 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0216
- 8,395 View
- 224 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- The worldwide diabetes epidemic is estimated to currently afflict almost 500 million persons. Long-term diabetes damages multiple organ systems with the blood vessels, eyes, kidneys and nervous systems being particularly vulnerable. These complications of diabetes reduce lifespan, impede quality of life and impose a huge social and economic burden on both the individual and society. Peripheral neuropathy is a debilitating complication that will impact over half of all persons with diabetes. There is no treatment for diabetic neuropathy and a disturbingly long history of therapeutic approaches showing promise in preclinical studies but failing to translate to the clinic. These failures have prompted re-examination of both the animal models and clinical trial design. This review focuses on the functional and structural parameters used as indices of peripheral neuropathy in preclinical and clinical studies and the extent to which they share a common pathogenesis and presentation. Nerve conduction studies in large myelinated fibers have long been the mainstay of preclinical efficacy screening programs and clinical trials, supplemented by quantitative sensory tests. However, a more refined approach is emerging that incorporates measures of small fiber density in the skin and cornea alongside these traditional assays at both preclinical and clinical phases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Peripheral Neuropathy in Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Diagnostic Options
Raffaele Galiero, Alfredo Caturano, Erica Vetrano, Domenico Beccia, Chiara Brin, Maria Alfano, Jessica Di Salvo, Raffaella Epifani, Alessia Piacevole, Giuseppina Tagliaferri, Maria Rocco, Ilaria Iadicicco, Giovanni Docimo, Luca Rinaldi, Celestino Sardu, T
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3554. CrossRef - Bidirectional association between diabetic peripheral neuropathy and vitamin B12 deficiency: Two longitudinal 9-year follow-up studies using a national sample cohort
Heung Yong Jin, Kyung Ae Lee, Yu Ji Kim, In Sun Gwak, Tae Sun Park, Sang Woo Yeom, Jong Seung Kim
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(5): 436. CrossRef - Advanced Drug Delivery System for Management of Chronic Diabetes
Wound Healing
Harish Bhardwaj, Sulekha Khute, Ram Sahu, Rajendra Kumar Jangde
Current Drug Targets.2023; 24(16): 1239. CrossRef - A Real-World Analysis of High-Frequency 10 kHz Spinal Cord Stimulation for the Treatment of Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Jeffrey L. Chen, Andrew W. Hesseltine, Sara E. Nashi, Shawn M. Sills, Tory L. McJunkin, Sandeep Patil, Manish Bharara, David L. Caraway, Elizabeth S. Brooks
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2022; 16(2): 282. CrossRef - Using Corneal Confocal Microscopy to Identify Therapeutic Agents for Diabetic Neuropathy
Corinne G. Jolivalt, May Madi Han, Annee Nguyen, Fiona Desmond, Carlos Henrique Alves Jesus, Daniela C. Vasconselos, Andrea Pedneault, Natalie Sandlin, Sage Dunne-Cerami, Katie E. Frizzi, Nigel A. Calcutt
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2307. CrossRef - Glycyrrhizic acid promotes sciatic nerves recovery in type 1 diabetic rats and protects Schwann cells from high glucose-induced cytotoxicity
Min Shi, Xiangcheng Zhang, Ridong Zhang, Hong Zhang, Dalong Zhu, Xiao Han
The Journal of Biomedical Research.2022; 36(3): 181. CrossRef - Novel mechanisms of pain in painful diabetic neuropathy
Rayaz A. Malik
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2022; 18(8): 459. CrossRef - An induced pluripotent stem cell-based model identifies molecular targets of vincristine neurotoxicity
Neng-Wei Tsai, Cheng-Chen Lin, Ti-Yen Yeh, Yu-An Chiu, Hsin-Hui Chiu, Hsiang-Po Huang, Sung-Tsang Hsieh
Disease Models & Mechanisms.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Corneal Confocal Microscopy: A Biomarker for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Ioannis N. Petropoulos, Georgios Ponirakis, Maryam Ferdousi, Shazli Azmi, Alise Kalteniece, Adnan Khan, Hoda Gad, Bilal Bashir, Andrew Marshall, Andrew J.M. Boulton, Handrean Soran, Rayaz A. Malik
Clinical Therapeutics.2021; 43(9): 1457. CrossRef - Lost in Translation? Measuring Diabetic Neuropathy in Humans and Animals (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:27-42)
Otto Jesus Hernandez Fustes
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 452. CrossRef - Lost in Translation? Measuring Diabetic Neuropathy in Humans and Animals (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:27-42)
Heung Yong Jin, Seong-Su Moon, Nigel A. Calcutt
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 457. CrossRef - Sterculia tragacantha Lindl Leaf Extract Ameliorates STZ-Induced Diabetes, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Neuronal Impairment
Amos Sunday Onikanni, Bashir Lawal, Augustine O Olusola, Janet O Olugbodi, Saidu Sani, Basiru Olaitan Ajiboye, Omotayo B Ilesanmi, Mohammed Alqarni, Gomaa Mostafa-Hedeab, Ahmad J Obaidullah, Gaber El-Saber Batiha, Alexander TH Wu
Journal of Inflammation Research.2021; Volume 14: 6749. CrossRef
- Peripheral Neuropathy in Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Diagnostic Options
- Complications
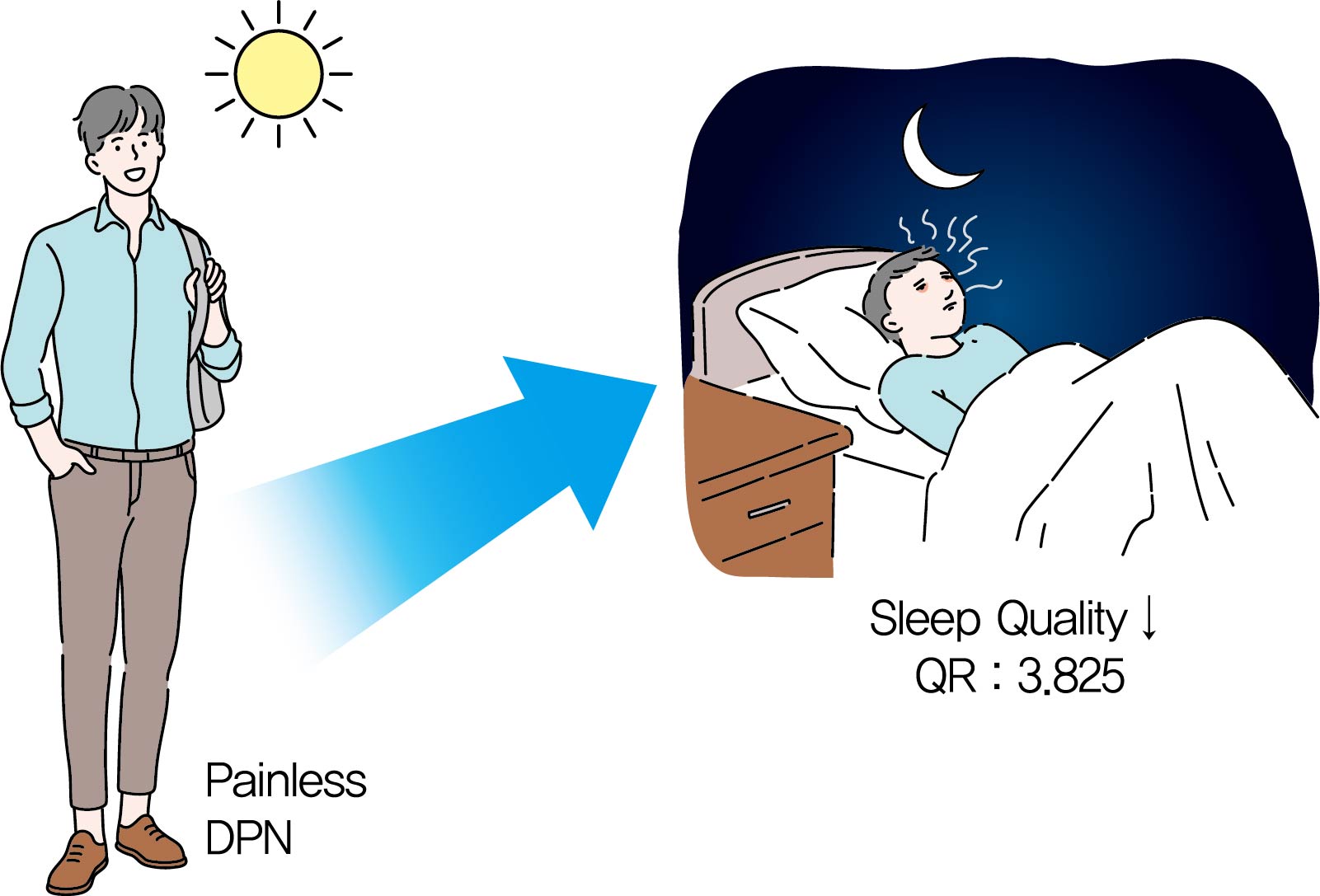
- Association between Sleep Quality and Painless Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Assessed by Current Perception Threshold in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Dughyun Choi, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chan-Hee Jung, Chul-Hee Kim, Ji-Oh Mok
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):358-367. Published online August 6, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0219
- 5,948 View
- 155 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
Background It is known that the painful sensation of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) results in sleep problems in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, it is not known that the painless DPN also is associated with poor sleep quality in T2DM. The purpose of the current study was to investigate the association between painless DPN and poor sleep quality in T2DM.
