
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- 2023 Diabetic Kidney Disease Fact Sheet in Korea
- Nam Hoon Kim, Mi-Hae Seo, Jin Hyung Jung, Kyung Do Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Nan Hee Kim, on Behalf of Diabetic Kidney Disease Research Group of the Korean Diabetes Association
- Received July 30, 2023 Accepted January 26, 2024 Published online March 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0310 [Epub ahead of print]
- 720 View
- 52 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
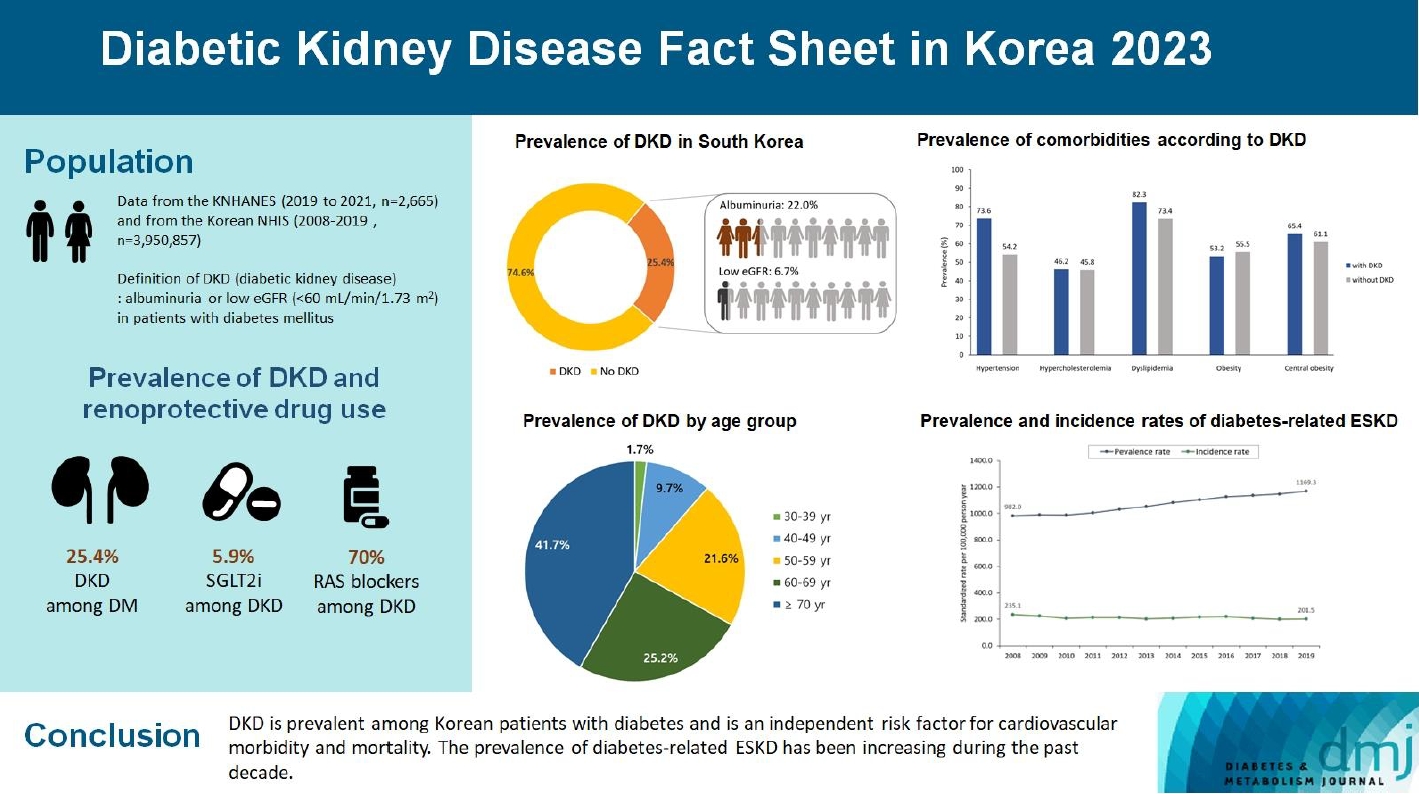
To investigate the prevalence, incidence, comorbidities, and management status of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) and diabetes-related end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) in South Korea.
Methods
We used the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data (2019 to 2021, n=2,665) for the evaluation of prevalence, comorbidities, control rate of glycemia and comorbidities in DKD, and the Korean Health Insurance Service-customized database (2008 to 2019, n=3,950,857) for the evaluation of trends in the incidence and prevalence rate of diabetes-related ESKD, renin-angiotensin system (RAS) blockers and sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors use for DKD, and the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) and mortality according to DKD stages. DKD was defined as albuminuria or low estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Results
The prevalence of DKD was 25.4% (albuminuria, 22.0%; low eGFR, 6.73%) in patients with diabetes mellitus aged ≥30 years. Patients with DKD had a higher rate of comorbidities, including hypertension, dyslipidemia, and central obesity; however, their control rates were lower than those without DKD. Prescription rate of SGLT2 inhibitors with reduced eGFR increased steadily, reaching 5.94% in 2019. Approximately 70% of DKD patients were treated with RAS blockers. The prevalence rate of diabetesrelated ESKD has been steadily increasing, with a higher rate in older adults. ASCVD and mortality were significantly associated with an in increase in DKD stage.
Conclusion
DKD is prevalent among Korean patients with diabetes and is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, which requiring intensive management of diabetes and comorbidities. The prevalence of diabetes-related ESKD has been increasing, especially in the older adults, during past decade. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endothelial NOX5 Obliterates the Reno-Protective Effect of Nox4 Deletion by Promoting Renal Fibrosis via Activation of EMT and ROS-Sensitive Pathways in Diabetes
Karin A. M. Jandeleit-Dahm, Haritha R. Kankanamalage, Aozhi Dai, Jaroslawna Meister, Sara Lopez-Trevino, Mark E. Cooper, Rhian M. Touyz, Christopher R. J. Kennedy, Jay C. Jha
Antioxidants.2024; 13(4): 396. CrossRef
- Endothelial NOX5 Obliterates the Reno-Protective Effect of Nox4 Deletion by Promoting Renal Fibrosis via Activation of EMT and ROS-Sensitive Pathways in Diabetes
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Two-Year Changes in Diabetic Kidney Disease Phenotype and the Risk of Heart Failure: A Nationwide Population-Based Study in Korea
- Seung Eun Lee, Juhwan Yoo, Han Seok Choi, Kyungdo Han, Kyoung-Ah Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):523-534. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0096
- 1,719 View
- 100 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
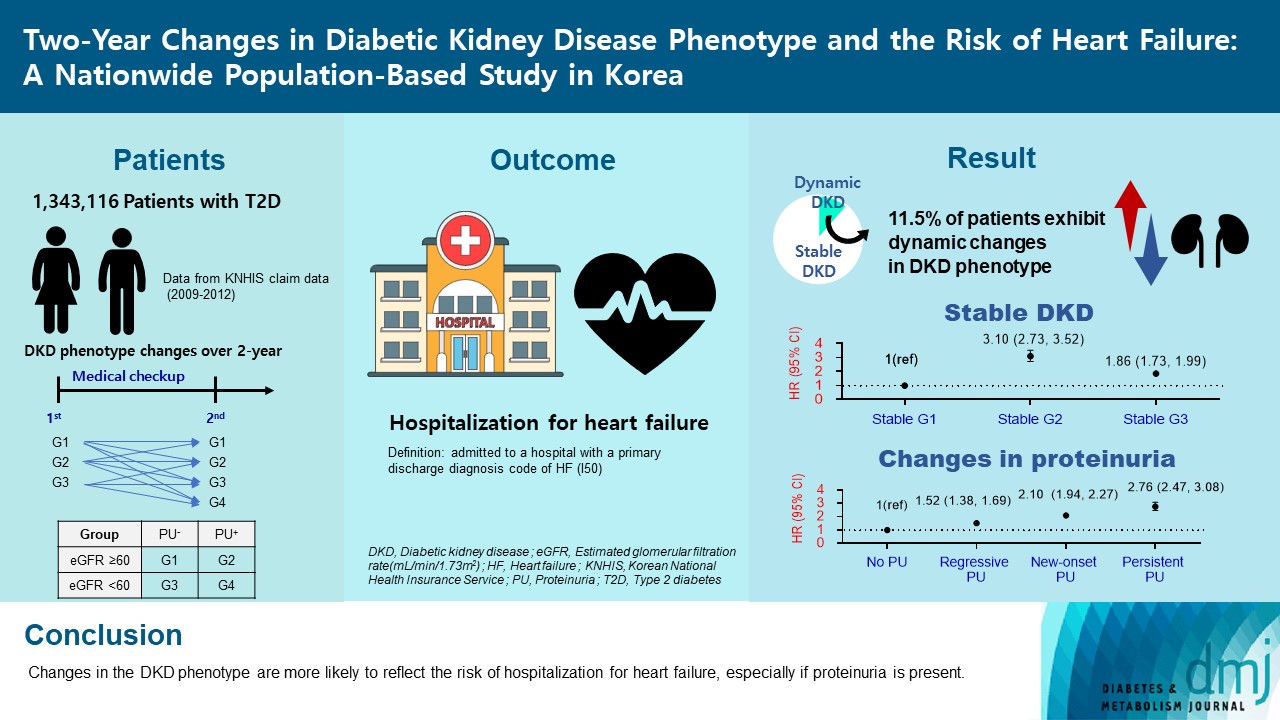
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a risk factor for hospitalization for heart failure (HHF). DKD could be classified into four phenotypes by estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR, normal vs. low) and proteinuria (PU, negative vs. positive). Also, the phenotype often changes dynamically. This study examined HHF risk according to the DKD phenotype changes across 2-year assessments.
Methods
The study included 1,343,116 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) from the Korean National Health Insurance Service database after excluding a very high-risk phenotype (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2) at baseline, who underwent two cycles of medical checkups between 2009 and 2014. From the baseline and 2-year eGFR and PU results, participants were divided into 10 DKD phenotypic change categories.
Results
During an average of 6.5 years of follow-up, 7,874 subjects developed HHF. The cumulative incidence of HHF from index date was highest in the eGFRlowPU– phenotype, followed by eGFRnorPU+ and eGFRnorPU–. Changes in DKD phenotype differently affect HHF risk. When the persistent eGFRnorPU– category was the reference, hazard ratios for HHF were 3.10 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.73 to 3.52) in persistent eGFRnorPU+ and 1.86 (95% CI, 1.73 to 1.99) in persistent eGFRlowPU–. Among altered phenotypes, the category converted to eGFRlowPU+ showed the highest risk. In the normal eGFR category at the second examination, those who converted from PU– to PU+ showed a higher risk of HHF than those who converted from PU+ to PU–.
Conclusion
Changes in DKD phenotype, particularly with the presence of PU, are more likely to reflect the risk of HHF, compared with DKD phenotype based on a single time point in patients with T2DM.
- Complications
- Pathophysiologic Mechanisms and Potential Biomarkers in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Chan-Young Jung, Tae-Hyun Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):181-197. Published online March 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0329
- 11,987 View
- 789 Download
- 41 Web of Science
- 45 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Although diabetic kidney disease (DKD) remains the leading cause of end-stage kidney disease eventually requiring chronic kidney replacement therapy, the prevalence of DKD has failed to decline over the past 30 years. In order to reduce disease prevalence, extensive research has been ongoing to improve prediction of DKD onset and progression. Although the most commonly used markers of DKD are albuminuria and estimated glomerular filtration rate, their limitations have encouraged researchers to search for novel biomarkers that could improve risk stratification. Considering that DKD is a complex disease process that involves several pathophysiologic mechanisms such as hyperglycemia induced inflammation, oxidative stress, tubular damage, eventually leading to kidney damage and fibrosis, many novel biomarkers that capture one specific mechanism of the disease have been developed. Moreover, the increasing use of high-throughput omic approaches to analyze biological samples that include proteomics, metabolomics, and transcriptomics has emerged as a strong tool in biomarker discovery. This review will first describe recent advances in the understanding of the pathophysiology of DKD, and second, describe the current clinical biomarkers for DKD, as well as the current status of multiple potential novel biomarkers with respect to protein biomarkers, proteomics, metabolomics, and transcriptomics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Role of polyphenols in the management of diabetic complications
Jeevika Raina, Atika Firdous, Gurvinder Singh, Rajesh Kumar, Charanjit Kaur
Phytomedicine.2024; 122: 155155. CrossRef - Role of MCP-1 as an inflammatory biomarker in nephropathy
Yanlong Liu, Ke Xu, Yuhua Xiang, Boyan Ma, Hailong Li, Yuan Li, Yue Shi, Shuju Li, Yan Bai
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Urinary podocyte stress marker as a prognostic indicator for diabetic kidney disease
Lingfeng Zeng, Jack Kit-Chung Ng, Winston Wing-Shing Fung, Gordon Chun-Kau Chan, Kai-Ming Chow, Cheuk-Chun Szeto
BMC Nephrology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification and validation of immune and cuproptosis - related genes for diabetic nephropathy by WGCNA and machine learning
Yubing Chen, Lijuan Liao, Baoju Wang, Zhan Wu
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Specific Alternation of Gut Microbiota and the Role of Ruminococcus gnavus in the Development of Diabetic Nephropathy
Jinni Hong, Tingting Fu, Weizhen Liu, Yu Du, Junmin Bu, Guojian Wei, Miao Yu, Yanshan Lin, Cunyun Min, Datao Lin
Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology.2024; 34(3): 547. CrossRef - A Narrative Review of New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy
Aadhira Pillai, Darshna Fulmali
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bamboo leaf: A review of traditional medicinal property, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and purification technology
Yaqian Cheng, Siqi Wan, Linna Yao, Ding Lin, Tong Wu, Yongjian Chen, Ailian Zhang, Chenfei Lu
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2023; 306: 116166. CrossRef - Molecular Pathways of Diabetic Kidney Disease Inferred from Proteomics
Lan Wei, Yuanyuan Han, Chao Tu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 117. CrossRef - Omics and Artificial Intelligence in Kidney Diseases
Nadja Grobe, Josef Scheiber, Hanjie Zhang, Christian Garbe, Xiaoling Wang
Advances in Kidney Disease and Health.2023; 30(1): 47. CrossRef - Intestinal microbiome diversity of diabetic and non-diabetic kidney disease: Current status and future perspective
Soumik Das, Ramanathan Gnanasambandan
Life Sciences.2023; 316: 121414. CrossRef - Pediatric Diabetic Nephropathy: Novel Insights from microRNAs
Francesca Lanzaro, Annalisa Barlabà, Angelica De Nigris, Federica Di Domenico, Valentina Verde, Emanuele Miraglia del Giudice, Anna Di Sessa
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(4): 1447. CrossRef - Novel Biomarkers of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Jorge Rico-Fontalvo, Gustavo Aroca-Martínez, Rodrigo Daza-Arnedo, José Cabrales, Tomás Rodríguez-Yanez, María Cardona-Blanco, Juan Montejo-Hernández, Dairo Rodelo Barrios, Jhonny Patiño-Patiño, Elber Osorio Rodríguez
Biomolecules.2023; 13(4): 633. CrossRef - Diabetic vascular diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies
Yiwen Li, Yanfei Liu, Shiwei Liu, Mengqi Gao, Wenting Wang, Keji Chen, Luqi Huang, Yue Liu
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic phenotypes and risk of end-stage kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Lijun Zhao, Yutong Zou, Yucheng Wu, Linli Cai, Yuancheng Zhao, Yiting Wang, Xiang Xiao, Qing Yang, Jia Yang, Honghong Ren, Nanwei Tong, Fang Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of a New RNA and Protein Integrated Biomarker Panel Associated with Kidney Function Impairment in DKD: Translational Implications
Alessandra Scamporrino, Stefania Di Mauro, Agnese Filippello, Grazia Di Marco, Antonino Di Pino, Roberto Scicali, Maurizio Di Marco, Emanuele Martorana, Roberta Malaguarnera, Francesco Purrello, Salvatore Piro
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(11): 9412. CrossRef - Increased serum PCSK9 levels are associated with renal function impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Zhicai Feng, Xiangyu Liao, Hao Zhang, Juan Peng, Zhijun Huang, Bin Yi
Renal Failure.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Serum Pyrodeath Re-lated Proteins and Renal Injury in Patients with Type 2 DKD
茹洁 马
Asian Case Reports in Emergency Medicine.2023; 11(02): 53. CrossRef - Loganin reduces diabetic kidney injury by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
Xiangri Kong, Yunyun Zhao, Xingye Wang, Yongjiang Yu, Ying Meng, Guanchi Yan, Miao Yu, Lihong Jiang, Wu Song, Bingmei Wang, Xiuge Wang
Chemico-Biological Interactions.2023; 382: 110640. CrossRef - Machine-learning algorithm-based prediction of a diagnostic model based on oxidative stress-related genes involved in immune infiltration in diabetic nephropathy patients
Heng-Mei Zhu, Na Liu, Dong-Xuan Sun, Liang Luo
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The roles of gut microbiota and its metabolites in diabetic nephropathy
Hui Zhao, Cheng-E Yang, Tian Liu, Ming-Xia Zhang, Yan Niu, Ming Wang, Jun Yu
Frontiers in Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - High triglyceride levels increase the risk of diabetic microvascular complications: a cross-sectional study
Jiahang Li, Lei Shi, Guohong Zhao, Fei Sun, Zhenxing Nie, Zhongli Ge, Bin Gao, Yan Yang
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation of Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and Nephrin Levels in Iraqi Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy
Raghda Hisham Aljorani, Eman Saadi Saleh , Khalaf Gata Hussein Al Mohammadawi
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2023; 5: 99. CrossRef - Diabetic Nephropathy: Significance of Determining Oxidative Stress and Opportunities for Antioxidant Therapies
Marina Darenskaya, Sergey Kolesnikov, Natalya Semenova, Lyubov Kolesnikova
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(15): 12378. CrossRef - Evaluation of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio, Low-Density Lipoprotein/Albumin Ratio, and Red Cell Distribution Width/Albumin Ratio in the Estimation of Proteinuria in Uncontrolled Diabetic Patients
Duygu Tutan, Murat Doğan
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hedysarum polybotrys polysaccharide attenuates renal inflammatory infiltration and fibrosis in diabetic mice by inhibiting the HMGB1/RAGE/TLR4 pathway
Changqing Xu, Yanxu Cheng, Zongmei Liu, Xiaoyan Fu
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Abdominal adipose tissue and type 2 diabetic kidney disease: adipose radiology assessment, impact, and mechanisms
Fei Lu, Jinlei Fan, Fangxuan Li, Lijing Liu, Zhiyu Chen, Ziyu Tian, Liping Zuo, Dexin Yu
Abdominal Radiology.2023; 49(2): 560. CrossRef - Inhibition of MD2 by natural product-drived JM-9 attenuates renal inflammation and diabetic nephropathy in mice
Minxiu Wang, Qianhui Zhang, Shuaijie Lou, Leiming Jin, Gaojun Wu, Wenqi Wu, Qidong Tang, Yi Wang, Xiaohong Long, Ping Huang, Wu Luo, Guang Liang
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 168: 115660. CrossRef - Multifaceted relationship between diabetes and kidney diseases: Beyond diabetes
Pasquale Esposito, Daniela Picciotto, Francesca Cappadona, Francesca Costigliolo, Elisa Russo, Lucia Macciò, Francesca Viazzi
World Journal of Diabetes.2023; 14(10): 1450. CrossRef - Mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein: a potential therapeutic target in renal disease
Meng Wu, Zhiyin Pei, Guangfeng Long, Hongbing Chen, Zhanjun Jia, Weiwei Xia
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Research progress on multiple cell death pathways of podocytes in diabetic kidney disease
Can Yang, Zhen Zhang, Jieting Liu, Peijian Chen, Jialing Li, Haiying Shu, Yanhui Chu, Luxin Li
Molecular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantitative profiling of carboxylic compounds by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for revealing biomarkers of diabetic kidney disease
Rongrong Zhu, Yan Yuan, Rourou Qi, Jianying Liang, Yan Shi, Hongbo Weng
Journal of Chromatography B.2023; 1231: 123930. CrossRef - Jiangtang Decoction Ameliorates Diabetic Kidney Disease Through the Modulation of the Gut Microbiota
Jinni Hong, Tingting Fu, Weizhen Liu, Yu Du, Junmin Bu, Guojian Wei, Miao Yu, Yanshan Lin, Cunyun Min, Datao Lin
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3707. CrossRef - GLP-1RA Combined with SGLT2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Meta Analysis
莹 郭
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(11): 18117. CrossRef - Potential application of Klotho as a prognostic biomarker for patients with diabetic kidney disease: a meta-analysis of clinical studies
Li Xia Yu, Min Yue Sha, Yue Chen, Fang Tan, Xi Liu, Shasha Li, Qi-Feng Liu
Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals RAC1 Involvement in Macrophages Efferocytosis in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Yi Song, Yifan Liu, Feng Guo, Lin Zhao, Guijun Qin
Inflammation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Research progress of natural active compounds on improving podocyte function to reduce proteinuria in diabetic kidney disease
Le Gong, Rui Wang, Xinyu Wang, Jing Liu, Zhaodi Han, Qian Li, Yi Jin, Hui Liao
Renal Failure.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of potential crosstalk genes and mechanisms between periodontitis and diabetic nephropathy through bioinformatic analysis
Huijuan Lu, Jia Sun, Jieqiong Sun
Medicine.2023; 102(52): e36802. CrossRef - Mitochondrial RNAs as Potential Biomarkers of Functional Impairment in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Stefania Di Mauro, Alessandra Scamporrino, Agnese Filippello, Maurizio Di Marco, Maria Teresa Di Martino, Francesca Scionti, Antonino Di Pino, Roberto Scicali, Roberta Malaguarnera, Francesco Purrello, Salvatore Piro
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(15): 8198. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - Partial Synthetic PPARƳ Derivative Ameliorates Aorta Injury in Experimental Diabetic Rats Mediated by Activation of miR-126-5p Pi3k/AKT/PDK 1/mTOR Expression
Yasmin M. Ahmed, Raha Orfali, Nada S. Abdelwahab, Hossam M. Hassan, Mostafa E. Rateb, Asmaa M. AboulMagd
Pharmaceuticals.2022; 15(10): 1175. CrossRef - Polydatin attenuates tubulointerstitial fibrosis in diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting YAP expression and nuclear translocation
Manlin He, Lan Feng, Yang Chen, Bin Gao, Yiwei Du, Lu Zhou, Fei Li, Hongbao Liu
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of diabetic nephropathy in the diabetes mellitus population: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis
Sicheng Li, Huidi Xie, Yang Shi, Hongfang Liu
Medicine.2022; 101(42): e31232. CrossRef - Stratification of diabetic kidney diseases via data-independent acquisition proteomics–based analysis of human kidney tissue specimens
Qinghua Huang, Xianming Fei, Zhaoxian Zhong, Jieru Zhou, Jianguang Gong, Yuan Chen, Yiwen Li, Xiaohong Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel biomarkers and therapeutic approaches for diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy: Recent progress and future perspectives
Ziyan Xie, Xinhua Xiao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetic Kidney Disease
Susanne B. Nicholas, Amy K. Mottl
Nephrology Self-Assessment Program.2022; 21(5): 394. CrossRef
- Role of polyphenols in the management of diabetic complications
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Microvascular Complications in Chinese Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Qianwen Huang, Daizhi Yang, Hongrong Deng, Hua Liang, Xueying Zheng, Jinhua Yan, Wen Xu, Xiangwen Liu, Bin Yao, Sihui Luo, Jianping Weng
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):93-103. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0240
- 5,661 View
- 203 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
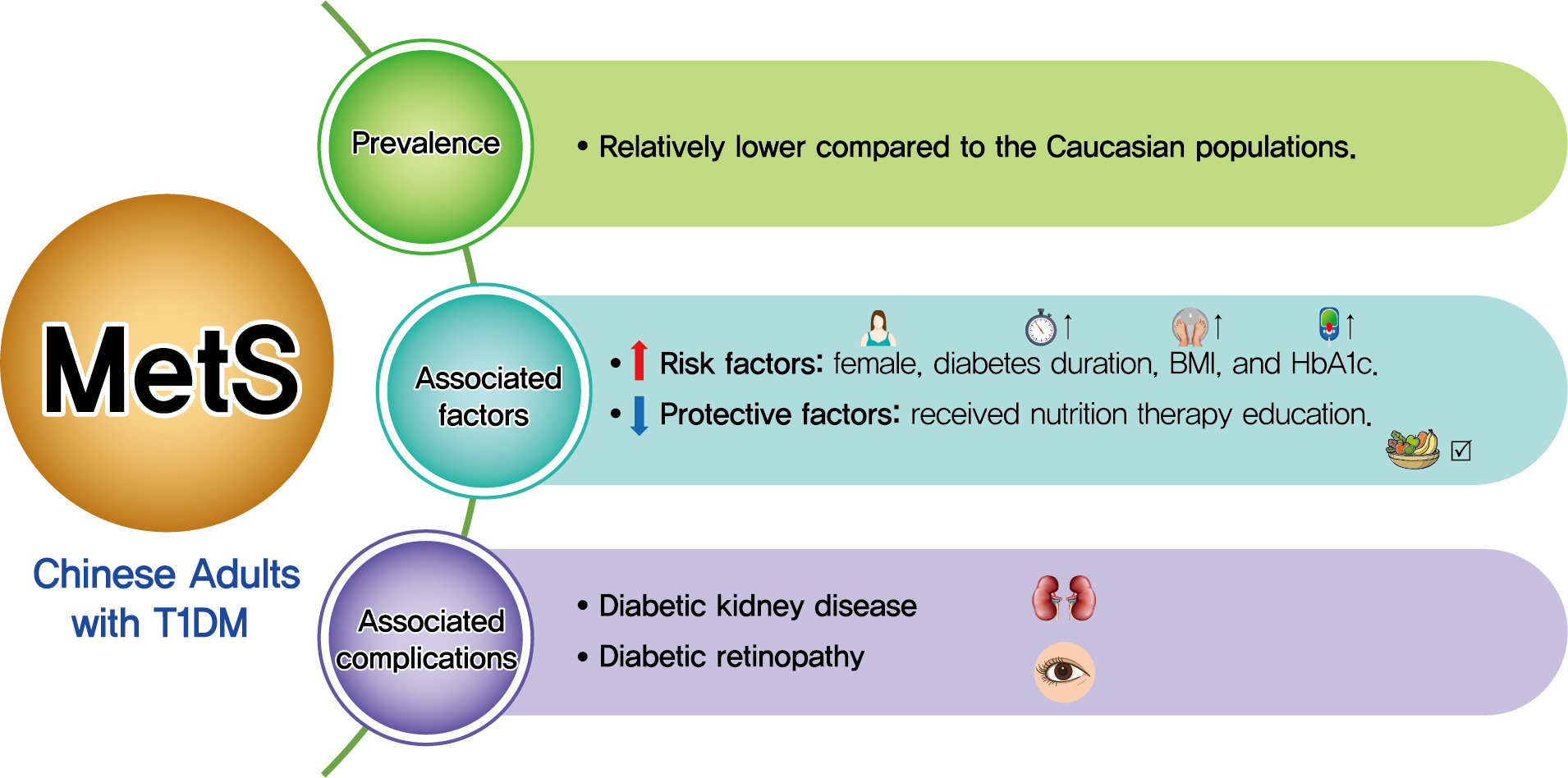
Both type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and metabolic syndrome (MetS) are associated with an elevated risk of morbidity and mortality yet with increasing heterogeneity. This study primarily aimed to evaluate the prevalence of MetS among adult patients with T1DM in China and investigate its associated risk factors, and relationship with microvascular complications.
Methods
We included adult patients who had been enrolled in the Guangdong T1DM Translational Medicine Study conducted from June 2010 to June 2015. MetS was defined according to the updated National Cholesterol Education Program criterion. Logistic regression models were used to estimate the odds ratio (OR) for the association between MetS and the risk of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) and diabetic retinopathy (DR).
Results
Among the 569 eligible patients enrolled, the prevalence of MetS was 15.1%. While female gender, longer diabetes duration, higher body mass index, and glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) were risk factors associated with MetS (OR, 2.86, 1.04, 1.14, and 1.23, respectively), received nutrition therapy education was a protective factor (OR, 0.46). After adjustment for gender, age, diabetes duration, HbA1c, socioeconomic and lifestyle variables, MetS status was associated with an increased risk of DKD and DR (OR, 2.14 and 3.72, respectively; both P<0.05).