Methods A total of 146 patients of T2DM who do not have any painful symptoms of DPN were recruited into the study. Among the patients, painless DPN was diagnosed by using the current perception threshold test. Sleep quality was assessed using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index questionnaire.
Results The percentage of painless DPN was significantly higher in the poor sleep quality group than the good sleep quality group (70.0% vs. 35.5%,
P <0.001). In the subscale results, stimulus values at 2,000 Hz, hypoesthesia and hyperesthesia were more common in the poor sleep quality group than in the good sleep quality group (45.7% vs. 25.0%,P =0.009; 34.3% vs. 18.4%,P =0.029; 40.0% vs. 19.7%,P =0.007, respectively). The association of painless DPN and poor sleep quality remained significant after adjustment for significant covariates (odds ratio, 3.825; 95% confidence interval, 1.674 to 8.742;P <0.001).Conclusion The current study showed that painless DPN was associated with poor sleep quality. Future studies are required to clarify the pathophysiologic causal relationship between painless DPN and sleep quality.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Deteriorated sleep quality and associate factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Lin Fu, Liping Zhong, Xin Liao, Lingrui Wang, Youyi Wang, Xiuquan Shi, Yanna Zhou
PeerJ.2024; 12: e16789. CrossRef - Sleep impairment: Is it an overlooked burden in painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy? A single-centre, cross-sectional study from south India
Adlin Lawrence, Himsikhar Khataniar, Sinimol Joseph, Thenmozhi Nagarajan, Soumya Umesh, John Michael Raj A
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2022; 16(8): 102568. CrossRef - Sleep: an emerging therapeutic target in diabetes care
Nishant Raizada, S. V. Madhu
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2021; 41(1): 1. CrossRef
- Deteriorated sleep quality and associate factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- Drug/Regimen
- γ-Linolenic Acid versus α-Lipoic Acid for Treating Painful Diabetic Neuropathy in Adults: A 12-Week, Double-Placebo, Randomized, Noninferiority Trial
- Jong Chul Won, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Seong-Su Moon, Sung Wan Chun, Chong Hwa Kim, Ie Byung Park, In Joo Kim, Jihyun Lee, Bong Yun Cha, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):542-554. Published online November 4, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0099
- 7,978 View
- 245 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background This study was a multicenter, parallel-group, double-blind, double-dummy, randomized, noninferiority trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of γ-linolenic acid (GLA) relative to α-lipoic acid (ALA) over a 12-week treatment period in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN).
Methods This study included 100 T2DM patients between 20 and 75 years of age who had painful DPN and received either GLA (320 mg/day) and placebo or ALA (600 mg/day) and placebo for 12 weeks. The primary outcome measures were mean changes in pain intensities as measured by the visual analogue scale (VAS) and the total symptom scores (TSS).
Results Of the 100 subjects who initially participated in the study, 73 completed the 12-week treatment period. Per-protocol analyses revealed significant decreases in the mean VAS and TSS scores compared to baseline in both groups, but there were no significant differences between the groups. The treatment difference for the VAS (95% confidence interval [CI]) between the two groups was −0.65 (−1.526 to 0.213) and the upper bound of the 95% CI did not exceed the predefined noninferiority margin (δ1=0.51). For the TSS, the treatment difference was −0.05 (−1.211 to 1.101) but the upper bound of the 95% CI crossed the noninferiority margin (δ2=0.054). There were no serious adverse events associated with the treatments.
Conclusion GLA treatment in patients with painful DPN was noninferior to ALA in terms of reducing pain intensity measured by the VAS over 12 weeks.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cell metabolism pathways involved in the pathophysiological changes of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Yaowei Lv, Xiangyun Yao, Xiao Li, Yuanming Ouyang, Cunyi Fan, Yun Qian
Neural Regeneration Research.2024; 19(3): 598. CrossRef - Diyabet Tedavisinde Antioksidan Etki: Alfa Lipoik Asit
Umut DALMIŞ, Emine Merve EKİCİ
Avrasya Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2024; 7(1): 68. CrossRef - Ranking Alpha Lipoic Acid and Gamma Linolenic Acid in Terms of Efficacy and Safety in the Management of Adults With Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis
Mario B. Prado, Karen Joy B. Adiao
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive comparison of a new technology with traditional methods for extracting Ougan (Citrus reticulata cv. Suavissima) seed oils: Physicochemical properties, fatty acids, functional components, and antioxidant activities
Huaxia Yang, Yudan Lin, Xiaoxu Zhu, Haishuo Mu, Yi Li, Shuangyang Chen, Jia Li, Xuedan Cao
LWT.2024; 197: 115857. CrossRef - Genetic and Transcriptomic Background of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidative Therapies in Late Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review
Gašper Tonin, Vita Dolžan, Jasna Klen
Antioxidants.2024; 13(3): 277. CrossRef - Alpha-lipoic acid activates AMPK to protect against oxidative stress and apoptosis in rats with diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Tianya Zhang, Dong Zhang, Zhihong Zhang, Jiaxin Tian, Jingwen An, Wang Zhang, Ying Ben
Hormones.2023; 22(1): 95. CrossRef - Pathogenetic treatments for diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Dan Ziegler
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 206: 110764. CrossRef - Omega-3 Nutrition Therapy for the Treatment of Diabetic Sensorimotor
Polyneuropathy
Deepak Menon, Evan J. H. Lewis, Bruce A. Perkins, Vera Bril
Current Diabetes Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Alpha-Lipoic Acid in the Treatment of Diabetic Neuropathy: A Systematic Review
Saleh A Abubaker, Abdulaziz M Alonazy, Albasseet Abdulrahman
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Insight into the possible mechanism(s) involved in the antinociceptive and antineuropathic activity of Descurainia sophia L. Webb ex Prantl essential oil
Donya Ziafatdoost Abed, Sajjad Jabbari, Zainul Amiruddin Zakaria, Saeed Mohammadi
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2022; 298: 115638. CrossRef - A novel approach to alpha-lipoic acid therapy in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Alicja Sementina, Mateusz Cierzniakowski, Julia Rogalska, Izabela Piechowiak, Marek Spichalski, Aleksandra Araszkiewicz
Journal of Medical Science.2022; : e714. CrossRef - Pathogenesis and Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Seon Mee Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(4): 222. CrossRef - Diabetic Neuropathy: a Critical, Narrative Review of Published Data from 2019
Ameet S. Nagpal, Jennifer Leet, Kaitlyn Egan, Rudy Garza
Current Pain and Headache Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Therapeutic Potential of Ursolic Acid in Cancer and Diabetic Neuropathy Diseases
Manzar Alam, Sabeeha Ali, Sarfraz Ahmed, Abdelbaset Mohamed Elasbali, Mohd Adnan, Asimul Islam, Md. Imtaiyaz Hassan, Dharmendra Kumar Yadav
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(22): 12162. CrossRef - Diagnosis and treatment of the early stages of diabetic polyneuropathy
V. N. Khramilin, A. N. Zavyalov, I. Yu. Demidova
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2020; (7): 56. CrossRef
- Cell metabolism pathways involved in the pathophysiological changes of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- Others
- Increased Nociceptive Responses in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats and the Related Expression of Spinal NR2B Subunit of
N -Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptors - Che Aishah Nazariah Ismail, Rapeah Suppian, Che Badariah Abd Aziz, Khalilah Haris, Idris Long
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(2):222-235. Published online November 19, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0020
- 4,735 View
- 52 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study investigated the role of NR2B in a modulated pain process in the painful diabetic neuropathy (PDN) rat using various pain stimuli.
Methods Thirty-two Sprague-Dawley male rats were randomly allocated into four groups (n=8): control, diabetes mellitus (DM) rats and diabetic rats treated with ifenprodil at a lower dose (0.5 µg/day) (I 0.5) or higher dose (1.0 µg/day) (I 1.0). DM was induced by a single injection of streptozotocin at 60 mg/kg on day 0 of experimentation. Diabetic status was assessed on day 3 of the experimentation. The responses on both tactile and thermal stimuli were assessed on day 0 (baseline), day 14 (pre-intervention), and day 22 (post-intervention). Ifenprodil was given intrathecally for 7 days from day 15 until day 21. On day 23, 5% formalin was injected into the rats' hind paw and the nociceptive responses were recorded for 1 hour. The rats were sacrificed 72 hours post-formalin injection and an analysis of the spinal NR2B expression was performed.
Results DM rats showed a significant reduction in pain threshold in response to the tactile and thermal stimuli and higher nociceptive response during the formalin test accompanied by the higher expression of phosphorylated spinal NR2B in both sides of the spinal cord. Ifenprodil treatment for both doses showed anti-allodynic and anti-nociceptive effects with lower expression of phosphorylated and total spinal NR2B.
Conclusion We suggest that the pain process in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat that has been modulated is associated with the higher phosphorylation of the spinal NR2B expression in the development of PDN, which is similar to other models of neuropathic rats.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Painful diabetic neuropathy: The role of ion channels
Qi Wang, Yifei Ye, Linghui Yang, Lifan Xiao, Jin Liu, Wensheng Zhang, Guizhi Du
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2024; 173: 116417. CrossRef - Therapeutic potential of progesterone in spinal cord injury‐induced neuropathic pain: At the crossroads between neuroinflammation and N‐methyl‐D‐aspartate receptor
Sol Ferreyra, Susana González
Journal of Neuroendocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemical, pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic characterization of the GluN2B receptor antagonist 3-(4-phenylbutyl)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine-1,7-diol – starting point for PET tracer development
Marvin Korff, Ruben Steigerwald, Elena Bechthold, Dirk Schepmann, Julian A. Schreiber, Sven G. Meuth, Guiscard Seebohm, Bernhard Wünsch
Biological Chemistry.2023; 404(4): 279. CrossRef - Mechanisms of Transmission and Processing of Pain: A Narrative Review
Girolamo Di Maio, Ines Villano, Ciro Rosario Ilardi, Antonietta Messina, Vincenzo Monda, Ashlei Clara Iodice, Chiara Porro, Maria Antonietta Panaro, Sergio Chieffi, Giovanni Messina, Marcellino Monda, Marco La Marra
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(4): 3064. CrossRef - Indazole as a Phenol Bioisostere: Structure–Affinity Relationships of GluN2B-Selective NMDA Receptor Antagonists
Judith Lüken, Gunnar Goerges, Nadine Ritter, Paul Disse, Julian A. Schreiber, Judith Schmidt, Bastian Frehland, Dirk Schepmann, Guiscard Seebohm, Bernhard Wünsch
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2023; 66(16): 11573. CrossRef - Synthesis of oxazolo‐annulated 3‐benzazepines designed by merging two negative allosteric NMDA receptor modulators
Alexander Markus, Dirk Schepmann, Bernhard Wünsch
Archiv der Pharmazie.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Phenol—Benzoxazolone bioisosteres: Synthesis and biological evaluation of tricyclic GluN2B‐selective N‐methyl‐d‐aspartate receptor antagonists
Alexander Markus, Julian A. Schreiber, Gunnar Goerges, Bastian Frehland, Guiscard Seebohm, Dirk Schepmann, Bernhard Wünsch
Archiv der Pharmazie.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Ifenprodil Reduced Expression of Activated Microglia, BDNF and DREAM Proteins in the Spinal Cord Following Formalin Injection During the Early Stage of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy in Rats
Che Aishah Nazariah Ismail, Rapeah Suppian, Che Badariah Ab Aziz, Idris Long
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience.2021; 71(2): 379. CrossRef - Ifenprodil Stereoisomers: Synthesis, Absolute Configuration, and Correlation with Biological Activity
Elena Bechthold, Julian A. Schreiber, Kirstin Lehmkuhl, Bastian Frehland, Dirk Schepmann, Freddy A. Bernal, Constantin Daniliuc, Inés Álvarez, Cristina Val Garcia, Thomas J. Schmidt, Guiscard Seebohm, Bernhard Wünsch
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2021; 64(2): 1170. CrossRef - The anti-diabetic effects of betanin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats through modulating AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB signaling pathway
Nasim Abedimanesh, Somayyeh Asghari, Kosar Mohammadnejad, Zahra Daneshvar, Soudeh Rahmani, Samaneh Shokoohi, Amir Hasan Farzaneh, Seyed Hojjat Hosseini, Iraj Jafari Anarkooli, Maryam Noubarani, Sina Andalib, Mohammad Reza Eskandari, Behrooz Motlagh
Nutrition & Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetic neuropathy and neuropathic pain: a (con)fusion of pathogenic mechanisms?
Nigel A. Calcutt
Pain.2020; 161(Supplement): S65. CrossRef - N-Acetylcysteine causes analgesia in a mouse model of painful diabetic neuropathy
Serena Notartomaso, Pamela Scarselli, Giada Mascio, Francesca Liberatore, Emanuela Mazzon, Santa Mammana, Agnese Gugliandolo, Giorgio Cruccu, Valeria Bruno, Ferdinando Nicoletti, Giuseppe Battaglia
Molecular Pain.2020; 16: 174480692090429. CrossRef - Effect of aerobic exercise on innate immune responses and inflammatory mediators in the spinal cord of diabetic rats
A. Kaki, M. Nikbakht, A.H. Habibi, H.F. Moghadam
Comparative Exercise Physiology.2020; 16(4): 293. CrossRef
- Painful diabetic neuropathy: The role of ion channels
- Complications
- Update on the Impact, Diagnosis and Management of Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes: What Is Defined, What Is New, and What Is Unmet
- Vincenza Spallone
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(1):3-30. Published online November 2, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0259
- 16,070 View
- 404 Download
- 153 Web of Science
- 157 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader The burden of diabetic cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy (CAN) is expected to increase due to the diabetes epidemic and its early and widespread appearance. CAN has a definite prognostic role for mortality and cardiovascular morbidity. Putative mechanisms for this are tachycardia, QT interval prolongation, orthostatic hypotension, reverse dipping, and impaired heart rate variability, while emerging mechanisms like inflammation support the pervasiveness of autonomic dysfunction. Efforts to overcome CAN under-diagnosis are on the table: by promoting screening for symptoms and signs; by simplifying cardiovascular reflex tests; and by selecting the candidates for screening. CAN assessment allows for treatment of its manifestations, cardiovascular risk stratification, and tailoring therapeutic targets. Risk factors for CAN are mainly glycaemic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and, in addition, hypertension, dyslipidaemia, and obesity in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), while preliminary data regard glycaemic variability, vitamin B12 and D changes, oxidative stress, inflammation, and genetic biomarkers. Glycaemic control prevents CAN in T1DM, whereas multifactorial intervention might be effective in T2DM. Lifestyle intervention improves autonomic function mostly in pre-diabetes. While there is no conclusive evidence for a disease-modifying therapy, treatment of CAN manifestations is available. The modulation of autonomic function by SGLT2i represents a promising research field with possible clinical relevance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rectal sensitivity correlated with gastrointestinal‐mediated glucose disposal, but not the incretin effect
Sondre Meling, Erling Tjora, Heike Eichele, Rasmus B. Nedergaard, Filip K. Knop, Niels Ejskjaer, Siri Carlsen, Pål R. Njølstad, Christina Brock, Eirik Søfteland
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glucose metabolism and autonomic function in healthy individuals and patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at rest and during exercise
Takuto Hamaoka, Urs A. Leuenberger, Rachel C. Drew, Matthew Murray, Cheryl Blaha, Jonathan Carter Luck, Lawrence I. Sinoway, Jian Cui
Experimental Physiology.2024; 109(2): 214. CrossRef - Quantification of lipoproteins by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-NMRS) improves the prediction of cardiac autonomic dysfunction in patients with type 1 diabetes
L. Nattero-Chávez, M. Insenser, N. Amigó, S. Samino, N. Martínez-Micaelo, B. Dorado Avendaño, A. Quintero Tobar, H. F. Escobar-Morreale, M. Luque-Ramírez
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of pacemaker requirement in patients with implantable loop recorder and unexplained syncope: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Moein Zangiabadian, Kiarash Soltani, Yasaman Gholinejad, Reyhane Yahya, Shayan Bastami, Mohammad Ali Akbarzadeh, Mohammad Sharifian Ardestani, Azadeh Aletaha
Clinical Cardiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impaired Cardiovagal Activity as a Link Between Hyperglycemia and Arterial Stiffness in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among an Eastern Indian Population: A Cross-sectional Study
Nibedita Priyadarsini, Devineni Likhitha, Madumathy Ramachandran, Kishore Kumar Behera
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2024; 48(3): 147. CrossRef - No clear evidence of neuropathy among patients with high risk for the development of prediabetes/diabetes—a pilot study
Anna E. Körei, Magdolna Békeffy, Adrienn Menyhárt, Karola Osgyán, Ildikó Istenes, Viktor J. Horváth, Péter Kempler
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Physical Cues on Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles toward Neuropathy Applications
Danyale Berry, Justice Ene, Aakash Nathani, Mandip Singh, Yan Li, Changchun Zeng
Biomedicines.2024; 12(3): 489. CrossRef - Oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, and N-acetylcysteine in type-2 diabetes mellitus
Xin Li, Junyong Zou, Aiping Lin, Jingshu Chi, Hong Hao, Hong Chen, Zhenguo Liu
Antioxidants & Redox Signaling.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - High dose cholecalciferol supplementation causing morning blood pressure reduction in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy
João Felício, Lorena Moraes, Gabriela Lemos, Ícaro Souza, Giovana Vieira, Lilian Silva, Natércia Queiroz, Ana Carolina Souza, Franciane Melo, João Felício Abrahão Neto, Hana Britto, Manuela Lemos, Márcia Santos, Priscila Figueiredo, Ana Regina Motta, Meli
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcutaneous vagal nerve stimulation for treating gastrointestinal symptoms in individuals with diabetes: a randomised, double-blind, sham-controlled, multicentre trial