Conclusion
Although the prevalence of MetS in adult patients with T1DM in China was relatively low, patients with MetS were more likely to have DKD and DR. A comprehensive management including lifestyle modification might reduce their risk of microvascular complications in adults with T1DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Risk Factors Influence on Microvascular Complications in Patients With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Asad Riaz, Shoaib Asghar, Salman Shahid, Haider Tanvir, Muhammad Hamza Ejaz, Mamuna Akram
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Simplified integration of optimal self-management behaviors is associated with improved HbA1c in patients with type 1 diabetes
C. Deng, Y. Xie, F. Liu, X. Tang, L. Fan, X. Yang, Y. Chen, Z. Zhou, X. Li
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Dynamic Changes in Metabolic Status Are Associated With Risk of Ocular Motor Cranial Nerve Palsies
Daye Diana Choi, Kyung-Ah Park, Kyungdo Han, Sei Yeul Oh
Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of an age-sex-ethnicity-specific metabolic syndrome score in the Chinese adults
Shujuan Yang, Bin Yu, Wanqi Yu, Shaoqing Dai, Chuanteng Feng, Ying Shao, Xing Zhao, Xiaoqing Li, Tianjing He, Peng Jia
Nature Communications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Endotoxemia with Low-Grade Inflammation, Metabolic Syndrome and Distinct Response to Lipopolysaccharide in Type 1 Diabetes
Aleksejs Fedulovs, Leonora Pahirko, Kaspars Jekabsons, Liga Kunrade, Jānis Valeinis, Una Riekstina, Valdis Pīrāgs, Jelizaveta Sokolovska
Biomedicines.2023; 11(12): 3269. CrossRef - Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Microvascular Complications in Chinese Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:93-103)
Qianwen Huang, Sihui Luo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 515. CrossRef - Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Microvascular Complications in Chinese Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:93-103)
Gyuri Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 512. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome associated with higher glycemic variability in type 1 diabetes: A multicenter cross-sectional study in china
Keyu Guo, Liyin Zhang, Jianan Ye, Xiaohong Niu, Hongwei Jiang, Shenglian Gan, Jian Zhou, Lin Yang, Zhiguang Zhou
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Risk Factors Influence on Microvascular Complications in Patients With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Basic Research
- Sulforaphane Ameliorates Diabetes-Induced Renal Fibrosis through Epigenetic Up-Regulation of BMP-7
- Lili Kong, Hongyue Wang, Chenhao Li, Huiyan Cheng, Yan Cui, Li Liu, Ying Zhao
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):909-920. Published online June 4, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0168
- 5,395 View
- 141 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
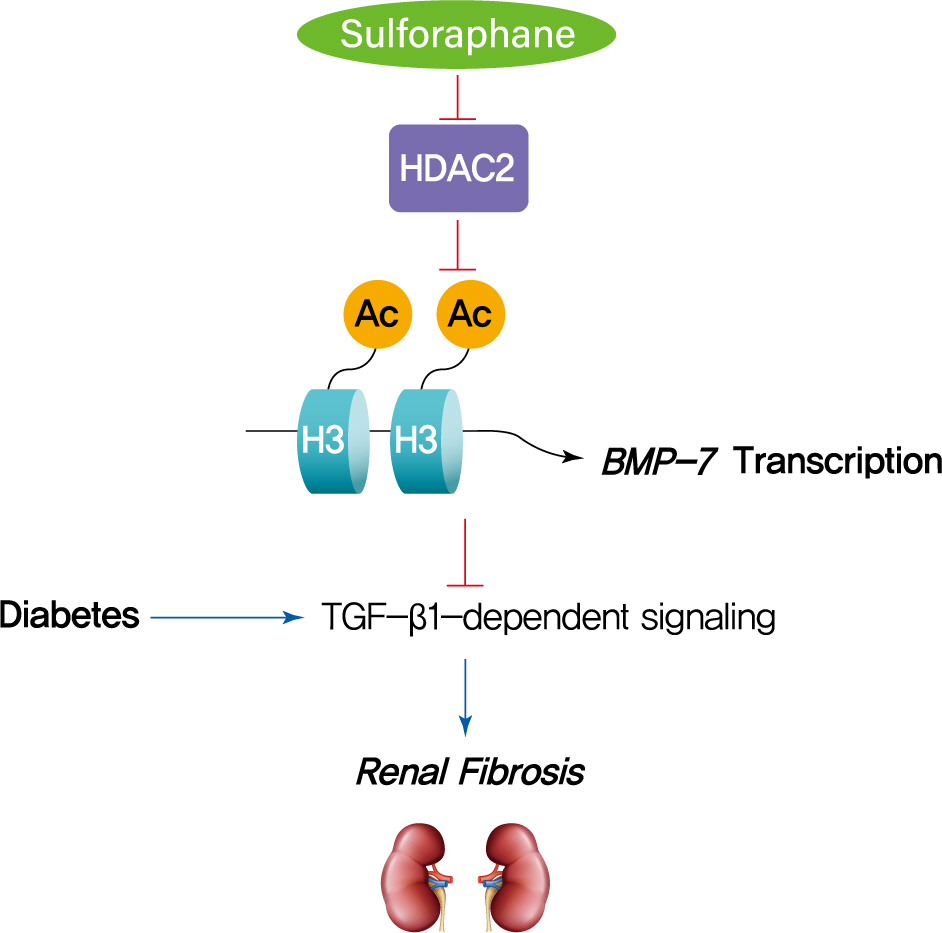
The dietary agent sulforaphane (SFN) has been reported to reduce diabetes-induced renal fibrosis, as well as inhibit histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity. Bone morphologic protein 7 (BMP-7) has been shown to reduce renal fibrosis induced by transforming growth factor-beta1. The aim of this study was to investigate the epigenetic effect of SFN on BMP-7 expression in diabetes-induced renal fibrosis.
Methods
Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice and age-matched controls were subcutaneously injected with SFN or vehicle for 4 months to measure the in vivo effects of SFN on the kidneys. The human renal proximal tubular (HK11) cell line was used to mimic diabetic conditions in vitro. HK11 cells were transfected to over-express HDAC2 and treated with high glucose/palmitate (HG/Pal) to explore the epigenetic modulation of BMP-7 in SFN-mediated protection against HG/Pal-induced renal fibrosis.
Results
SFN significantly attenuated diabetes-induced renal fibrosis in vivo. Among all of the HDACs we detected, HDAC2 activity was markedly elevated in the STZ-induced diabetic kidneys and HG/Pal-treated HK11 cells. SFN inhibited the diabetes-induced increase in HDAC2 activity which was associated with histone acetylation and transcriptional activation of the BMP-7 promoter. HDAC2 over-expression reduced BMP-7 expression and abolished the SFN-mediated protection against HG/Pal-induced fibrosis in vitro.
Conclusion
Our study demonstrates that the HDAC inhibitor SFN protects against diabetes-induced renal fibrosis through epigenetic up-regulation of BMP-7. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sulforaphane reduces adipose tissue fibrosis via promoting M2 macrophages polarization in HFD fed-mice
Zhenzhen Zhang, Huali Chen, Cheng Pan, Rui Li, Wangsheng Zhao, Tianzeng Song
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2024; 1871(2): 119626. CrossRef - Potential of Plant-Derived Compounds in Preventing and Reversing Organ Fibrosis and the Underlying Mechanisms
Patrícia dos Santos Azeredo, Daping Fan, E. Angela Murphy, Wayne E. Carver
Cells.2024; 13(5): 421. CrossRef - Beneficial role of broccoli and its active ingredient, sulforaphane in the treatment of diabetes
Aminu Mohammed, Hafsat Abdullahi Mohammed
Phytomedicine Plus.2023; 3(2): 100431. CrossRef - The Role of Histone Modifications in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Christodoula Kourtidou, Konstantinos Tziomalos
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(6): 6007. CrossRef - Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of NRF2 in Kidney Injury and Diseases
Da-Wei Lin, Yung-Chien Hsu, Cheng-Chih Chang, Ching-Chuan Hsieh, Chun-Liang Lin
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(7): 6053. CrossRef - Beneficial Effects of Sulforaphane on Diabetes and Its Complications via Both Nrf2-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms
Minhyuk Kim, Joo Young Lee
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sulforaphane exhibits potent renoprotective effects in preclinical models of kidney diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Elisa B. Monteiro, Matheus Ajackson, Milena B. Stockler-Pinto, Fitsum Guebre-Egziabher, Julio B. Daleprane, Christophe O. Soulage
Life Sciences.2023; 322: 121664. CrossRef - Integrated single-cell RNA-seq analysis revealed podocyte injury through activation of the BMP7/AMPK/mTOR mediated autophagy pathway
Hongzhou Lin, Huihui Chen, Rengcheng Qian, Guoqi Tang, Yinjuan Ding, Yalan Jiang, Congde Chen, Dexuan Wang, Maoping Chu, Xiaoling Guo
Chemico-Biological Interactions.2023; 382: 110559. CrossRef - Underlying mechanisms and molecular targets of genistein in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus and related complications
Tao Jiang, Yuhe Dong, Wanying Zhu, Tong Wu, Linyan Chen, Yuantong Cao, Xi Yu, Ye Peng, Ling Wang, Ying Xiao, Tian Zhong
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Sulforaphane: A nutraceutical against diabetes-related complications
Sinenhlanhla X.H. Mthembu, Sithandiwe E. Mazibuko-Mbeje, Marakiya T. Moetlediwa, Ndivhuwo Muvhulawa, Sonia Silvestri, Patrick Orlando, Bongani B. Nkambule, Christo J.F. Muller, Duduzile Ndwandwe, Albertus K. Basson, Luca Tiano, Phiwayinkosi V. Dludla
Pharmacological Research.2023; 196: 106918. CrossRef - Nrf2/HO-1 as a therapeutic target in renal fibrosis
Emad H.M. Hassanein, Islam M. Ibrahim, Esraa K. Abd-alhameed, Zeina W. Sharawi, Fatima A. Jaber, Hanan S. Althagafy
Life Sciences.2023; 334: 122209. CrossRef - A mechanistic overview of sulforaphane and its derivatives application in diabetes and its complications
Neda Mohamadi, Vafa Baradaran Rahimi, Mohammad Reza Fadaei, Fatemeh Sharifi, Vahid Reza Askari
Inflammopharmacology.2023; 31(6): 2885. CrossRef - The HDAC2/SP1/miR-205 feedback loop contributes to tubular epithelial cell extracellular matrix production in diabetic kidney disease
Zongji Zheng, Shuting Zhang, Jiaqi Chen, Meina Zou, Yanlin Yang, Wen Lu, Shijing Ren, Xiangyu Wang, Wenhui Dong, Zikun Zhang, Ling Wang, Meiping Guan, Gladys L.Y. Cheing, Yaoming Xue, Yijie Jia
Clinical Science.2022; 136(3): 223. CrossRef - BMP-7 Upregulates Id2 Through the MAPK Signaling Pathway to Improve Diabetic Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis and the Intervention of Oxymatrine
Yawen Xiao, Dan Liang, Zhiyang Li, Zhaowei Feng, Zhiping Yuan, Fan Zhang, Yuanyuan Wang, Yuxia Zhou, Mingjun Shi, Lingling Liu, Ying Xiao, Bing Guo
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - HDAC1 Promotes Myocardial Fibrosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by
Inhibiting BMP-7 Transcription Through Histone Deacetylation
Chun Ouyang, Lei Huang, Xiaoqiang Ye, Mingming Ren, Zhen Han
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2022; 130(10): 660. CrossRef - Class IIa histone deacetylase inhibition ameliorates acute kidney injury by suppressing renal tubular cell apoptosis and enhancing autophagy and proliferation
Jialu Li, Chao Yu, Fengchen Shen, Binbin Cui, Na Liu, Shougang Zhuang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms of histone deacetylases and inhibitors in renal fibrosis progression
Jiayu Wang, Jiaxing Li, Xin Zhang, Min Zhang, Xiaopeng Hu, Hang Yin
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The improvement of sulforaphane in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and related complications: A review
Mengjiao Wang, Min Chen, Rui Guo, Yangyang Ding, Haihui Zhang, Yuanqing He
Trends in Food Science & Technology.2022; 129: 397. CrossRef - Defining therapeutic targets for renal fibrosis: Exploiting the biology of pathogenesis
Hao Yan, Jiangxin Xu, Zhifei Xu, Bo Yang, Peihua Luo, Qiaojun He
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2021; 143: 112115. CrossRef
- Sulforaphane reduces adipose tissue fibrosis via promoting M2 macrophages polarization in HFD fed-mice
- Complications
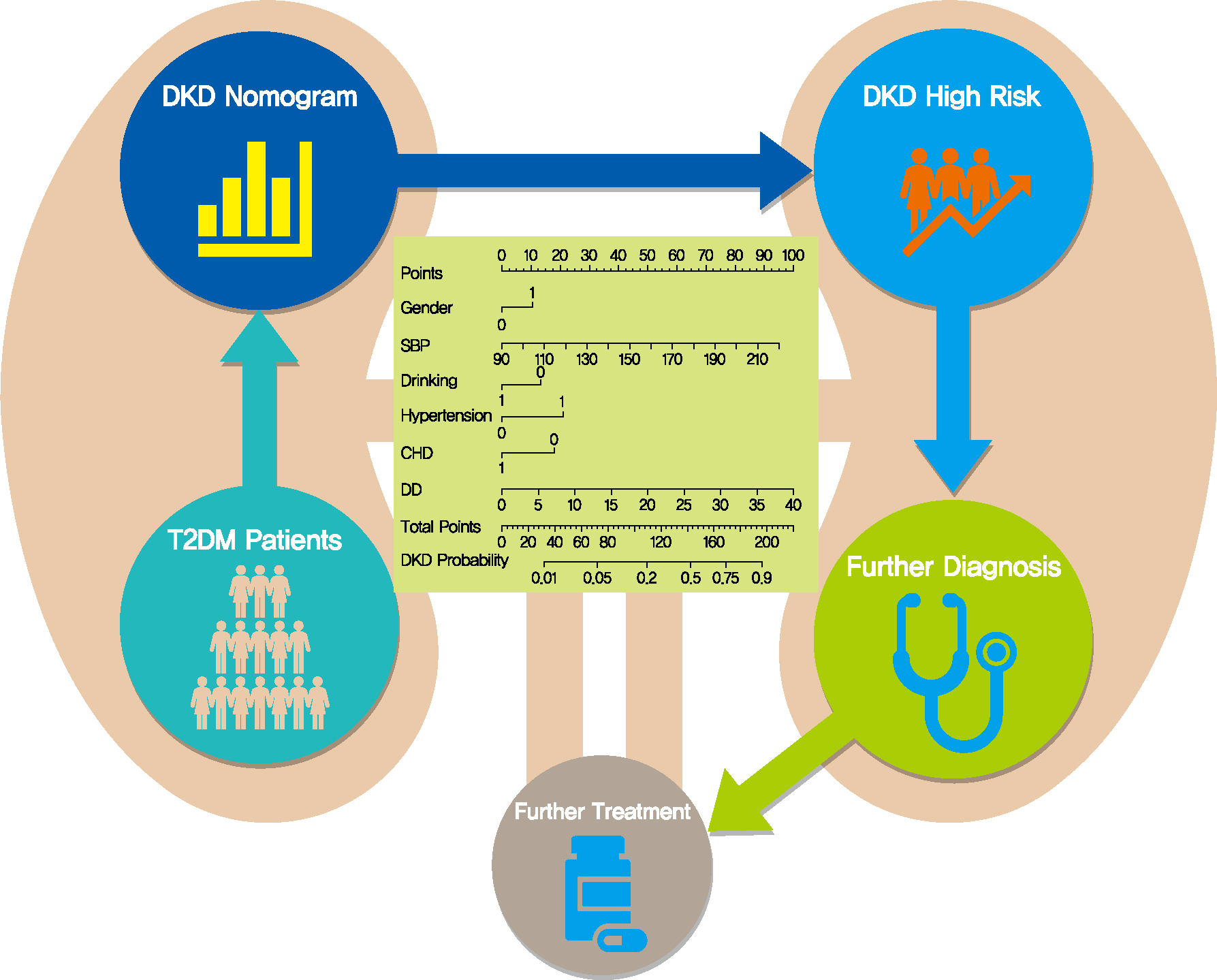
- Screening Tools Based on Nomogram for Diabetic Kidney Diseases in Chinese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Ganyi Wang, Biyao Wang, Gaoxing Qiao, Hao Lou, Fei Xu, Zhan Chen, Shiwei Chen
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):708-718. Published online April 13, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0117
- 6,920 View
- 141 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
The influencing factors of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) were explored to develop and validate a DKD diagnostic tool based on nomogram approach for patients with T2DM.