Ditte S. Kornum, Davide Bertoli, Huda Kufaishi, Anne-Marie Wegeberg, Tina Okdahl, Esben B. Mark, Katrine L. Høyer, Jens B. Frøkjær, Birgitte Brock, Klaus Krogh, Christian S. Hansen, Filip K. Knop, Christina Brock, Asbjørn M. Drewes
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Independent and interactive associations of heart rate and obesity with type 2 diabetes mellites: A population‐based study
Tianxin Zhu, Qingyu Chen, Hongxing Chen, Lili You, Dan Liu, Xiaoyun Zhang, Feng Li, Hongshi Wu, Juying Tang, Diaozhu Lin, Kan Sun, Li Yan, Meng Ren
Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Bladder dysfunction in adolescents with type 1 diabetes
Vinni Faber Rasmussen, Mathilde Thrysøe, Páll Karlsson, Mette Madsen, Esben Thyssen Vestergaard, Jens Randel Nyengaard, Astrid Juhl Terkelsen, Konstantinos Kamperis, Kurt Kristensen
Journal of Pediatric Urology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mortality risk factors in newly diagnosed diabetic cardiac autonomic neuropathy
Bruce A. Chase, Sylwia Pocica, Roberta Frigerio, Katerina Markopoulou, Demetrius M. Maraganore, Navamon Aunaetitrakul, Alexander Epshteyn, Alexandru C. Barboi
Clinical Autonomic Research.2023; 33(6): 903. CrossRef - Autonomic symptoms and associated factors in patients with chronic heart failure
Hellen Da Silva, Sofie Pardaens, Marc Vanderheyden, Johan De Sutter, Heleen Demeyer, Michel De Pauw, Laurent Demulier, Jan Stautemas, Patrick Calders
Acta Cardiologica.2023; 78(2): 203. CrossRef - Incretins and microvascular complications of diabetes: neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy and microangiopathy
Jonathan Goldney, Jack A. Sargeant, Melanie J. Davies
Diabetologia.2023; 66(10): 1832. CrossRef - Functional and morphometric assessment of small-fibre damage in late-onset hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis with polyneuropathy: the controversial relation between small-fibre-related symptoms and diagnostic test findings
Eleonora Galosi, Luca Leonardi, Pietro Falco, Giuseppe Di Pietro, Alessandra Fasolino, Nicoletta Esposito, Caterina Leone, Giulia Di Stefano, Maurizio Inghilleri, Marco Luigetti, Antonini Giovanni, Andrea Truini
Amyloid.2023; 30(1): 59. CrossRef - In vivo molecular imaging of cardiac angiogenesis in persons with and without type 2 diabetes: A cross‐sectional 68 Ga‐RGD‐PET study
Jens Christian Laursen, Ida Kirstine Bull Rasmussen, Emilie Hein Zobel, Philip Hasbak, Lene Holmvang, Christian Stevns Hansen, Bernt Johan von Scholten, Marie Frimodt‐Møller, Peter Rossing, Tine Willum Hansen, Andreas Kjaer, Rasmus Sejersten Ripa
Diabetic Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiac innervations in diabetes mellitus—Anatomical evidence of neuropathy
Natalija Filipović, Maja Marinović Guić, Vana Košta, Katarina Vukojević
The Anatomical Record.2023; 306(9): 2345. CrossRef - Clinical Predictors of Pacing Device Implantation in Implantable Cardiac Monitor Recipients for Unexplained Syncope
Reina Tonegawa-Kuji, Yuko Y. Inoue, Michikazu Nakai, Koshiro Kanaoka, Yoko Sumita, Yuichiro Miyazaki, Akinori Wakamiya, Keiko Shimamoto, Nobuhiko Ueda, Kenzaburo Nakajima, Naoya Kataoka, Mitsuru Wada, Kenichiro Yamagata, Kohei Ishibashi, Koji Miyamoto, Sa
CJC Open.2023; 5(4): 259. CrossRef - Cardiovascular autonomic reflex tests using a handheld device in the diagnosis of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in patients with schizophrenia
Laura Blok-Husum, Milka Ane Rank Brcelic, Hanin Kawa Farman Kawal Bassi, Svend Eggert Jensen, Rene Ernst Nielsen, Kristian Kragholm, Jesper Fleischer, Esben Laugesen, Christoffer Polcwiartek
American Heart Journal Plus: Cardiology Research and Practice.2023; 26: 100252. CrossRef - Causal association between vitamin D and diabetic neuropathy: a Mendelian randomization analysis
Wei Huang, Lei Gu, Jingwen Wang, Yiqi Wang, Fangzheng Cao, Tianyu Jin, Yifan Cheng
Endocrine.2023; 80(2): 328. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Failure: Epidemiology, Pathophysiologic Mechanisms, and the Role of SGLT2 Inhibitors
Panagiotis Theofilis, Evangelos Oikonomou, Konstantinos Tsioufis, Dimitris Tousoulis
Life.2023; 13(2): 497. CrossRef - Sex differences and sex steroids influence on the presentation and severity of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy of patients with type 1 diabetes
Lía Nattero-Chávez, María Insenser, Alejandra Quintero Tobar, Elena Fernández-Durán, Beatriz Dorado Avendaño, Tom Fiers, Jean-Marc Kaufman, Manuel Luque-Ramírez, Héctor F. Escobar-Morreale
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Early Gastrointestinal Neuropathy Assessed by Wireless Motility Capsules in Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
Vinni Faber Rasmussen, Mathilde Thrysøe, Páll Karlsson, Esben Thyssen Vestergaard, Kurt Kristensen, Ann-Margrethe Rønholt Christensen, Jens Randel Nyengaard, Astrid Juhl Terkelsen, Christina Brock, Klaus Krogh
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(5): 1925. CrossRef - Heart rate variability in people with metabolic syndrome
Kostiantyn Apykhtin, Svitlana Drozdovska, Olha Hurenko, Anastasiia Nahorna, Anatoly Pisaruk, Yuliia Panchenko, Olena Andrieieva
Ageing & Longevity.2023; (1 2023): 1. CrossRef - Heart rate variability in people with metabolic syndrome
Kostiantyn Apykhtin, Svitlana Drozdovska, Olha Hurenko, Anastasiia Nahorna, Anatoly Pisaruk, Yuliia Panchenko, Olena Andrieieva
JOURNAL OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES OF UKRAINE.2023; (1 2023): 1. CrossRef - Potential of electronic devices for detection of health problems in older adults at home: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Yu-ting Cao, Xin-xin Zhao, Yi-ting Yang, Shi-jie Zhu, Liang-dong Zheng, Ting Ying, Zhou Sha, Rui Zhu, Tao Wu
Geriatric Nursing.2023; 51: 54. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus in der Akut- und Notfallmedizin
Leo Benning, Julian Krehl, Felix Patricius Hans
Notfallmedizin up2date.2023; 18(01): 45. CrossRef - Correlation between Heart rate recovery and Left Atrial phasic functions evaluated by 2D speckle-tracking Echocardiography after Acute Myocardial infarction
Behruz Mashayekhi, Reza Mohseni-Badalabadi, Ali Hosseinsabet, Tahereh Ahmadian
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pancreatic sympathetic innervation disturbance in type 1 diabetes
Senlin Li, Huimin Yuan, Keshan Yang, Qing Li, Ming Xiang
Clinical Immunology.2023; 250: 109319. CrossRef - A Nonrandomized Trial of the Effects of Passive Simulated Jogging on Short-Term Heart Rate Variability in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects
Jose A. Adams, Jose R. Lopez, Veronica Banderas, Marvin A. Sackner, Mark Yorek
Journal of Diabetes Research.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Evaluating treatment options for cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review
Jasmine KaiLi Goh, Leroy Koh
Diabetology International.2023; 14(3): 224. CrossRef - Autonomic neuropathic symptoms in patients with diabetes: practical tools for screening in daily routine
Ana Raquel Souza de Azevedo Vieira, Lara Benigno Porto-Dantas, Flaviene Alves do Prado Romani, Patrícia Souza Carvalho, Rodica Pop-Busui, Hermelinda Cordeiro Pedrosa
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - “Arterial stiffness is not associated with changes in the circadian pattern of blood pressure in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction”
Lía Nattero-Chávez, Ane Bayona Cebada, Elena Fernández-Durán, Alejandra Quintero Tobar, Beatriz Dorado Avendaño, Héctor Escobar-Morreale, Manuel Luque-Ramírez
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2023; 20(3): 147916412311736. CrossRef - Frontiers in diagnostic and therapeutic approaches in diabetic sensorimotor neuropathy (DSPN)
Sanjeev Sharma, Gerry Rayman
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - In Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, normalization of hemoglobin A1c accompanies reduced sensitivity to pressure at the sternum
Jens Faber, Søren Ballegaard, Nanna Ørsted, Ebbe Eldrup, Benny Karpatschof, Finn Gyntelberg, Sofie Korsgaard Hecquet, Albert Gjedde
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Functional status associated with postural dizziness, but not postural hypotension, in older adults: a community-based study
Hsiang-Ju Cheng, Zih-Jie Sun, Feng-Hwa Lu, Yi-Ching Yang, Chih-Jen Chang, Jin-Shang Wu
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of baricitinib, empagliflozin, linagliptin and telmisartan on cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in type 1 diabetes: An exploratory, randomized, open‐label, crossover trial
Jens Christian Laursen, Viktor Rotbain Curovic, Marjolein Y. A. M. Kroonen, Niels Jongs, Emilie H. Zobel, Tine W. Hansen, Marie Frimodt‐Møller, Gozewijn D. Laverman, Adriaan Kooy, Frederik Persson, Hiddo J. L. Heerspink, Christian Stevns Hansen, Peter Ros
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(10): 3064. CrossRef - The Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Is Associated with Systemic Neurodegeneration in Long-Term Type 1 Diabetes
Christina Brock, Anne-Marie Wegeberg, Thomas Arendt Nielsen, Bassam Karout, Per M. Hellström, Asbjørn Mohr Drewes, Henrik Vorum
Translational Vision Science & Technology.2023; 12(6): 23. CrossRef - The Use of Empirical Mode Decomposition on Heart Rate Variability Signals to Assess Autonomic Neuropathy Progression in Type 2 Diabetes
Sandra Cossul, Felipe Rettore Andreis, Mateus Andre Favretto, Jefferson Luiz Brum Marques
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(13): 7824. CrossRef - Topical capsaicin for the management of painful diabetic neuropathy: a narrative systematic review
Brandon Goodwin, Maanas Chiplunkar, Ryan Salerno, Kylon Coombs, Umar Sannoh, Vrushank Shah, Nicholas Averell, Usmaan Al-Shebab, Deanna Janora
Pain Management.2023; 13(5): 309. CrossRef - Adynamic response to cold pain reflects dysautonomia in type 1 diabetes and polyneuropathy
Thomas Arendt Nielsen, Søren Lundbye-Christensen, Yoanna Krasimirova Dimitrova, Sam Riahi, Birgitte Brock, Asbjørn Mohr Drewes, Christina Brock
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Autonomic Nerve Function Tests in Patients with Diabetes
Heung Yong Jin, Tae Sun Park
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(2): 71. CrossRef - Understanding the role of hyperglycemia and the molecular mechanism associated with diabetic neuropathy and possible therapeutic strategies
Mandeep Kaur, Sakshi Misra, Priyanka Swarnkar, Preeti Patel, Balak Das Kurmi, Ghanshyam Das Gupta, Amrita Singh
Biochemical Pharmacology.2023; 215: 115723. CrossRef - A three-month physical training program improves cardiovascular autonomic function in patients with metabolic syndrome with and without diabetes – a pilot study
Anna Vágvölgyi, Judit Erzsébet Ábrahám, Éva Máthéné Köteles, Andrea Korom, Mária Barnai, Mónika Szűcs, Andrea Orosz, Péter Kempler, Adrienn Menyhárt, Attila Nemes, Tamás Várkonyi, István Baczkó, István Kósa, Csaba Lengyel
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes with and without sensorimotor polyneuropathy
Emil Peters, Mustapha Itani, Alexander G. Kristensen, Astrid Juhl Terkelsen, Thomas Krøigård, Hatice Tankisi, Troels S. Jensen, Nanna B. Finnerup, Sandra Sif Gylfadottir
Journal of the Peripheral Nervous System.2023; 28(3): 450. CrossRef - Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy in Prediabetes: A Case-Control Study
Pavan Gujjar, Y. S. Ravikumar, Lakshmi Nagendra, Hiya Boro, Saptarshi Bhattacharya
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 27(4): 325. CrossRef - Diabetic Neuropathies
Melissa A. Elafros, Brian C. Callaghan
CONTINUUM: Lifelong Learning in Neurology.2023; 29(5): 1401. CrossRef - Determinants of the heart rate variability in type 1 diabetes mellitus
Máté Hajdu, Konstandia Garmpis, Vivien Vértes, Noémi Vorobcsuk-Varga, Gergő Attila Molnár, László Hejjel, István Wittmann, Réka Faludi
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Exercise on Cardiovascular Autonomic Nervous Function in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review
Hidetaka Hamasaki
Healthcare.2023; 11(19): 2668. CrossRef - Influence of Fibrinogen/Albumin Ratio and Fibrinogen/Pre-Albumin Ratio on Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes
Subei Zhao, Zheng Yang, Meng Yu, Linyu Xiang, Yuhuan Lv, Chunyan Tian, Rong Li
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3249. CrossRef - In Ischemic Heart Disease, Reduced Sensitivity to Pressure at the Sternum Accompanies Lower Mortality after Five Years: Evidence from a Randomized Controlled Trial
Søren Ballegaard, Jens Faber, Christian Selmer, Finn Gyntelberg, Svend Kreiner, Benny Karpatschof, Tobias Wirenfeldt Klausen, Åke Hjalmarson, Albert Gjedde
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(24): 7585. CrossRef - Assessment of the relationship of systemic vascular dysfunction and cardiac autonomic neuropathy (CAN) with diabetic retinopathy
KJ Hari Prakash, Sucheta Parija, Manisha Kar
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2023; 12(12): 3236. CrossRef - Autonomic Neuropathy in Ambulatory Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Single-arm Prospective, Observational Study
Kaustav Saha, Shatavisa Mukherjee, Animesh Maiti, Santanu Kumar Tripathi
Journal of the Practice of Cardiovascular Sciences.2023; 9(3): 178. CrossRef - Insomnia and type 2 diabetes: how to help the patient. Modern view of a neurologist
E. S. Akarachkova, O. V. Kotova, V. L. Klimov, D. I. Lebedeva
FOCUS. Endocrinology.2023; 4(4): 12. CrossRef - Carvedilol improves heart rate variability indices, biomarkers but not cardiac nerve density in streptozotocin-induced T2DM model of diabetic cardiac autonomic neuropathy
Olawale Mathias Akinlade, Bamidele Owoyele, Olufemi Ayodele Soladoye
Journal of Basic and Clinical Physiology and Pharmacology.2022; 33(2): 213. CrossRef - Cardiovascular autonomic responses during head-up tilt test in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes
Esteban Jorge-Galarza, Margarita Torres-Tamayo, María del Rocío Martínez-Alvarado, Berenice Peña-Aparicio, Carmen González-Salazar, Juan Reyes-Barrera, Manuel Sierra-Beltrán, Erika Fajardo-Flores, Andrey Kostin, J. Antonio González-Hermosillo
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2022; 191(5): 2077. CrossRef - Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and incident diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, Min Sun Choi, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 184: 109181. CrossRef - Kardiovaskuläre Risiken in der 4.–6. Lebensdekade mit Diabetes mellitus Typ 1
Young Hee Lee-Barkey, Bernd Stratmann, Diethelm Tschöpe
Der Diabetologe.2022; 18(2): 131. CrossRef - Mechanisms of cardiac dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy: molecular abnormalities and phenotypical variants
Francesca Romana Prandi, Isabella Evangelista, Domenico Sergi, Alberto Palazzuoli, Francesco Romeo
Heart Failure Reviews.2022; 28(3): 597. CrossRef - Comparison of Risk Assessment Strategies for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and Stable Chest Pain: A Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography Study
Jia Zhao, Shuo Wang, Pengyu Zhao, Yong Huo, Chunjie Li, Jia Zhou, Pawel Kleczynski
Journal of Diabetes Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - BOND study: a randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled trial over 12 months to assess the effects of benfotiamine on morphometric, neurophysiological and clinical measures in patients with type 2 diabetes with symptomatic polyneuropathy
Gidon J Bönhof, Gundega Sipola, Alexander Strom, Christian Herder, Klaus Strassburger, Birgit Knebel, Claudia Reule, Jan-Christoph Wollmann, Andrea Icks, Hadi Al-Hasani, Michael Roden, Oliver Kuss, Dan Ziegler
BMJ Open.2022; 12(2): e057142. CrossRef - Pragmatic Clinic-Based Investigation of Glycemic Variability in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes in Routine Clinical Practice and Its Association With Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy: A Pilot Study
Lucianne R.M. Tannus, Marilia B. Gomes
Endocrine Practice.2022; 28(5): 465. CrossRef - Longitudinal effects of one‐leg standing time on neuropathy outcomes in association with glycemic control in non‐elderly patients with type 2 diabetes
Kazuhiro Sugimoto, Takashi Sozu, Takehiko Hoshino, Yuko Watanabe, Akira Tamura, Toshiro Yamazaki, Setsu Ohta, Susumu Suzuki, Takuro Shimbo
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(6): 1039. CrossRef - Thermal quantitative sensory testing as a screening tool for cardiac autonomic neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus
Veronika Potockova, Sarka Mala, Lucie Hoskovcova, Vaclav Capek, Tomas Nedelka, Lucie Riedlbauchova, Daniel Baumgartner, Livie Mensova, Radim Mazanec
Brain and Behavior.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular Autonomic Reflex Tests and 7 Heart Rate Variability Indices for Early Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Individuals
Yeelen Ballesteros Atala, Mozânia Reis De Matos, Denise Engelbrecht Zantut-Wittmann, Alejandro Rosell Castillo, Daniele P Santos-Bezerra, Maria Lucia Correa-Giannella, Maria Cândida Ribeiro Parisi
Current Diabetes Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Design, synthesis, in vitro and in silico studies of naproxen derivatives as dual lipoxygenase and α-glucosidase inhibitors
Asma Sardar, Obaid-ur-Rahman Abid, Saima Daud, M. Fakhar-e-Alam, Muhammad Hussnain Siddique, Muhammad Ashraf, Wardah Shahid, Syeda Abida Ejaz, M. Atif, Shafiq Ahmad, Sulman Shafeeq, Muhammad Afzal
Journal of Saudi Chemical Society.2022; 26(3): 101468. CrossRef - Clinical manifestations and evaluation of cardiac autonomic neuropathy in diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome
L. S. Moshkhoeva, A. N. Barinov
Neurology, Neuropsychiatry, Psychosomatics.2022; 14(2): 71. CrossRef - The relationship between vitamin B12 levels and electrocardiographic ventricular repolarization markers
Emre Yılmaz, Devrim Kurt, Aslı Vural, Ertan Aydın, Sencer Çamcı, Ercan Aydın
Nutrición Hospitalaria.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of liraglutide on cardiac autonomic function in type 2 diabetes: A prespecified secondary analysis from the LIRAFLAME randomized, double‐blinded, placebo‐controlled trial
Suvanjaa Sivalingam, Emilie Hein Zobel, Christian S. Hansen, Rasmus S. Ripa, Bernt J. von Scholten, Viktor Rotbain Curovic, Andreas Kjaer, Jacob K. Jensen, Tine W. Hansen, Peter Rossing
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(8): 1638. CrossRef - Heart Rate Variability and Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Wei Shi, Jing Zhang, Dan Chen, Xiaolei Chen, Wei Duan, Hongmei Zhang, Fahd Abd Algalil
Applied Bionics and Biomechanics.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Spectrum of cardiac autonomic neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A North India perspective
PrativaPriyadarshani Sethi, Basavraj Jatteppanavar, Ravi Kant, Monika Pathania, MukeshChand Bairwa
Journal of Cardio-diabetes and metabolic disorders.2022; 2(1): 23. CrossRef - Cardiac Autonomic Dysfunction Is Associated With Risk of Diabetic Kidney Disease Progression in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Haixia Zeng, Jianmo Liu, Zheng Chen, Peng Yu, Jianping Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Tools, Biomarkers, and Treatments in Diabetic polyneuropathy
and Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy
Gidon J. Bönhof, Christian Herder, Dan Ziegler
Current Diabetes Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride glucose index is related with cardiac autonomic dysfunction in patients with metabolic syndrome
Akif Serhat Balcıoğlu, Ekrem Aksu, Ahmet Çağrı Aykan
Kardiologiia.2022; 62(6): 45. CrossRef - Pathogenesis of Distal Symmetrical Polyneuropathy in Diabetes