Methods
A total of 2,163 in-hospital patients with diabetes diagnosed from March 2015 to March 2017 were enrolled. Specified logistic regression models were used to screen the factors and establish four different diagnostic tools based on nomogram according to the final included variables. Discrimination and calibration were used to assess the performance of screening tools.
Results
Among the 2,163 participants with diabetes (1,227 men and 949 women), 313 patients (194 men and 120 women) were diagnosed with DKD. Four different screening equations (full model, laboratory-based model 1 [LBM1], laboratory-based model 2 [LBM2], and simplified model) showed good discriminations and calibrations. The C-indexes were 0.8450 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.8202 to 0.8690) for full model, 0.8149 (95% CI, 0.7892 to 0.8405) for LBM1, 0.8171 (95% CI, 0.7912 to 0.8430) for LBM2, and 0.8083 (95% CI, 0.7824 to 0.8342) for simplified model. According to Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test, good agreement between the predicted and observed DKD events in patients with diabetes was observed for full model (χ2=3.2756, P=0.9159), LBM1 (χ2=7.749, P=0.4584), LBM2 (χ2=10.023, P=0.2634), and simplified model (χ2=12.294, P=0.1387).
Conclusion
LBM1, LBM2, and simplified model exhibited excellent predictive performance and availability and could be recommended for screening DKD cases among Chinese patients with diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Serum Lactate Level-Based Nomograms for Predicting Diabetic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Chunxia Jiang, Xiumei Ma, Jiao Chen, Yan Zeng, Man Guo, Xiaozhen Tan, Yuping Wang, Peng Wang, Pijun Yan, Yi Lei, Yang Long, Betty Yuen Kwan Law, Yong Xu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2024; Volume 17: 1051. CrossRef - Changes in urinary exosomal protein CALM1 may serve as an early noninvasive biomarker for diagnosing diabetic kidney disease
Tao Li, Tian ci Liu, Na Liu, Man Zhang
Clinica Chimica Acta.2023; 547: 117466. CrossRef - Developing screening tools to estimate the risk of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Xu Cao, Xiaomei Pei
Technology and Health Care.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Development and validation of a novel nomogram to predict diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetic mellitus and proteinuric kidney disease
Hui Zhuan Tan, Jason Chon Jun Choo, Stephanie Fook-Chong, Yok Mooi Chin, Choong Meng Chan, Chieh Suai Tan, Keng Thye Woo, Jia Liang Kwek
International Urology and Nephrology.2022; 55(1): 191. CrossRef - Nomogram-Based Chronic Kidney Disease Prediction Model for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Using Routine Pathological Data
Nakib Hayat Chowdhury, Mamun Bin Ibne Reaz, Sawal Hamid Md Ali, Shamim Ahmad, María Liz Crespo, Andrés Cicuttin, Fahmida Haque, Ahmad Ashrif A. Bakar, Mohammad Arif Sobhan Bhuiyan
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(9): 1507. CrossRef - Development and assessment of diabetic nephropathy prediction model using hub genes identified by weighted correlation network analysis
Xuelian Zhang, Yao Wang, Zhaojun Yang, Xiaoping Chen, Jinping Zhang, Xin Wang, Xian Jin, Lili Wu, Xiaoyan Xing, Wenying Yang, Bo Zhang
Aging.2022; 14(19): 8095. CrossRef
- Development of Serum Lactate Level-Based Nomograms for Predicting Diabetic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Complications
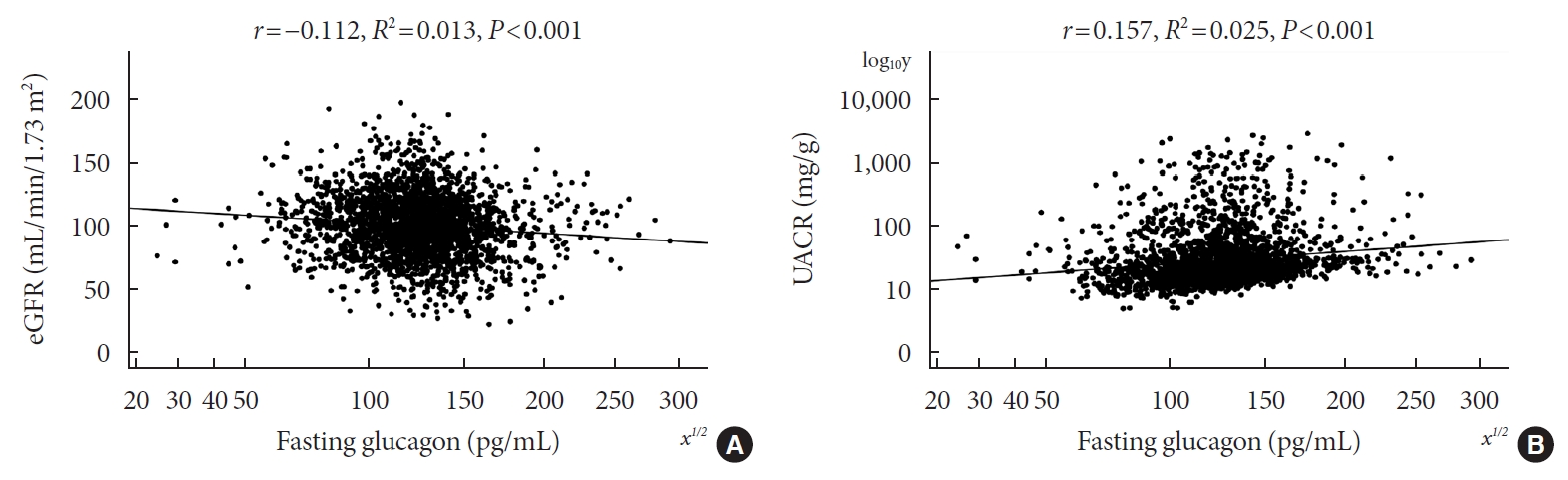
- Associations of Plasma Glucagon Levels with Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate, Albuminuria and Diabetic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Hua-Xing Huang, Liang-Lan Shen, Hai-Yan Huang, Li-Hua Zhao, Feng Xu, Dong-Mei Zhang, Xiu-Lin Zhang, Tong Chen, Xue-Qin Wang, Yan Xie, Jian-Bin Su
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):868-879. Published online March 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0149
- 5,879 View
- 173 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is characterized by elevated fasting glucagon and impaired suppression of postprandial glucagon secretion, which may participate in diabetic complications. Therefore, we investigated the associations of plasma glucagon with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), albuminuria and diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in T2DM patients.
Methods
Fasting glucagon and postchallenge glucagon (assessed by area under the glucagon curve [AUCgla]) levels were determined during oral glucose tolerance tests. Patients with an eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and/or a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) ≥30 mg/g who presented with diabetic retinopathy were identified as having DKD.
Results
Of the 2,436 recruited patients, fasting glucagon was correlated with eGFR and UACR (r=–0.112 and r=0.157, respectively; P<0.001), and AUCgla was also correlated with eGFR and UACR (r=–0.267 and r=0.234, respectively; P<0.001). Moreover, 31.7% (n=771) presented with DKD; the prevalence of DKD was 27.3%, 27.6%, 32.5%, and 39.2% in the first (Q1), second (Q2), third (Q3), and fourth quartile (Q4) of fasting glucagon, respectively; and the corresponding prevalence for AUCgla was 25.9%, 22.7%, 33.7%, and 44.4%, respectively. Furthermore, after adjusting for other clinical covariates, the adjusted odds ratios (ORs; 95% confidence intervals) for DKD in Q2, Q3, and Q4 versus Q1 of fasting glucagon were 0.946 (0.697 to 1.284), 1.209 (0.895 to 1.634), and 1.521 (1.129 to 2.049), respectively; the corresponding ORs of AUCgla were 0.825 (0.611 to 1.114), 1.323 (0.989 to 1.769), and 2.066 (1.546 to 2.760), respectively. Additionally, when we restricted our analysis in patients with glycosylated hemoglobin <7.0% (n=471), we found fasting glucagon and AUCgla were still independently associated with DKD.
Conclusion
Both increased fasting and postchallenge glucagon levels were independently associated with DKD in T2DM patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glucagon in type 2 diabetes: Friend or foe?
Irene Caruso, Nicola Marrano, Giuseppina Biondi, Valentina Annamaria Genchi, Rossella D'Oria, Gian Pio Sorice, Sebastio Perrini, Angelo Cignarelli, Annalisa Natalicchio, Luigi Laviola, Francesco Giorgino
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Glucagon in type 2 diabetes: Friend or foe?
- Complications
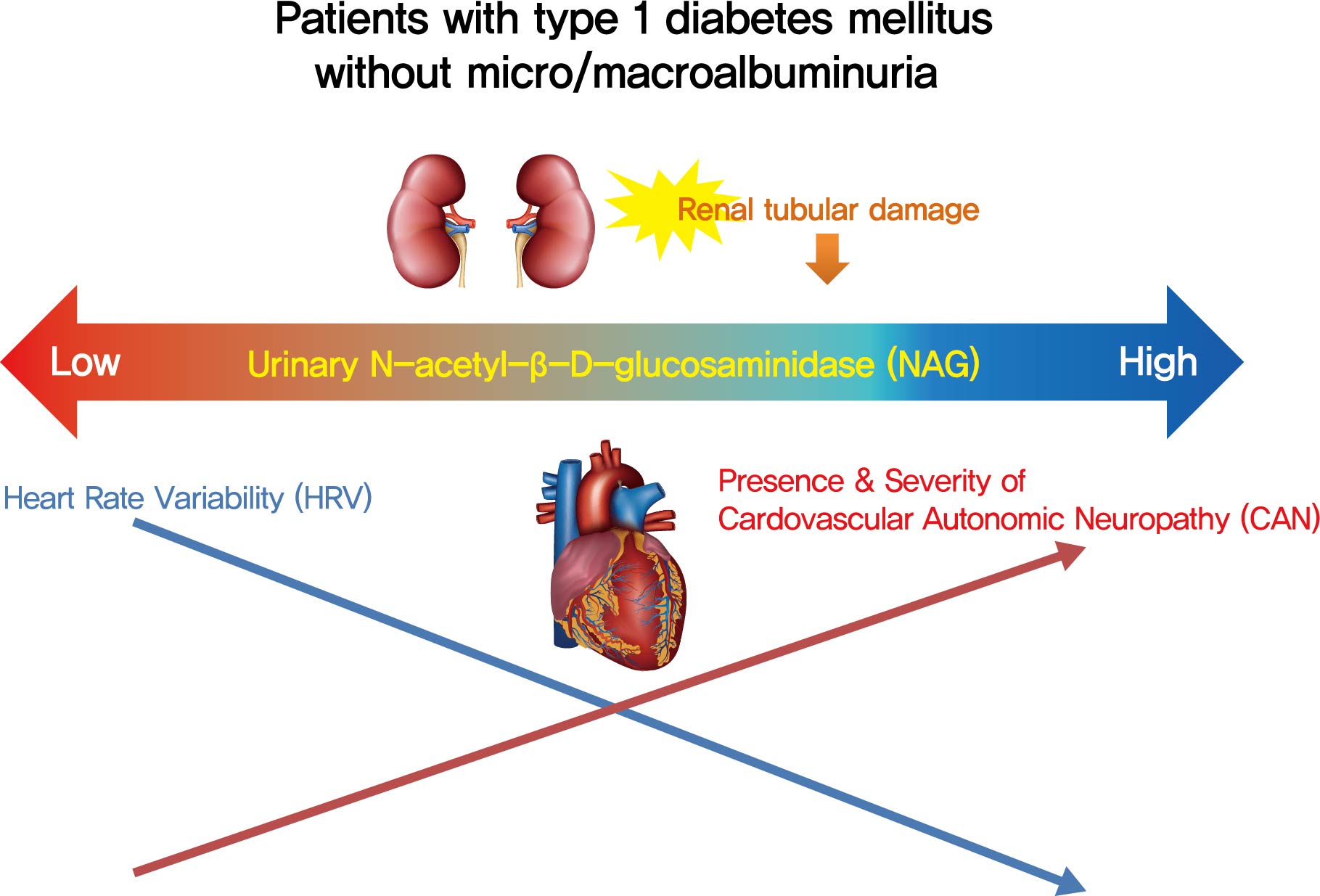
- Association of Urinary N-Acetyl-β-D-Glucosaminidase with Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus without Nephropathy
- Min Sun Choi, Ji Eun Jun, Sung Woon Park, Jee Hee Yoo, Jiyeon Ahn, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Moon-Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):349-357. Published online February 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0211
- 5,635 View
- 121 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy (CAN) is a common microvascular complication of diabetes and related to albuminuria in diabetic nephropathy (DN). Urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (uNAG) is a renal tubular injury marker which has been reported as an early marker of DN even in patients with normoalbuminuria. This study evaluated whether uNAG is associated with the presence and severity of CAN in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) without nephropathy.
Methods
This cross-sectional study comprised 247 subjects with T1DM without chronic kidney disease and albuminuria who had results for both uNAG and autonomic function tests within 3 months. The presence of CAN was assessed by age-dependent reference values for four autonomic function tests. Total CAN score was assessed as the sum of the partial points of five cardiovascular reflex tests and was used to estimatethe severity of CAN. The correlations between uNAG and heart rate variability (HRV) parameters were analyzed.
Results
The association between log-uNAG and presence of CAN was significant in a multivariate logistic regression model (adjusted odds ratio, 2.39; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.08 to 5.28; P=0.031). Total CAN score was positively associated with loguNAG (β=0.261, P=0.026) in the multivariate linear regression model. Log-uNAG was inversely correlated with frequency-domain and time-domain indices of HRV.
Conclusion
This study verified the association of uNAG with presence and severity of CAN and changes in HRV in T1DM patients without nephropathy. The potential role of uNAG should be further assessed for high-risk patients for CAN in T1DM patients without nephropathy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Determination of Diabetes-associated Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Risk Factors among Insulin and Non-insulin Dependent Diabetics
Ibrahim Abdulsada, Zain Alabdeen Obaid, Farah Almerza, Mays Alwaeli, Anmar Al-Elayawi, Taha Al-Dayyeni, Harir Al-Tuhafy
The Journal of Medical Research.2023; 9(6): 141. CrossRef - Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef
- Determination of Diabetes-associated Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Risk Factors among Insulin and Non-insulin Dependent Diabetics
- Complications
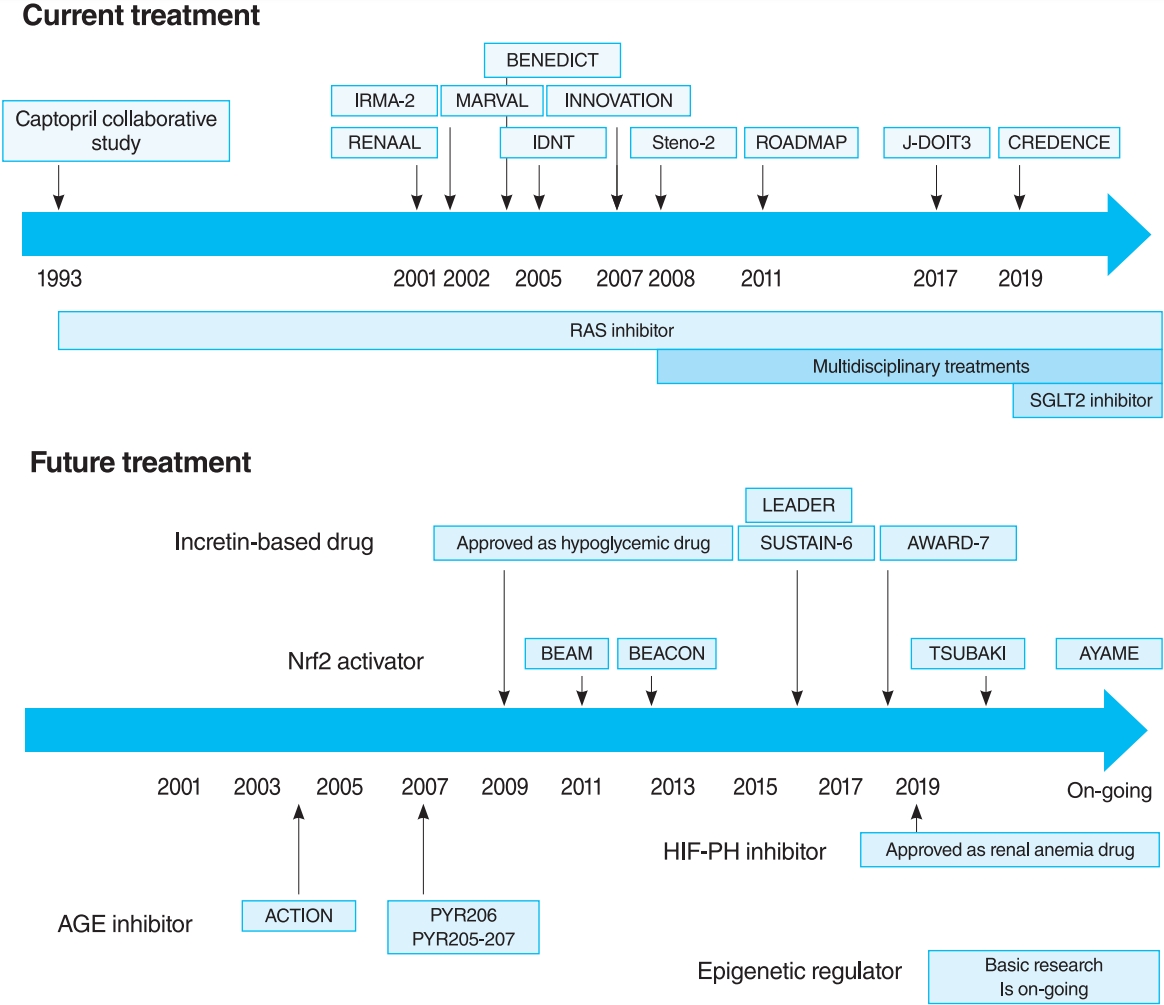
- Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: Current and Future
- Tomotaka Yamazaki, Imari Mimura, Tetsuhiro Tanaka, Masaomi Nangaku
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):11-26. Published online January 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0217
- 19,259 View
- 1,328 Download
- 92 Web of Science
- 92 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is the major cause of end-stage kidney disease. However, only renin-angiotensin system inhibitor with multidisciplinary treatments is effective for DKD. In 2019, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor showed efficacy against DKD in Canagliflozin and Renal Events in Diabetes with Established Nephropathy Clinical Evaluation (CREDENCE) trial, adding a new treatment option. However, the progression of DKD has not been completely controlled. The patients with transient exposure to hyperglycemia develop diabetic complications, including DKD, even after normalization of their blood glucose. Temporary hyperglycemia causes advanced glycation end product (AGE) accumulations and epigenetic changes as metabolic memory. The drugs that improve metabolic memory are awaited, and AGE inhibitors and histone modification inhibitors are the focus of clinical and basic research. In addition, incretin-related drugs showed a renoprotective ability in many clinical trials, and these trials with renal outcome as their primary endpoint are currently ongoing. Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors recently approved for renal anemia may be renoprotective since they improve tubulointerstitial hypoxia. Furthermore, NF-E2–related factor 2 activators improved the glomerular filtration rate of DKD patients in Bardoxolone Methyl Treatment: Renal Function in chronic kidney disease/Type 2 Diabetes (BEAM) trial and Phase II Study of Bardoxolone Methyl in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes (TSUBAKI) trial. Thus, following SGLT2 inhibitor, numerous novel drugs could be utilized in treating DKD. Future studies are expected to provide new insights.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical value of serum MMP-3 in chronic kidney disease
Yulin Fu, Cheng Song, Yuan Qin, Tianyu Zheng, Xiumei Zhou, Xueqin Zhao, Jian Zou, Biao Huang
Clinica Chimica Acta.2024; 553: 117725. CrossRef - β2-Adrenergic receptor agonists as a treatment for diabetic kidney disease
Ehtesham Arif, Danira Medunjanin, Ashish Solanki, Xiaofeng Zuo, Yanhui Su, Yujing Dang, Brennan Winkler, Kasey Lerner, Ahmed I. Kamal, Oleg Palygin, Marc-Andre Cornier, Bethany J. Wolf, Kelly J. Hunt, Joshua H. Lipschutz
American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology.2024; 326(1): F20. CrossRef - β2-Adrenergic receptor agonists: a new treatment for diabetic kidney disease?
Zhiwen Liu, Zheng Dong
American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology.2024; 326(1): F1. CrossRef - Urinary exosomal microRNA-145-5p and microRNA-27a-3p act as noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers for diabetic kidney disease
Lu-Lu Han, Sheng-Hai Wang, Ming-Yan Yao, Hong Zhou
World Journal of Diabetes.2024; 15(1): 92. CrossRef - Placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect against diabetic kidney disease by upregulating autophagy-mediated SIRT1/FOXO1 pathway
Honghong Liu, Jiao Wang, Guanru Yue, Jixiong Xu
Renal Failure.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of serum Nrf2 protein levels with disease activity and renal impairment in lupus nephritis
Jicui Li, Qiaoyan Guo, Xianping Wei, Yuexin Zhu, Manyu Luo, Ping Luo
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Qidan Tangshen Granule on diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Hua Yang, Shisi Xia, Yilei Cong, Xinyu Yang, Jie Min, Tengfei Wu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 209: 111128. CrossRef - Comparison of conventional mathematical model and machine learning model based on recent advances in mathematical models for predicting diabetic kidney disease
Yingda Sheng, Caimei Zhang, Jing Huang, Dan Wang, Qian Xiao, Haocheng Zhang, Xiaoqin Ha
DIGITAL HEALTH.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Experimental Verification to Reveal the Mitophagy-Associated Mechanism of Tangshen Formula in the Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy
Yinfeng Chen, Xiaying Wang, Jie Min, Jie Zheng, Xuanli Tang, Xiaoling Zhu, Dongrong Yu, De Jin
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2024; Volume 17: 739. CrossRef - Senolytic combination of dasatinib and quercetin protects against diabetic kidney disease by activating autophagy to alleviate podocyte dedifferentiation via the Notch pathway
Xinwang Zhu, Congxiao Zhang, Linlin Liu, Li Xu, Li Yao
International Journal of Molecular Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Decreased risk of renal cell carcinoma in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with sodium glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitors
Chun‐Huei Chiu, Wei‐Yao Wang, Hung‐Yi Chen, Pei‐Lun Liao, Gwo‐Ping Jong, Tsung‐Yuan Yang
Cancer Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - System Biology Approaches for Systemic Diseases: Emphasis on Type II Diabetes Mellitus and Allied Metabolism
Mohan Das, Moumita Chakraborty, Promi Das, Sayantan Santra, Abhishek Mukherjee, Sarobi Das, Krisztian Banyai, Souvik Roy, Lopamudra Choudhury, Rudrak Gupta, Tama Dey, Dibya Das, Anirbandeep Bose, Balasubramanian Ganesh, Rintu Banerjee
Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology.2024; : 103176. CrossRef - Beneficial effects of ginsenosides on diabetic nephropathy: A systematical review and meta-analysis of preclinical evidence
Xiao-Mei Chen, Gui-Xuan Lin, Xue Wang, Hong-Yan Ma, Ru-Shang Wang, Shu-Mei Wang, Dan Tang
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2023; 302: 115860. CrossRef - Waist circumference and end‐stage renal disease based on glycaemic status: National Health Insurance Service data 2009–2018
Yun Kyung Cho, Ji Hye Huh, Shinje Moon, Yoon Jung Kim, Yang‐Hyun Kim, Kyung‐do Han, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung‐Hee Ihm
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(1): 585. CrossRef - A Narrative Review of New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy
Aadhira Pillai, Darshna Fulmali
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Shenkang recipe alleviates renal aging in diabetic kidney disease by interfering with the lysine-specific demethylase KDM6B to modulate the PPAR-γ signaling pathway
Anna Zuo, Jiarun Xie, Junqiao Shao, Shuyu Li, Haoyu Lin, Shaoting Wang, Wei Sun, Jinjin Xia, Weiqiang Jiang, Jia Sun, Ming Wang
Pharmacological Research - Modern Chinese Medicine.2023; 6: 100216. CrossRef - miR-223-3p mediates the diabetic kidney disease progression by targeting IL6ST/STAT3 pathway
Ping Tang, Yushan Xu, Jingrong Zhang, Juanli Nan, Ruxian Zhong, Jingmei Luo, Dazhi Xu, Shaoqing Shi, Lihua Zhang
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2023; 648: 50. CrossRef - miR‐124‐3p improves mitochondrial function of renal tubular epithelial cells in db/db mice
Luqun Liang, Chunxin Wo, Yao Yuan, Hongjuan Cao, Wanlin Tan, Xingcheng Zhou, Dan Wang, Rongyu Chen, Mingjun Shi, Fan Zhang, Ying Xiao, Lingling Liu, Yuxia Zhou, Tian Zhang, Yuanyuan Wang, Bing Guo
The FASEB Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-Prolyl-Hydroxylase and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors for Low-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome-Related Anemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Report of Three Cases
Satoshi Yamasaki, Takahiko Horiuchi
Hematology Reports.2023; 15(1): 180. CrossRef - Diagnostic significance of hsa_circ_0000146 and hsa_circ_0000072 biomarkers for Diabetic Kidney Disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Amul Badr, Omayma Elkholy, Mona Said, Sally Fahim, Mohamed El-Khatib, Dina Sabry, Radwa Gaber
Journal of Medical Biochemistry.2023; 42(2): 239. CrossRef - The emerging insight into E3 ligases as the potential therapeutic target for diabetic kidney disease
Vivek Akhouri, Syamantak Majumder, Anil Bhanudas Gaikwad
Life Sciences.2023; 321: 121643. CrossRef - Klotho’s impact on diabetic nephropathy and its emerging connection to diabetic retinopathy
Anqi Tang, Yu Zhang, Ling Wu, Yong Lin, Lizeyu Lv, Liangbin Zhao, Bojun Xu, Youqun Huang, Mingquan Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences and Clinical Significance of Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 and Vasohibin-1 (VASH-1) Levels in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy and Different Renal Injuries
Hui Liu, Dongyan Wang, Jingnan Tang, Linlin Yu, Shanshan Su
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 1085. CrossRef - Medial Arterial Calcification and the Risk of Amputation of Diabetic Foot Ulcer in Patients With Diabetic Kidney Disease
Joon Myeong So, Ji Ho Park, Jin Gyeong Kim, Il Rae Park, Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Chul Hyun Park, Woo-Sung Yun, Tae-Gon Kim, Woong Kim, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Heparanase-2 protein and peptides have a protective effect on experimental glomerulonephritis and diabetic nephropathy
Baranca Buijsers, Marjolein Garsen, Mark de Graaf, Marinka Bakker-van Bebber, Chunming Guo, Xue Li, Johan van der Vlag
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis on the renal functional status in patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic kidney disease
Z.Ya. Кotsiubiichuk, O.S. Khukhlina, А.А. Аntoniv, O.Ye. Mandryk
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(2): 100. CrossRef - Roles of extracellular vesicles in ageing-related chronic kidney disease: Demon or angel
Siqi Yin, Zixuan Zhou, Peiwen Fu, Chaoying Jin, Peipei Wu, Cheng Ji, Yunjie Shan, Linru Shi, Min Xu, Hui Qian
Pharmacological Research.2023; 193: 106795. CrossRef - Role of Natural and Synthetic Compounds in Modulating NRF2/KEAP1 Signaling Pathway in Prostate Cancer
Giovanni Tossetta, Sonia Fantone, Daniela Marzioni, Roberta Mazzucchelli
Cancers.2023; 15(11): 3037. CrossRef - Risk factors for heart, cerebrovascular, and kidney diseases: evaluation of potential side effects of medications to control hypertension, hyperglycemia, and hypercholesterolemia
Kazumitsu Nawata
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Rationale and design of a prospective, clinical study of kidney biopsies in people with type 2 diabetes and severely increased albuminuria (the PRIMETIME 2 study)
Marie Møller, Rikke Borg, Iain Bressendorff, Lisbeth N Fink, Eva Gravesen, Karina Haar Jensen, Torben Hansen, Dorrit Krustrup, Frederik Persson, Peter Rossing, Frederikke E Sembach, Anne C B Thuesen, Ditte Hansen
BMJ Open.2023; 13(6): e072216. CrossRef - Oral Chinese patent medicines for diabetic kidney disease: An overview of systematic reviews
Xue Xue, Ke-ying Li, Shang-zhi Liu, Jia-xuan Li, Xin-yan Jin, Xue-han Liu, La-mei Lin, Xin-rong Zou, Chun-li Lu, Fang-fang Zhao, Jian-ping Liu, Xiao-qin Wang
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2023; 61: 102269. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Proteinuric Kidney Disease/Nephrotic Syndrome: Lessons from Knockout/Transgenic Mouse Models
Ryosuke Saiki, Kan Katayama, Kaoru Dohi
Biomedicines.2023; 11(7): 1803. CrossRef - Epigenetic regulation of angiogenesis and ischemic response by long noncoding RNA LEENE in diabetes
Imari Mimura, Masaomi Nangaku
Kidney International.2023; 104(6): 1048. CrossRef - Advances in the pharmacological study of Chinese herbal medicine to alleviate diabetic nephropathy by improving mitochondrial oxidative stress
Ming Chen, Yao Chen, Wenhui Zhu, Xiaoming Yan, Jing Xiao, Peiqing Zhang, Peng Liu, Ping Li
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 165: 115088. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone Therapy in Patients with Cardiovascular and Chronic Kidney Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
FNU Jyotsna, Kamran Mahfooz, Tirath Patel, FNU Parshant, Fnu Simran, Fnu Harsha, Fnu Neha, Dev Jyotishna, Dipesh Mishra, Sirjana Subedi, Mahima Khatri, Satesh Kumar, Giustino Varrassi
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular implications of glycosaminoglycans in diabetes pharmacotherapy
Tanya Waseem, Madiha Ahmed, Tausif Ahmed Rajput, Mustafeez Mujtaba Babar
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 247: 125821. CrossRef - SGLT2 Inhibitors in the Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: More than Just Glucose Regulation
Jasna Klen, Vita Dolžan
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(7): 1995. CrossRef - CUL3 induces mitochondrial dysfunction via MRPL12 ubiquitination in renal tubular epithelial cells
Xingzhao Ji, Xiaoli Yang, Xia Gu, Lingju Chu, Shengnan Sun, Jian Sun, Peng Song, Qian Mu, Ying Wang, Xiaoming Sun, Dun Su, Tong Su, Shaoshuai Hou, Yao Lu, Chen Ma, Mingqiang Liu, Tianyi Zhang, Weiying Zhang, Yi Liu, Qiang Wan
The FEBS Journal.2023; 290(22): 5340. CrossRef - HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
Chuanqiang Zhou, Min Wu, Gaolun Liu, Li Zhou
Open Life Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review of the Potential of Nuclear Factor [Erythroid-Derived 2]-like 2 Activation in Autoimmune Diseases
Ilker Ates, Ayşe Didem Yılmaz, Brigitta Buttari, Marzia Arese, Luciano Saso, Sibel Suzen
Brain Sciences.2023; 13(11): 1532. CrossRef - Astragalus membranaceus and Salvia miltiorrhiza ameliorate diabetic kidney disease via the “gut-kidney axis”
Zhen Shen, Tao Cui, Yao Liu, Shuai Wu, Cong Han, Jie Li
Phytomedicine.2023; 121: 155129. CrossRef - The relevance of the non-invasive biomarkers lncRNA GAS5/miR-21 ceRNA regulatory network in the early identification of diabetes and diabetic nephropathy
He Sun, Tong Chen, Xin Li, Yonghong Zhu, Shuang Zhang, Ping He, Yali Peng, Qiuling Fan
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Activation of acetyl-CoA synthetase 2 mediates kidney injury in diabetic nephropathy
Jian Lu, Xue Qi Li, Pei Pei Chen, Jia Xiu Zhang, Liang Liu, Gui Hua Wang, Xiao Qi Liu, Ting Ting Jiang, Meng Ying Wang, Wen Tao Liu, Xiong Zhong Ruan, Kun Ling Ma
JCI Insight.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - SET7, a lysine-specific methyl transferase: An intriguing epigenetic target to combat diabetic nephropathy
Samarth Dwivedi, Atharva Chavan, Atish T. Paul
Drug Discovery Today.2023; 28(10): 103754. CrossRef - Dznep, a histone modification inhibitor, inhibits HIF1α binding to TIMP2 gene and suppresses TIMP2 expression under hypoxia
Tomotaka Yamazaki, Imari Mimura, Yu Kurata, Tetsuhiro Tanaka, Masaomi Nangaku
Physiological Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - GLP-1RAs inhibit the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway to regulate mouse renal podocyte pyroptosis
Xiang Li, Xiao Jiang, Mei Jiang, Zhi-feng Wang, Tao Zhao, Si-ming Cao, Qiu-Mei Li
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 61(2): 225. CrossRef - Highly Sensitive, Portable Detection System for Multiplex Chemiluminescence Analysis
Yannan Yu, Wei Nie, Kaiqin Chu, Xi Wei, Zachary J. Smith
Analytical Chemistry.2023; 95(39): 14762. CrossRef - From normal population to prediabetes and diabetes: study of influencing factors and prediction models
Di Gong, Xiaohong Chen, Lin Yang, Yongjian Zhang, Qianqian Zhong, Jing Liu, Chen Yan, Yongjiang Cai, Weihua Yang, Jiantao Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes Monitoring through Urine Analysis Using ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy and Machine Learning
Sajid Farooq, Denise Maria Zezell
Chemosensors.2023; 11(11): 565. CrossRef - Treatment and practical considerations of diabetic kidney disease
Yara Bilen, Allaa Almoushref, Kenda Alkwatli, Omar Osman, Ali Mehdi, Hanny Sawaf
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Metabolomics and Traditional Chinese Medicine for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment
Jing Li, Na Zhu, Yaqiong Wang, Yanlei Bao, Feng Xu, Fengjuan Liu, Xuefeng Zhou
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 4269. CrossRef - Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and incident diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, Min Sun Choi, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 184: 109181. CrossRef - Lipidomic Analysis Reveals the Protection Mechanism of GLP-1 Analogue Dulaglutide on High-Fat Diet-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease in Mice
Martin Ho Yin Yeung, Ka Long Leung, Lai Yuen Choi, Jung Sun Yoo, Susan Yung, Pui-Kin So, Chi-Ming Wong
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - GLP-1 receptor agonists in diabetic kidney disease: current evidence and future directions
Ji Hee Yu, So Young Park, Da Young Lee, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 41(2): 136. CrossRef - Evolving Type 2 diabetes management focuses on clinical outcomes
Caroline Fenton, Connie Kang
Drugs & Therapy Perspectives.2022; 38(4): 165. CrossRef - Pathophysiologic Mechanisms and Potential Biomarkers in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Chan-Young Jung, Tae-Hyun Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 181. CrossRef - Critical shear stress of red blood cells as a novel integrated biomarker for screening chronic kidney diseases in cases of type 2 diabetes
Il Rae Park, Jimi Choi, Eun Young Ha, Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Sehyun Shin, Sin Gon Kim, Kyu Chang Won
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation.2022; 81(4): 293. CrossRef - Inhibition of ChREBP ubiquitination via the ROS/Akt-dependent downregulation of Smurf2 contributes to lysophosphatidic acid-induced fibrosis in renal mesangial cells
Donghee Kim, Ga-Young Nam, Eunhui Seo, Hee-Sook Jun
Journal of Biomedical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Pathophysiological Basis of Diabetic Kidney Protection by Inhibition of SGLT2 and SGLT1
Yuji Oe, Volker Vallon
Kidney and Dialysis.2022; 2(2): 349. CrossRef - Dapagliflozin for the treatment of chronic kidney disease
Yu Kurata, Masaomi Nangaku
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 17(4): 275. CrossRef - Repurposing drugs for highly prevalent diseases: pentoxifylline, an old drug and a new opportunity for diabetic kidney disease
Javier Donate-Correa, María Dolores Sanchez-Niño, Ainhoa González-Luis, Carla Ferri, Alberto Martín-Olivera, Ernesto Martín-Núñez, Beatriz Fernandez-Fernandez, Víctor G Tagua, Carmen Mora-Fernández, Alberto Ortiz, Juan F Navarro-González
Clinical Kidney Journal.2022; 15(12): 2200. CrossRef - Cyproheptadine, a SET7/9 inhibitor, reduces hyperglycaemia-induced ER stress alleviating inflammation and fibrosis in renal tubular epithelial cells
Himanshu Sankrityayan, Ajinath Kale, Vishwadeep Shelke, Anil Bhanudas Gaikwad
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Pan-Src kinase inhibitor treatment attenuates diabetic kidney injury via inhibition of Fyn kinase-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress
Debra Dorotea, Songling Jiang, Eun Seon Pak, Jung Beom Son, Hwan Geun Choi, Sung-Min Ahn, Hunjoo Ha
Experimental & Molecular Medicine.2022; 54(8): 1086. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - Effect of once-weekly dulaglutide on renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease
Sungmin Kim, Jung Nam An, Young Rim Song, Sung Gyun Kim, Hyung Seok Lee, AJin Cho, Jwa-Kyung Kim, Tomislav Bulum
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(8): e0273004. CrossRef - Oxidative Stress and NRF2/KEAP1/ARE Pathway in Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD): New Perspectives
Daniela Maria Tanase, Evelina Maria Gosav, Madalina Ioana Anton, Mariana Floria, Petronela Nicoleta Seritean Isac, Loredana Liliana Hurjui, Claudia Cristina Tarniceriu, Claudia Florida Costea, Manuela Ciocoiu, Ciprian Rezus
Biomolecules.2022; 12(9): 1227. CrossRef - Preventive and healing effect of high dosing grape seed flour on CKD patients of various stages and aetiologies
Wiem Bejaoui, Mohamed Mahmoudi, Kamel Charradi, Monia Abbes-Belhadj, Habib Boukhalfa, Mossadok Ben-Attia, Ferid Limam, Ezzedine Aouani
Biomarkers.2022; 27(8): 795. CrossRef - Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) in type 2 diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to therapeutics
Miyesaier Abudureyimu, Xuanming Luo, Xiang Wang, James R Sowers, Wenshuo Wang, Junbo Ge, Jun Ren, Yingmei Zhang, Wei-Ping Jia
Journal of Molecular Cell Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent Advances in the Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Diabetic Kidney Diseases
Wei Huang, Yi-Yuan Chen, Zi-Qi Li, Fang-Fang He, Chun Zhang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(18): 10882. CrossRef - Serum isthmin-1 levels are positively and independently correlated with albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chuan Wang, Mingyue Xu, Ruiying Feng, Lei Zhang, Xiaofei Yin, Ruoqi Feng, Kai Liang, Jinbo Liu
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(5): e002972. CrossRef - hucMSC-sEVs-Derived 14-3-3ζ Serves as a Bridge between YAP and Autophagy in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Siqi Yin, Wanzhu Liu, Cheng Ji, Yuan Zhu, Yunjie Shan, Zixuan Zhou, Wenya Chen, Leilei Zhang, Zixuan Sun, Wenqin Zhou, Hui Qian, Chaoliang Tang
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Adenosine receptors as emerging therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease
Eun Seon Pak, Jin Joo Cha, Dae Ryong Cha, Keizo Kanasaki, Hunjoo Ha
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 41(Suppl 2): S74. CrossRef - REDD1 Ablation Attenuates the Development of Renal Complications in Diabetic Mice
Siddharth Sunilkumar, Esma I. Yerlikaya, Allyson L. Toro, William P. Miller, Han Chen, Kebin Hu, Scot R. Kimball, Michael D. Dennis
Diabetes.2022; 71(11): 2412. CrossRef - The Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha in Renal Disease
Huixia Liu, Yujuan Li, Jing Xiong
Molecules.2022; 27(21): 7318. CrossRef - Resistant Starch as a Dietary Intervention to Limit the Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Anna M. Drake, Melinda T. Coughlan, Claus T. Christophersen, Matthew Snelson
Nutrients.2022; 14(21): 4547. CrossRef - Aggravated renal fibrosis is positively associated with the activation of HMGB1-TLR2/4 signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice
Yan Yuan, Yuanxia Liu, Mengyao Sun, Huijing Ye, Yuchen Feng, Zhenzhen Liu, Lingyu Pan, Hongbo Weng
Open Life Sciences.2022; 17(1): 1451. CrossRef - Single-cell multiomics reveals the complexity of TGFβ signalling to chromatin in iPSC-derived kidney organoids
Jessica L. Davis, Ciaran Kennedy, Shane Clerkin, Niall J. Treacy, Thomas Dodd, Catherine Moss, Alison Murphy, Derek P. Brazil, Gerard Cagney, Dermot F. Brougham, Rabi Murad, Darren Finlay, Kristiina Vuori, John Crean
Communications Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Oxidized Albumin: Evaluation of Oxidative Stress as a Marker for the Progression of Kidney Disease
Hiroshi Watanabe
Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin.2022; 45(12): 1728. CrossRef - Whether Renal Pathology Is an Independent Predictor for End-Stage Renal Disease in Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients with Nephrotic Range Proteinuria: A Biopsy-Based Study
Tingli Wang, Junlin Zhang, Yiting Wang, Lijun Zhao, Yucheng Wu, Honghong Ren, Yutong Zou, Rui Zhang, Huan Xu, Zhonglin Chai, Mark Cooper, Jie Zhang, Fang Liu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(1): 88. CrossRef - What’s New in the Molecular Mechanisms of Diabetic Kidney Disease: Recent Advances
Kimio Watanabe, Emiko Sato, Eikan Mishima, Mariko Miyazaki, Tetsuhiro Tanaka
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 24(1): 570. CrossRef - Clinical efficacy and safety of astragalus injection combined with ACEI/ARB in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis
Zhiyue Zhu, Qi Zhang, Le Liu, Pengjie Bao, Shilin Liu, Chaoqun Song, Wenbo Yang, Zheng Nan
Medicine.2022; 101(49): e31490. CrossRef - Cudrania tricuspidata Root Extract Prevents Methylglyoxal-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Regulation of the PKC-NOX4 Pathway in Human Kidney Cells
Donghee Kim, Jayeon Cheon, Haelim Yoon, Hee-Sook Jun, Evangelia Dounousi
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Pleiotropic Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors: Renoprotective Mechanisms beyond Glycemic Control
Tomoaki Takata, Hajime Isomoto
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(9): 4374. CrossRef - HIF-α Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors and Their Implications for Biomedicine: A Comprehensive Review
Kiichi Hirota
Biomedicines.2021; 9(5): 468. CrossRef - Nephropathie bei Diabetes
Roland E. Schmieder
CardioVasc.2021; 21(3): 31. CrossRef - Clinical Predictors of Nondiabetic Kidney Disease in Patients with Diabetes: A Single-Center Study
Francesco Fontana, Rossella Perrone, Francesco Giaroni, Gaetano Alfano, Silvia Giovanella, Giulia Ligabue, Riccardo Magistroni, Gianni Cappelli, Udeme Ekrikpo
International Journal of Nephrology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Activated Histone Acetyltransferase p300/CBP-Related Signalling Pathways Mediate Up-Regulation of NADPH Oxidase, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in Diabetic Kidney
Alexandra-Gela Lazar, Mihaela-Loredana Vlad, Adrian Manea, Maya Simionescu, Simona-Adriana Manea
Antioxidants.2021; 10(9): 1356. CrossRef - Plasma and urine biomarkers in chronic kidney disease: closer to clinical application
Azadeh Zabetian, Steven G. Coca
Current Opinion in Nephrology & Hypertension.2021; 30(6): 531. CrossRef - Therapeutic effect and mechanism of combined use of FGF21 and insulin on diabetic nephropathy
Fanrui Meng, Yukai Cao, Mir Hassan Khoso, Kai Kang, Guiping Ren, Wei Xiao, Deshan Li
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics.2021; 713: 109063. CrossRef - Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Daiji Kawanami, Yuichi Takashi, Yoshimi Muta, Naoki Oda, Dai Nagata, Hiroyuki Takahashi, Makito Tanabe
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcription Factor ChREBP Mediates High Glucose-Evoked Increase in HIF-1α Content in Epithelial Cells of Renal Proximal Tubules
Aleksandra Owczarek, Katarzyna B. Gieczewska, Robert Jarzyna, Zuzanna Frydzinska, Katarzyna Winiarska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(24): 13299. CrossRef - The effect of modern hypoglycemic therapy on the course of chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
V.I. Katerenchuk
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2021; 17(8): 624. CrossRef
- Clinical value of serum MMP-3 in chronic kidney disease
- Complications
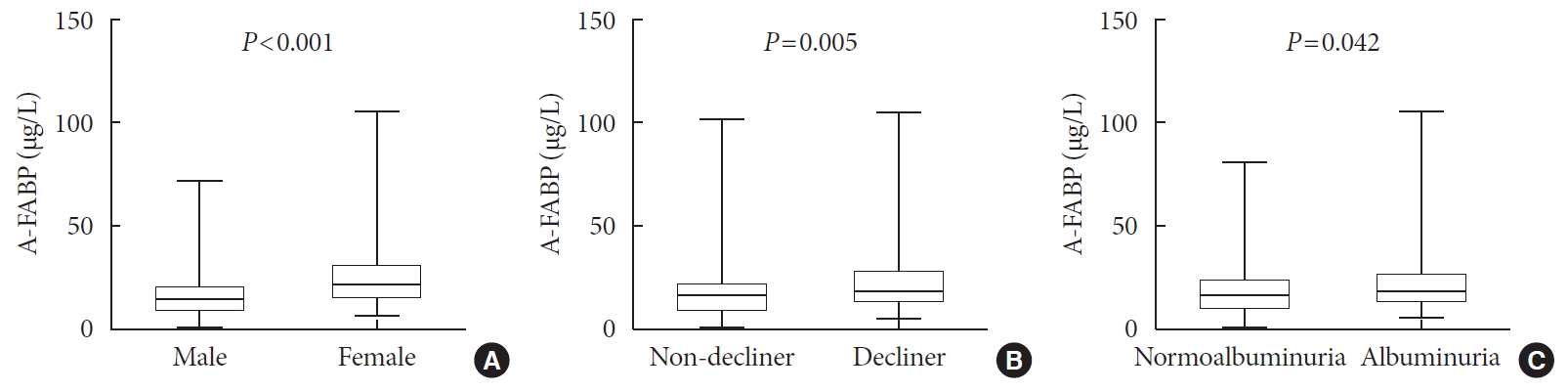
- Serum Levels of Adipocyte Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Are Associated with Rapid Renal Function Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Preserved Renal Function
- Da Hea Seo, Moonsuk Nam, Mihye Jung, Young Ju Suh, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, So Hun Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):875-886. Published online July 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0221
- 5,629 View
- 123 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Recent studies have demonstrated that the levels of adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein (A-FABP) are closely associated with diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This study aimed to examine the association between serum A-FABP level and rapid renal function decline in patients with T2DM and preserved renal function.
Methods This was a prospective observational study of 452 patients with T2DM and preserved renal function who had serial measurements of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Rapid renal function decline was defined as an eGFR decline of >4% per year. The association between baseline serum A-FABP level and rapid renal function decline was investigated.
Results Over a median follow-up of 7 years, 82 participants (18.1%) experienced rapid renal function decline. Median A-FABP levels were significantly higher in patients with rapid renal function decline, compared to non-decliners (20.2 ng/mL vs. 17.2 ng/mL,
P =0.005). A higher baseline level of A-FABP was associated with a greater risk of developing rapid renal function decline, independent of age, sex, duration of diabetes, body mass index, systolic blood pressure, history of cardiovascular disease, baseline eGFR, urine albumin creatinine ratio, total cholesterol, glycosylated hemoglobin, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and use of thiazolidinedione, insulin, angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II-receptor blockers and statin (odds ratio, 3.10; 95% confidence interval, 1.53 to 6.29;P =0.002).Conclusion A high level of serum A-FABP is associated with an increased risk of rapid renal function decline in patients with T2DM and preserved renal function. This suggests that A-FABP could play a role in the progression of DKD in the early stages.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Serum fatty acid-binding protein 4 as a biomarker for early detection of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes
Amr M. Shaker, Maggie E. Mohamed, Tarek Ramzy, Mayssa I. Ali
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Circulating thrombospondin-2 level for identifying individuals with rapidly declining kidney function trajectory in type 2 diabetes: a prospective study of the Hong Kong West Diabetes Registry
Chi-Ho Lee, David Tak-Wai Lui, Chloe Yu-Yan Cheung, Carol Ho-Yi Fong, Michele Mae-Ann Yuen, Wing-Sun Chow, Aimin Xu, Karen Siu-Ling Lam
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of inflammatory cytokines and estimated glomerular filtration rate decline in Japanese patients with diabetic kidney disease: a pilot study
Yuka Sugawara, Yosuke Hirakawa, Koki Mise, Kosuke Kashiwabara, Ko Hanai, Satoshi Yamaguchi, Akihiro Katayama, Yasuhiro Onishi, Yui Yoshida, Naoki Kashihara, Yutaka Matsuyama, Tetsuya Babazono, Masaomi Nangaku, Jun Wada
Biomarkers in Medicine.2022; 16(10): 759. CrossRef - The role of statins in patients with early diabetic nephropathy
Xi Zhao, Shu Chun Zhou, Xiu Fang Wang, Hong Wu Liao
Medicine.2022; 101(24): e29099. CrossRef - Serum Adipocyte Fatty-Acid Binding Protein as an Independent Marker of Peripheral Artery Disease in Patients with Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
Bang-Gee Hsu, Chin-Yee Mah, Du-An Wu, Ming-Chun Chen
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(15): 9459. CrossRef - Fatty acid-binding protein 4 in kidney diseases: From mechanisms to clinics
Weijing Lai, Min Shi, Rongshuang Huang, Ping Fu, Liang Ma
European Journal of Pharmacology.2022; 931: 175224. CrossRef - Serum fatty acid-binding protein 4 levels and responses of pancreatic islet β-cells and α-cells in patients with type 2 diabetes
Hong Wang, Jie Cao, Jian-bin Su, Xue-qin Wang, Xing Wang, Dong-mei Zhang, Xiao-hua Wang
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Low-Expression Variant of FABP4 Is Associated With Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes
Emma H. Dahlström, Jani Saksi, Carol Forsblom, Nicoline Uglebjerg, Nina Mars, Lena M. Thorn, Valma Harjutsalo, Peter Rossing, Tarunveer S. Ahluwalia, Perttu J. Lindsberg, Niina Sandholm, Per-Henrik Groop
Diabetes.2021; 70(10): 2391. CrossRef - White adipocyte-targeted dual gene silencing of FABP4/5 for anti-obesity, anti-inflammation and reversal of insulin resistance: Efficacy and comparison of administration routes
Jee Young Chung, Juhyeong Hong, Hyung-Jin Kim, Yoonsung Song, Seok-Beom Yong, Jieun Lee, Yong-Hee Kim
Biomaterials.2021; 279: 121209. CrossRef
- Serum fatty acid-binding protein 4 as a biomarker for early detection of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes
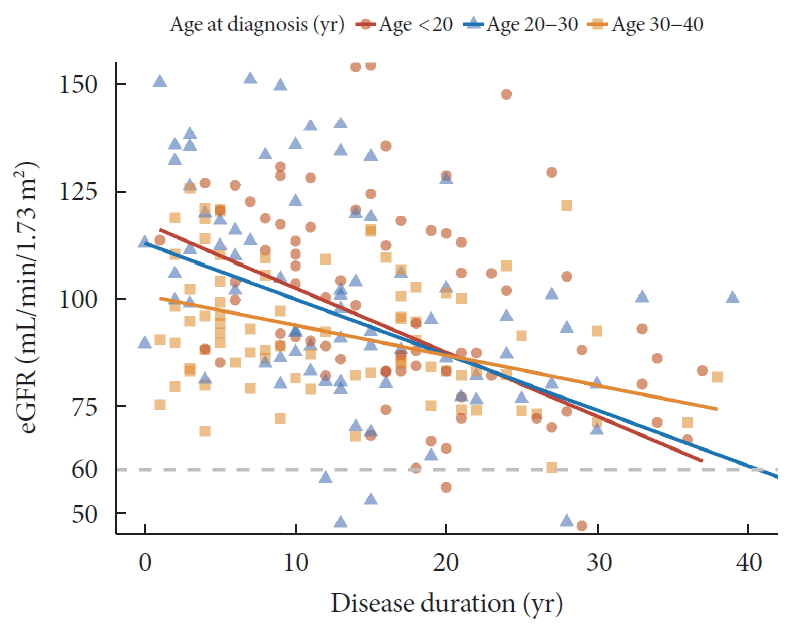
- Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jong Ha Baek, Woo Je Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Soo Kyoung Kim, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):46-54. Published online July 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0134
- 6,807 View
- 230 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background The aim of this study was to evaluate characteristics and risk of diabetic complications according to age at diagnosis among young adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM).
Methods A total of 255 T1DM patients aged less than 40 years were included. Patients were categorized into three groups (<20, 20 to 29, and 30 to 40 years) according to age at diagnosis. Diabetic nephropathy (DN) was defined when spot urine-albumin creatinine ratio was 300 mg/g or more and/or estimated glomerular filtration ratio (eGFR) level was 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or less.
Results Median age at diagnosis was 25 years and disease duration was 14 years. Individuals diagnosed with T1DM at childhood/adolescent (age <20 years) had lower stimulated C-peptide levels. They received more intensive insulin treatment with higher total daily insulin doses compared to older onset groups. The prevalence of DN was higher in the childhood/adolescent-onset group than in older onset groups (25.3% vs. 15.3% vs. 9.6%,
P =0.022). The eGFR was inversely associated with disease duration whilst the degree of decrease was more prominent in the childhood/adolescent-onset group than in the later onset group (aged 30 to 40 years;P <0.001). Childhood/adolescent-onset group was independently associated with the risk of DN compared to the older onset group (aged 30 to 40 years; odds ratio, 3.47; 95% confidence interval, 1.45 to 8.33;P =0.005).Conclusion In individuals with childhood/adolescent-onset T1DM, the reduction in renal function is more prominent with disease duration. Early age-onset T1DM is an independent risk of DN.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Age at onset of type 1 diabetes between puberty and 30 years old is associated with increased diabetic nephropathy risk
Yen-Bo Lin, Wayne Huey-Herng Sheu, Su-Huey Lo, Yen-Po Yeh, Chien-Ning Huang, Chii-Min Hwu, Chang-Hsun Hsieh, Horng-Yi Ou, Lee-Ming Chuang, Jung-Fu Chen, Yu-Cheng Chen, Yun-Hsing Peng, Szu-Tah Chen, Shang-Ren Hsu, Yi-Ling Hsieh, Chih-Hsun Chu, Chieg-Hsiang
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeted mapping and utilization of the perihepatic surface for therapeutic beta cell replacement and retrieval in diabetic non-human primates
David J. Leishman, Scott H. Oppler, Laura L. Hocum Stone, Timothy D. O’Brien, Sabarinathan Ramachandran, Bradley J. Willenberg, Andrew B. Adams, Bernhard J. Hering, Melanie L. Graham
Frontiers in Transplantation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison between a tubeless, on-body automated insulin delivery system and a tubeless, on-body sensor-augmented pump in type 1 diabetes: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Eun Seok Kang, Soo Heon Kwak, Yeoree Yang, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyun Bae, Jun Sung Moon, Chang Hee Jung, Ji Cheol Bae, Sunghwan Suh, Sun Joon Moon, Sun Ok Song, Suk Chon, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring with structured education in adults with type 2 diabetes managed by multiple daily insulin injections: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kang Hee Sim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Jae Hyoung Cho, Jun Sung Moon, Soo Lim, Eun Seok Kang, Cheol-Young Park, Sin Gon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Network-based identification and prioritization of key transcriptional factors of diabetic kidney disease
Ikhlak Ahmed, Mubarak Ziab, Sahar Da’as, Waseem Hasan, Sujitha P. Jeya, Elbay Aliyev, Sabah Nisar, Ajaz A. Bhat, Khalid Adnan Fakhro, Ammira S. Alshabeeb Akil
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.2023; 21: 716. CrossRef - Comparison of diabetes distress and depression screening results of emerging adults with type 1 diabetes onset at different ages: findings from the German early-onset T1D study and the German Diabetes Study (GDS)
Anna Stahl-Pehe, Christina Bächle, Kálmán Bódis, Oana-Patricia Zaharia, Karin Lange, Reinhard W. Holl, Michael Roden, Joachim Rosenbauer, M. Roden, H. Al-Hasani, B Belgardt, GJ. Bönhof, V Burkart, A. E. Buyken, G. Geerling, C. Herder, A. Icks, K. Jandelei
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hemoperfusion and functional state of the macula after simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation
IV Vorobyeva, EV Bulava, LK Moshetova, AV Pinchuk
Bulletin of Russian State Medical University.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Sigesbeckia orientalis Extract Ameliorates the Experimental Diabetic Nephropathy by Downregulating the Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Signaling Pathways
Chung-Ming Chen, Jer-Yiing Houng, Tsui-Ling Ko, Shu-Hui Juan, Hsiu-Chu Chou, Xing Li
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Impact of low-protein diet on cardiovascular risk factors and kidney function in diabetic nephropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials
Mohammad Hassan Sohouli, Parvin Mirmiran, Shaikh Sanjid Seraj, Emad Kutbi, Hadil Ali Mohammed Alkahmous, Faisal Almuqayyid, Omar Ahnaf Arafah, Abdul Rahman Riad Barakeh, Ahmed Abu-Zaid
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110068. CrossRef - Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:46-54)
Jong Ha Baek, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 281. CrossRef - Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:46-54)
Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 277. CrossRef - Role of magnetic resonance diffusion weighted imaging in diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy in children living with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Eman Nabil Wahba, Ashraf Elsharkawy, Mohammad Hosny Awad, Ashraf Abdel Rahman, Amr Sarhan
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 34(12): 1585. CrossRef
- Age at onset of type 1 diabetes between puberty and 30 years old is associated with increased diabetic nephropathy risk
- Complications
- Therapeutic Effects of Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 on Diabetic Nephropathy and the Possible Mechanism in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Mice
- Wenya Weng, Tingwen Ge, Yi Wang, Lulu He, Tinghao Liu, Wanning Wang, Zongyu Zheng, Lechu Yu, Chi Zhang, Xuemian Lu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):566-580. Published online May 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0089
- 5,913 View
- 102 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) has been only reported to prevent type 1 diabetic nephropathy (DN) in the streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) mouse model. However, the FVB (Cg)-Tg (Cryaa-Tag, Ins2-CALM1) 26OVE/PneJ (OVE26) transgenic mouse is a widely recommended mouse model to recapture the most important features of T1DM nephropathy that often occurs in diabetic patients. In addition, most previous studies focused on exploring the preventive effect of FGF21 on the development of DN. However, in clinic, development of therapeutic strategy has much more realistic value compared with preventive strategy since the onset time of DN is difficult to be accurately predicted. Therefore, in the present study OVE26 mice were used to investigate the potential therapeutic effects of FGF21 on DN.
Methods Four-month-old female OVE26 mice were intraperitoneally treated with recombinant FGF21 at a dose of 100 µg/kg/day for 3 months. The diabetic and non-diabetic control mice were treated with phosphate-buffered saline at the same volume. Renal functions, pathological changes, inflammation, apoptosis, oxidative stress and fibrosis were examined in mice of all groups.
Results The results showed that severe renal dysfunction, morphological changes, inflammation, apoptosis, and fibrosis were observed in OVE26 mice. However, all the renal abnormalities above in OVE26 mice were significantly attenuated by 3-month FGF21 treatment associated with improvement of renal adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity and sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) expression.
Conclusion Therefore, this study demonstrated that FGF21 might exert therapeutic effects on DN through AMPK-SIRT1 pathway.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fibroblast growth factor 21 alleviates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
Wenhui Zhong, Yuheng Jiang, Huizhen Wang, Xiang Luo, Tao Zeng, Huimi Huang, Ling Xiao, Nan Jia, Aiqing Li
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2024; 1871(2): 119620. CrossRef - Urinary Excretion of Biomolecules Related to Cell Cycle, Proliferation, and Autophagy in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
Anton I. Korbut, Vyacheslav V. Romanov, Vadim V. Klimontov
Biomedicines.2024; 12(3): 487. CrossRef - New developments in the biology of fibroblast growth factors
David M. Ornitz, Nobuyuki Itoh
WIREs Mechanisms of Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - SIRT1–SIRT7 in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
Wenxiu Qi, Cheng Hu, Daqing Zhao, Xiangyan Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Fibrotic Diseases
Min-Qi Jia, Cha-Xiang Guan, Jia-Hao Tao, Yong Zhou, Liang-Jun Yan
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease increases the risk of end-stage renal disease in patients with biopsy-confirmed diabetic nephropathy: a propensity-matched cohort study
Yutong Zou, Lijun Zhao, Junlin Zhang, Yiting Wang, Yucheng Wu, Honghong Ren, Tingli Wang, Yuancheng Zhao, Huan Xu, Lin Li, Nanwei Tong, Fang Liu
Acta Diabetologica.2022; 60(2): 225. CrossRef - FGF21 and Chronic Kidney Disease
João Victor Salgado, Miguel Angelo Goes, Natalino Salgado Filho
Metabolism.2021; 118: 154738. CrossRef - The Multiple Roles of Fibroblast Growth Factor in Diabetic Nephropathy
Junyu Deng, Ye Liu, Yiqiu Liu, Wei Li, Xuqiang Nie
Journal of Inflammation Research.2021; Volume 14: 5273. CrossRef - Therapeutic effect and mechanism of combined use of FGF21 and insulin on diabetic nephropathy
Fanrui Meng, Yukai Cao, Mir Hassan Khoso, Kai Kang, Guiping Ren, Wei Xiao, Deshan Li
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics.2021; 713: 109063. CrossRef - FGF19 and FGF21 for the Treatment of NASH—Two Sides of the Same Coin? Differential and Overlapping Effects of FGF19 and FGF21 From Mice to Human
Emma Henriksson, Birgitte Andersen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - FGF21: An Emerging Therapeutic Target for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis and Related Metabolic Diseases
Erik J. Tillman, Tim Rolph
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Fibroblast growth factor 21 alleviates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Basic Research
-
- Inhibition of Ceramide Accumulation in Podocytes by Myriocin Prevents Diabetic Nephropathy
- Chang-Yun Woo, Ji Yeon Baek, Ah-Ram Kim, Chung Hwan Hong, Ji Eun Yoon, Hyoun Sik Kim, Hyun Ju Yoo, Tae-Sik Park, Ranjan Kc, Ki-Up Lee, Eun Hee Koh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):581-591. Published online November 4, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0063
- 6,165 View
- 165 Download
- 26 Web of Science
- 29 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Ceramides are associated with metabolic complications including diabetic nephropathy in patients with diabetes. Recent studies have reported that podocytes play a pivotal role in the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Also, mitochondrial dysfunction is known to be an early event in podocyte injury. Thus, we tested the hypothesis that ceramide accumulation in podocytes induces mitochondrial damage through reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in patients with diabetic nephropathy.
Methods We used Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice. We fed the animals either a control- or a myriocin-containing diet to evaluate the effects of the ceramide. Also, we assessed the effects of ceramide on intracellular ROS generation and on podocyte autophagy in cultured podocytes.
Results OLETF rats and HFD-fed mice showed albuminuria, histologic features of diabetic nephropathy, and podocyte injury, whereas myriocin treatment effectively treated these abnormalities. Cultured podocytes exposed to agents predicted to be risk factors (high glucose, high free fatty acid, and angiotensin II in combination [GFA]) showed an increase in ceramide accumulation and ROS generation in podocyte mitochondria. Pretreatment with myriocin reversed GFA-induced mitochondrial ROS generation and prevented cell death. Myriocin-pretreated cells were protected from GFA-induced disruption of mitochondrial integrity.
Conclusion We showed that mitochondrial ceramide accumulation may result in podocyte damage through ROS production. Therefore, this signaling pathway could become a pharmacological target to abate the development of diabetic kidney disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Interplay of lipid metabolism and inflammation in podocyte injury
Zilv Luo, Zhaowei Chen, Jijia Hu, Guohua Ding
Metabolism.2024; 150: 155718. CrossRef - Associations of plasma sphingolipids with measures of insulin sensitivity, β-cell function, and incident diabetes in Japanese Americans
Ji Cheol Bae, Pandora L. Wander, Rozenn N. Lemaitre, Amanda M. Fretts, Colleen M. Sitlani, Hai H. Bui, Melissa K. Thomas, Donna Leonetti, Wilfred Y. Fujimoto, Edward J. Boyko, Kristina M. Utzschneider
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024; 34(3): 633. CrossRef - A review of the mechanisms of abnormal ceramide metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus, Alzheimer’s disease, and their co-morbidities
Yun Pan, Jieying Li, Panjie Lin, Lihua Wan, Yiqian Qu, Lingyong Cao, Lei Wang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Ceramides and mitochondrial homeostasis
Song Ding, Guorui Li, Tinglv Fu, Tianyu Zhang, Xiao Lu, Ning Li, Qing Geng
Cellular Signalling.2024; 117: 111099. CrossRef - Reduced sphingolipid biosynthesis modulates proteostasis networks to enhance longevity
Nathaniel L. Hepowit, Eric Blalock, Sangderk Lee, Kimberly M. Bretland, Jason A. MacGurn, Robert C. Dickson
Aging.2023; 15(2): 472. CrossRef - Protective effect of natural products in the metabolic-associated kidney diseases via regulating mitochondrial dysfunction
Peng Liu, Yao Chen, Jing Xiao, Wenhui Zhu, Xiaoming Yan, Ming Chen
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - BCAA insufficiency leads to premature ovarian insufficiency via ceramide‐induced elevation of ROS
Xiao Guo, Yuemeng Zhu, Lu Guo, Yiwen Qi, Xiaocheng Liu, Jinhui Wang, Jiangtao Zhang, Linlin Cui, Yueyang Shi, Qichu Wang, Cenxi Liu, Guangxing Lu, Yilian Liu, Tao Li, Shangyu Hong, Yingying Qin, Xuelian Xiong, Hao Wu, Lin Huang, He Huang, Chao Gu, Bin Li,
EMBO Molecular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Chinese herbal medicine and its active compounds in attenuating renal injury via regulating autophagy in diabetic kidney disease
Peng Liu, Wenhui Zhu, Yang Wang, Guijie Ma, Hailing Zhao, Ping Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrated gas chromatography‐mass spectrometry and ultra‐high‐performance liquid chromatography‐mass spectrometry renal metabolomics and lipidomics deciphered the metabolic regulation mechanism of Gushudan on kidney‐yang‐deficiency‐syndrome rats
Qing Lu, Jing Zhang, Ling Xin, Yanwei Lou, Feng Qin, Longshan Zhao, Zhili Xiong
Journal of Separation Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in the pharmacological study of Chinese herbal medicine to alleviate diabetic nephropathy by improving mitochondrial oxidative stress
Ming Chen, Yao Chen, Wenhui Zhu, Xiaoming Yan, Jing Xiao, Peiqing Zhang, Peng Liu, Ping Li
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 165: 115088. CrossRef - Rodent models to study type 1 and type 2 diabetes induced human diabetic nephropathy
Amit Talukdar, Mandira Basumatary
Molecular Biology Reports.2023; 50(9): 7759. CrossRef - Art2 mediates selective endocytosis of methionine transporters during adaptation to sphingolipid depletion
Nathaniel L. Hepowit, Bradley Moon, Adam C. Ebert, Robert C. Dickson, Jason A. MacGurn
Journal of Cell Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Kidney lipid dysmetabolism and lipid droplet accumulation in chronic kidney disease
Alla Mitrofanova, Sandra Merscher, Alessia Fornoni
Nature Reviews Nephrology.2023; 19(10): 629. CrossRef - Research progress of autophagy in pathogenesis of diabetes nephropathy
Shengnan Zeng, Ying Li
Diabetic Nephropathy.2023; 3(3): 51. CrossRef - Lipidomic approaches to dissect dysregulated lipid metabolism in kidney disease
Judy Baek, Chenchen He, Farsad Afshinnia, George Michailidis, Subramaniam Pennathur
Nature Reviews Nephrology.2022; 18(1): 38. CrossRef - Podocyte Bioenergetics in the Development of Diabetic Nephropathy: The Role of Mitochondria
Irena Audzeyenka, Agnieszka Bierżyńska, Abigail C Lay
Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Acylcarnitines: Can They Be Biomarkers of