Sasha Smith, Pasha Normahani, Tristan Lane, David Hohenschurz-Schmidt, Nick Oliver, Alun Huw Davies
Life.2022; 12(7): 1074. CrossRef - Correlation between impaired hemodynamic response and cardiopulmonary fitness in middle-aged type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a case–control study
Jinjin Xie, Lianhua Yin, Jia Huang, Ying Xu, Yannan Chen, Jiawei Qin, Zhizhen Liu, Jing Tao
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2022; 122(10): 2295. CrossRef - Higher frequency of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in youth with type 2 compared to type 1 diabetes: Role of cardiometabolic risk factors
Benjamin J. Varley, Megan L. Gow, Yoon Hi Cho, Paul Benitez‐Aguirre, Janine Cusumano, Alison Pryke, Albert Chan, Vallimayil Velayutham, Kim C. Donaghue, Maria E. Craig
Pediatric Diabetes.2022; 23(7): 1073. CrossRef - The role of protein kinase C in diabetic microvascular complications
Deng Pan, Lin Xu, Ming Guo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors on cardiac autonomic function in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Dimitrios Patoulias, Alexandra Katsimardou, Nikolaos Fragakis, Christodoulos Papadopoulos, Michael Doumas
Acta Diabetologica.2022; 60(1): 1. CrossRef - Association between blood glucose levels and autonomic symptoms in Peru
Gabriel Angeles-Zurita, Margorie Narro-Fuentes, Antonio Bernabe-Ortiz
Primary Care Diabetes.2022; 16(5): 709. CrossRef - Clinical scoring systems for the risk of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: A simple tool
Marika Menduni, Cinzia D'Amato, Martina Leoni, Valentina Izzo, Mariateresa Staltari, Carla Greco, Andrea Abbatepassero, Giuseppe Seminara, Ilenia D'Ippolito, Davide Lauro, Vincenza Spallone
Journal of the Peripheral Nervous System.2022; 27(4): 259. CrossRef - Vagus nerve stimulation as a novel treatment for systemic lupus erythematous: study protocol for a randomised, parallel-group, sham-controlled investigator-initiated clinical trial, the SLE-VNS study
Amanda Hempel Zinglersen, Ida Lynghøj Drange, Katrine Aagaard Myhr, Andreas Fuchs, Mogens Pfeiffer-Jensen, Christina Brock, Søren Jacobsen
BMJ Open.2022; 12(9): e064552. CrossRef - To the interpretation of frequency components of the heart rate variability
N. V. Kuzmenko, V. A. Tsyrlin, M. G. Pliss
Translational Medicine.2022; 9(3): 35. CrossRef - Protein pyrrole adducts are associated with elevated glucose indices and clinical features of diabetic diffuse neuropathies
Xiao Chen, Zhuyi Jiang, Lianjing Zhang, Wei Liu, Xiaohu Ren, Luling Nie, Desheng Wu, Zhiwei Guo, Weimin Liu, Xifei Yang, Yan Wu, Zhen Liang, Peter Spencer, Jianjun Liu
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(10): 646. CrossRef - Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Management
Scott Williams, Siddig Abdel Raheim, Muhammad Ilyas Khan, Umme Rubab, Prathap Kanagala, Sizheng Steven Zhao, Anne Marshall, Emily Brown, Uazman Alam
Clinical Therapeutics.2022; 44(10): 1394. CrossRef - Pathophysiological and clinical aspects of the circadian rhythm of arterial stiffness in diabetes mellitus: A minireview
Victoria A. Serhiyenko, Ludmila M. Serhiyenko, Volodymyr B. Sehin, Alexandr A. Serhiyenko
Endocrine Regulations.2022; 56(4): 284. CrossRef - Heart rate-corrected QT interval prolongation is associated with decreased heart rate variability in patients with type 2 diabetes
Seon-Ah Cha
Medicine.2022; 101(45): e31511. CrossRef - Effect of the Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Autonomic Function in Subjects with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Carla Greco, Daniele Santi, Giulia Brigante, Chiara Pacchioni, Manuela Simoni
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 901. CrossRef - Diabetes-Induced Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy: Impact on Heart Function and Prognosis
Susumu Z. Sudo, Tadeu L. Montagnoli, Bruna de S. Rocha, Aimeé D. Santos, Mauro P. L. de Sá, Gisele Zapata-Sudo
Biomedicines.2022; 10(12): 3258. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Orthostatic Hypotension and Vitamin D Deficiency in Patients with Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ece YİĞİT, Ridvan SİVRİTEPE, Dilay KARABULUT, Umut KARABULUT
Online Türk Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2022; 7(2): 313. CrossRef - A study of heart rate variability in diabetic mellitus patients
Srinivasa Jayachandra, Satyanath Reddy Kodidala
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2022; 18(3): 153. CrossRef - The prevalence of cardiac autonomic neuropathy in prediabetes: a systematic review
Aikaterini Eleftheriadou, Scott Williams, Sarah Nevitt, Emily Brown, Rebecca Roylance, John P. H. Wilding, Daniel J. Cuthbertson, Uazman Alam
Diabetologia.2021; 64(2): 288. CrossRef - Risk of cardiac autonomic neuropathy in latent autoimmune diabetes in adults is similar to type 1 diabetes and lower compared to type 2 diabetes: A cross‐sectional study
Ernesto Maddaloni, Chiara Moretti, Rossella Del Toro, Sara Sterpetti, Maria Vittoria Ievolella, Gabriele Arnesano, Rocky Strollo, Silvia Irina Briganti, Luca D'Onofrio, Paolo Pozzilli, Raffaella Buzzetti
Diabetic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of lunar cycle on fasting plasma glucose, heart rate and blood pressure in type 2 diabetic patients
Sutanu Dutta Chowdhury, Subhasish Pramanik, Koena Bhattacharjee, Lakshmi Kanta Mondal
Chronobiology International.2021; 38(2): 270. CrossRef - Intensive Risk Factor Management and Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes: The ACCORD Trial
Yaling Tang, Hetal Shah, Carlos Roberto Bueno Junior, Xiuqin Sun, Joanna Mitri, Maria Sambataro, Luisa Sambado, Hertzel C. Gerstein, Vivian Fonseca, Alessandro Doria, Rodica Pop-Busui
Diabetes Care.2021; 44(1): 164. CrossRef - Decreased glomerular filtration rate and increased albuminuria for identification of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in subjects with and without diabetes
Ying-Chuen Lai, Hung-Yuan Li, Yi-Dier Jiang, Tien-Jyun Chang, Lee-Ming Chuang
Autonomic Neuroscience.2021; 230: 102757. CrossRef - Exposures influencing the developing central autonomic nervous system
Sarah D. Schlatterer, Adre J. du Plessis
Birth Defects Research.2021; 113(11): 845. CrossRef - Vitamin B12 Supplementation in Diabetic Neuropathy: A 1-Year, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Triantafyllos Didangelos, Eleni Karlafti, Evangelia Kotzakioulafi, Eleni Margariti, Parthena Giannoulaki, Georgios Batanis, Solomon Tesfaye, Kοnstantinos Kantartzis
Nutrients.2021; 13(2): 395. CrossRef - The Association Between Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Metrics and Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Outpatients with Type 2 Diabetes
Min Young Kim, Gyuri Kim, Ji Yun Park, Min Sun Choi, Ji Eun Jun, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2021; 23(6): 434. CrossRef - Insulin resistance is independently associated with cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes
Yingshan Liu, Yu Peng, Jing Jin, Yanshan Chen, Chuna Chen, Zhenguo Chen, Haishan Huang, Lingling Xu
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(9): 1651. CrossRef - SGLT2 inhibitors and the autonomic nervous system in diabetes: A promising challenge to better understand multiple target improvement
Vincenza Spallone, Paul Valensi
Diabetes & Metabolism.2021; 47(4): 101224. CrossRef - Reduction of Pressure Pain Sensitivity as Novel Non-pharmacological Therapeutic Approach to Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Trial
Jens Faber, Ebbe Eldrup, Christian Selmer, Caroline Pichat, Sofie Korsgaard Hecquet, Torquil Watt, Svend Kreiner, Benny Karpatschof, Finn Gyntelberg, Søren Ballegaard, Albert Gjedde
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between cardiac autonomic neuropathy and cardio-metabolic risk profile in adults with type 1 diabetes
M. Serdarova, R. Dimova, N. Chakarova, G. Grozeva, A. Todorova, T. Tankova
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 174: 108721. CrossRef - Differences and Similarities in Neuropathy in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review
Mar Sempere-Bigorra, Iván Julián-Rochina, Omar Cauli
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2021; 11(3): 230. CrossRef - Assessment of Gastrointestinal Autonomic Dysfunction: Present and Future Perspectives
Ditte S. Kornum, Astrid J. Terkelsen, Davide Bertoli, Mette W. Klinge, Katrine L. Høyer, Huda H. A. Kufaishi, Per Borghammer, Asbjørn M. Drewes, Christina Brock, Klaus Krogh
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(7): 1392. CrossRef - Diabetic heart disease: A clinical update
Jake Rajbhandari, Cornelius James Fernandez, Mayuri Agarwal, Beverly Xin Yi Yeap, Joseph M Pappachan
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(4): 383. CrossRef - Novel and Emerging Electrophysiological Biomarkers of Diabetic Neuropathy and Painful Diabetic Neuropathy
Anne Marshall, Uazman Alam, Andreas Themistocleous, Nigel Calcutt, Andrew Marshall
Clinical Therapeutics.2021; 43(9): 1441. CrossRef - Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy Is Not Reversed by Euglycemia Following Islet Transplantation
Tejas Deshmukh, Peter Emerson, Patricia Anderson, Eddy Kizana, Philip J. O’Connell, D. Jane Holmes-Walker, James J.H. Chong
Transplantation.2021; 105(5): 1125. CrossRef - Attenuation of Muscle Mass and Density Is Associated With Poor Outcomes Among Patients Undergoing Major Gynecologic Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Lu Che, Yan Zhang, Jiawen Yu, Li Xu, Yuguang Huang
Anesthesia & Analgesia.2021; 132(6): 1692. CrossRef - Association of Urinary N-Acetyl-β-D-Glucosaminidase with Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus without Nephropathy
Min Sun Choi, Ji Eun Jun, Sung Woon Park, Jee Hee Yoo, Jiyeon Ahn, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Moon-Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 349. CrossRef - Pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical management of diabetic sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy
Gordon Sloan, Dinesh Selvarajah, Solomon Tesfaye
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2021; 17(7): 400. CrossRef - Heart Rate Variability as a Potential Non-invasive Marker of Blood Glucose Level
L. R. Jarman, J. L. Elliott, T. Lees, R. Clifton-Bligh, A. M. Simpson, N. Nassif, S. Lal
Human Physiology.2021; 47(2): 209. CrossRef - Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in diabetes: Pathophysiology, clinical assessment and implications
Alice Duque, Mauro Felippe Felix Mediano, Andrea De Lorenzo, Luiz Fernando Rodrigues Jr
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(6): 855. CrossRef - Gaussian process-based kernel as a diagnostic model for prediction of type 2 diabetes mellitus risk using non-linear heart rate variability features
R. Shashikant, Uttam Chaskar, Leena Phadke, Chetankumar Patil
Biomedical Engineering Letters.2021; 11(3): 273. CrossRef - Possible Preventative/Rehabilitative Role of Gliflozins in OSA and T2DM. A Systematic Literature Review-Based Hypothesis
Vincenzo Maria Monda, Francesca Porcellati, Felice Strollo, Alessandro Fucili, Marcello Monesi, Ersilia Satta, Sandro Gentile
Advances in Therapy.2021; 38(8): 4195. CrossRef - Characteristics of cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction and association with quality of life in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
Amanda Hempel Zinglersen, Katrine Kjær Iversen, Henrik Christian Bidstrup Leffers, Esben Laugesen, Jesper Fleischer, Søren Jacobsen
Lupus Science & Medicine.2021; 8(1): e000507. CrossRef - Impaired vagal adaptation to an exercise task in women with gestational diabetes mellitus versus women with uncomplicated pregnancies
Marieta P. Theodorakopoulou, Areti Triantafyllou, Andreas Zafeiridis, Afroditi Κ. Boutou, Iris Grigoriadou, Evangelia Kintiraki, Stella Douma, Dimitrios G. Goulis, Konstantina Dipla
Hormones.2021; 20(4): 753. CrossRef - Cardioprotective Effects of Sodium-glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Regardless of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-analysis
Lucas Silva Sousa, Felipe de Araújo Nascimento, Juliano Rocha, Michelle Rocha-Parise
International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of diabetic neuropathy
Simona Cernea, Itamar Raz
Metabolism.2021; 123: 154867. CrossRef - Large fibre, small fibre and autonomic neuropathy in adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A systematic review
Vinni Faber Rasmussen, Troels Staehelin Jensen, Hatice Tankisi, Páll Karlsson, Esben Thyssen Vestergaard, Kurt Kristensen, Jens Randel Nyengaard, Astrid Juhl Terkelsen
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2021; 35(11): 108027. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Risk Management in Type 1 Diabetes
I. H. Teoh, P. Elisaus, J. D. Schofield
Current Diabetes Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Disturbances in the intraventricular conduction system in teenagers with type 1 diabetes. A pilot study
Agnieszka Zubkiewicz-Kucharska, Anna Noczyńska, Małgorzata Sobieszczańska, Małgorzata Poręba, Joanna Chrzanowska, Rafał Poręba, Monika Seifert, Anna Janocha, Krystyna Laszki-Szcząchor
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2021; 35(11): 108043. CrossRef - Peripheral and Autonomic Neuropathy Status of Young Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus at the Time of Transition From Pediatric Care to Adult-Oriented Diabetes Care
Anna Vágvölgyi, Ágnes Maróti, Mónika Szűcs, Csongor Póczik, Dóra Urbán-Pap, István Baczkó, Attila Nemes, Éva Csajbók, Krisztián Sepp, Péter Kempler, Andrea Orosz, Tamás Várkonyi, Csaba Lengyel
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency in diabetes is associated with autonomic dysfunction
Dag André Sangnes, Elisabeth Sandvik Bergmann, Rose Marie Moss, Trond Engjom, Eirik Søfteland
Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 56(10): 1222. CrossRef - Dependence of Heart Rate Variability Indices on the Mean Heart Rate in Women with Well-Controlled Type 2 Diabetes
Adriana Robles-Cabrera, José M. Torres-Arellano, Ruben Fossion, Claudia Lerma
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(19): 4386. CrossRef - Normative data on cardiovascular autonomic function in Greenlandic Inuit
Marie Mathilde Bjerg Christensen, Christian Stevns Hansen, Jesper Fleischer, Dorte Vistisen, Stine Byberg, Trine Larsen, Jens Christian Laursen, Marit Eika Jørgensen
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2021; 9(1): e002121. CrossRef - What Is in the Field for Genetics and Epigenetics of Diabetic Neuropathy: The Role of MicroRNAs
V. Spallone, C. Ciccacci, A. Latini, P. Borgiani, Karim Gariani
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Evaluation and treatment of peripheral nervous system dysfunction in patients with prediabetes
O. E. Zinovyeva, T. M. Ostroumova, M. V. Koniashova, N. A. Gorbachev
Neurology, Neuropsychiatry, Psychosomatics.2021; 13(5): 116. CrossRef - Manifestazioni cliniche della neuropatia autonomica diabetica: valutazione dei sintomi
Carla Greco, Chiara Pacchioni, Manuela Simoni
L'Endocrinologo.2021; 22(6): 514. CrossRef - Perspectives of glycemic variability in diabetic neuropathy: a comprehensive review
Xiaochun Zhang, Xue Yang, Bao Sun, Chunsheng Zhu
Communications Biology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association Between Cardiovascular Autonomic Function and Changes in Kidney and Myocardial Function in Type 2 Diabetes and Healthy Controls
Jens Christian Laursen, Ida Kirstine B. Rasmussen, Emilie H. Zobel, Philip Hasbak, Bernt Johan von Scholten, Lene Holmvang, Rasmus S. Ripa, Christian S. Hansen, Marie Frimodt-Moeller, Andreas Kjaer, Peter Rossing, Tine W. Hansen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Dependence of heart rate variability on indicators of type 1 diabetes mellitus control.
N. O. Pertseva, O. V. Gurzhiy, K. I. Moshenets
Medicni perspektivi (Medical perspectives).2020; 25(1): 88. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of evogliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, active‐controlled, randomized, double‐blind study with open‐label extension (the EVERGREEN study)
Gyuri Kim, Soo Lim, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon, Ie B. Park, Kyu J. Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park, Su K. Kwon, Hye S. Kim, Seok W. Park, Sin G. Kim, Min K. Moon, Eun S. Kim, Choon H. Chung, Kang S. Park, Mikyung Kim, Dong J. Chung, Chang B. Lee, Tae H. Kim, Moon‐Kyu Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2020; 22(9): 1527. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus and comorbidities: A bad romance
Niki Katsiki, Dimitrios Tousoulis
Hellenic Journal of Cardiology.2020; 61(1): 23. CrossRef - Features of the glucose influence on the heart activity and the changes in the potentials of the stomach and the intestines at the heart insufficiency conditions
V. V. Soltanov, L. M. Komarovskaya
Doklady of the National Academy of Sciences of Belarus.2020; 63(6): 736. CrossRef - Living Day to Day
Gerald Kayingo, Virginia McCoy Hass
Physician Assistant Clinics.2020; 5(2): 213. CrossRef - Source specific PM2.5 associated with heart rate variability in the elderly with coronary heart disease: A community-based panel study
Xi Chen, Bing Qiu, Qinpei Zou, Tian Qiu, Runkui Li, Ashley Truong, Yanmin Qi, Tao Liu, Limin Han, Tiebing Liu, Junrui Chang, Qi Sun, Ying Zhu, Dongqun Xu
Chemosphere.2020; 260: 127399. CrossRef - The Association of Autonomic Nervous System Function With Ischemic Stroke, and Treatment Strategies
Mengxi Zhao, Ling Guan, Yilong Wang
Frontiers in Neurology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiac diabetic autonomic neuropathy
L. T. Akhmedzhanova, T. A. Belyakova, Yu. A. Podkovko, Yu. M. Shor
Medical Council.2020; (21): 94. CrossRef - Diabetes, and its treatment, as an effector of autonomic nervous system circuits and its functions
Liliana Espinoza, Carie R Boychuk
Current Opinion in Pharmacology.2020; 54: 18. CrossRef - Morning blood pressure surge is associated with autonomic neuropathy and peripheral vascular disease in patients with diabetes
Federica Di Gennaro, Cinzia D’Amato, Roberto Morganti, Carla Greco, Susanna Longo, Diana Corradini, Davide Lauro, Vincenza Spallone
Journal of Human Hypertension.2020; 34(7): 495. CrossRef - The Compound Expression of HSP90 and INOS in the Testis of Diabetic Rats as Cellular and Pathologic Adverse Effects of Diabetes
Ali Alsarhan, Kawther Faisal Amawi, Inas Saleh Al-Mazari, Hashem Abu Hurirah, Ahed J. Alkhatib
Analytical Cellular Pathology.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Heart rate variability features from nonlinear cardiac dynamics in identification of diabetes using artificial neural network and support vector machine
Yogender Aggarwal, Joyani Das, Papiya Mitra Mazumder, Rohit Kumar, Rakesh Kumar Sinha
Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering.2020; 40(3): 1002. CrossRef - Distal Symmetric and Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathies in Brazilian Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Followed in a Primary Health Care Unit: A Cross-Sectional Study
Mozania Reis de Matos, Daniele Pereira Santos-Bezerra, Cristiane das Graças Dias Cavalcante, Jacira Xavier de Carvalho, Juliana Leite, Jose Antonio Januario Neves, Sharon Nina Admoni, Marisa Passarelli, Maria Candida Parisi, Maria Lucia Correa-Giannella
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(9): 3232. CrossRef - Awareness of hypoglycemia and spectral analysis of heart rate variability in type 1 diabetes
Ticiana Paes, L. Clemente Rolim, Celso Sallum Filho, João Roberto de Sa, Sérgio A. Dib
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2020; 34(8): 107617. CrossRef - Is there cardiac autonomic neuropathy in prediabetes?
Lindsay A. Zilliox, James W. Russell
Autonomic Neuroscience.2020; 229: 102722. CrossRef - Chronic Microvascular Complications in Prediabetic States—An Overview
Angelika Baranowska-Jurkun, Wojciech Matuszewski, Elżbieta Bandurska-Stankiewicz
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(10): 3289. CrossRef - Cardiac vagal tone as a novel screening tool to recognize asymptomatic cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy: Aspects of utility in type 1 diabetes
Anne-Marie Wegeberg, Elin D Lunde, Sam Riahi, Niels Ejskjaer, Asbjørn M Drewes, Birgitte Brock, Rodica Pop-Busui, Christina Brock
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 170: 108517. CrossRef - Assessment of baroreceptor reflex sensitivity in young obese Saudi males at rest and in response to physiological challenges
Abdullah N. AlShahrani, Lubna I. Al‐Asoom, Ahmed A. Alsunni, Nabil S. Elbahai, Talay Yar
Physiological Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between QT interval indices with cardiac autonomic neuropathy in diabetic patients: a case control study
Maryam Vasheghani, Farzaneh Sarvghadi, Mohammad Reza Beyranvand, Habib Emami
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Myocardial ischaemia reperfusion injury and cardioprotection in the presence of sensory neuropathy: Therapeutic options
Péter Bencsik, Kamilla Gömöri, Tamara Szabados, Péter Sántha, Zsuzsanna Helyes, Gábor Jancsó, Péter Ferdinandy, Anikó Görbe
British Journal of Pharmacology.2020; 177(23): 5336. CrossRef - Biological Activity of c-Peptide in Microvascular Complications of Type 1 Diabetes—Time for Translational Studies or Back to the Basics?
Aleksandra Ryk, Aleksandra Łosiewicz, Arkadiusz Michalak, Wojciech Fendler
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(24): 9723. CrossRef - Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: inter-relation of risk factors and treatment
Aman Sharma, Shweta Mittal, Rohan Aggarwal, Meenakshi K. Chauhan
Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy: A Clinical Update
Jugal Kishor Sharma, Anshu Rohatgi, Dinesh Sharma
Journal of the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh.2020; 50(3): 269. CrossRef - Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome and the Risk of Microvascular Complications in Patients with Diabetes mellitus
Niki Katsiki, Panagiotis Anagnostis, Kalliopi Kotsa, Dimitrios G. Goulis, Dimitri P. Mikhailidis
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2019; 25(18): 2051. CrossRef - Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy in Obesity, the Metabolic Syndrome and Prediabetes: A Narrative Review
Scott M. Williams, Aikaterini Eleftheriadou, Uazman Alam, Daniel J. Cuthbertson, John P. H. Wilding
Diabetes Therapy.2019; 10(6): 1995. CrossRef
- Rectal sensitivity correlated with gastrointestinal‐mediated glucose disposal, but not the incretin effect
- Complications
- Patterns of Nerve Conduction Abnormalities in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus According to the Clinical Phenotype Determined by the Current Perception Threshold
- Joong Hyun Park, Jong Chul Won
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(6):519-528. Published online October 24, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0068
- 5,507 View
- 77 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Clinical manifestations of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) vary along the course of nerve damage. Nerve conduction studies (NCS) have been suggested as a way to confirm diagnoses of DPN, but the results have limited utility for evaluating clinical phenotypes. The current perception threshold (CPT) is a complementary method for diagnosing DPN and assessing DPN symptoms. We compared NCS variables according to clinical phenotypes determined by CPT measurements.
Methods We retrospectively enrolled patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who underwent both NCS and CPT tests using a neurometer. CPT grades were used to determine the clinical phenotypes of DPN: normoesthesia (0 to 1.66), hyperesthesia (1.67 to 6.62), and hypoesthesia/anesthesia (6.63 to 12.0). The Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument (MNSI) was used to determine a subjective symptom score. DPN was diagnosed based on both patient symptoms (MNSI score ≥3) and abnormal NCS results.
Results A total of 202 patients (117 men and 85 women) were included in the final analysis. The average age was 62.6 years, and 71 patients (35.1%) were diagnosed with DPN. The CPT variables correlated with MNSI scores and NCS variables in patients with diabetes. Linear regression analyses indicated that hypoesthesia was associated with significantly lower summed velocities and sural amplitudes and velocities, and higher summed latencies, than normoesthesia. Sural amplitude was significantly lower in patients with hyperesthesia than in patients with normoesthesia.
Conclusion NCS variables differed among patients with diabetes according to clinical phenotypes based on CPT and decreased sural nerve velocities was associated with hyperesthesia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evoked sensations with transcutaneous electrical stimulation with different frequencies, waveforms, and electrode configurations
Eukene Imatz‐Ojanguren, Thierry Keller
Artificial Organs.2023; 47(1): 117. CrossRef - Cognitive function in individuals with and without painful and painless diabetic polyneuropathy—A cross‐sectional study in type 1 diabetes
Suganthiya S. Croosu, Mimoza Gjela, Johan Røikjer, Tine M. Hansen, Carsten D. Mørch, Jens B. Frøkjær, Niels Ejskjaer
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adherence and the Diabetic Foot: High Tech Meets High Touch?
Hadia Srass, J. Karim Ead, David G. Armstrong
Sensors.2023; 23(15): 6898. CrossRef - Glomerular filtration Rate, urine Albumin/ creatinine ratio and current perception threshold in patients with diabetic kidney disease
Cheng-Xian Pi, Teng-Juan Gui, Qi-Da He, Fang Yin, Ren-Jiao Cai, Yue Wang, Qiu-Xia Xue, Xin-Kui Tian, Tao Wang, Xing–Wei Zhe
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 189: 109934. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of α-Lipoic Acid and Low Dose Pregabalin Combination in Painful Diabetic Neuropathy
Ki-Tae Park, Jin-Kwang Lee, Se Jin Park
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2022; 26(4): 177. CrossRef - Association between Sleep Quality and Painless Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Assessed by Current Perception Threshold in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Dughyun Choi, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chan-Hee Jung, Chul-Hee Kim, Ji-Oh Mok
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 358. CrossRef - The relationship between exacerbated diabetic peripheral neuropathy and metformin treatment in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Manal Mohammed Hashem, Ahmed Esmael, Abdelfattah Kasem Nassar, Mohammed El-Sherif
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - New Perspective in Diabetic Neuropathy: From the Periphery to the Brain, a Call for Early Detection, and Precision Medicine
Heng Yang, Gordon Sloan, Yingchun Ye, Shuo Wang, Bihan Duan, Solomon Tesfaye, Ling Gao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - γ-Linolenic Acid versus α-Lipoic Acid for Treating Painful Diabetic Neuropathy in Adults: A 12-Week, Double-Placebo, Randomized, Noninferiority Trial
Jong Chul Won, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Seong-Su Moon, Sung Wan Chun, Chong Hwa Kim, Ie Byung Park, In Joo Kim, Jihyun Lee, Bong Yun Cha, Tae Sun Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 542. CrossRef - Supplementation with Korean Red Ginseng Improves Current Perception Threshold in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Kahui Park, YuSik Kim, Junghye Kim, Shinae Kang, Jong Suk Park, Chul Woo Ahn, Ji Sun Nam
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: advances in diagnosis and strategies for screening and early intervention
Dinesh Selvarajah, Debasish Kar, Kamlesh Khunti, Melanie J Davies, Adrian R Scott, Jeremy Walker, Solomon Tesfaye
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2019; 7(12): 938. CrossRef
- Evoked sensations with transcutaneous electrical stimulation with different frequencies, waveforms, and electrode configurations

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





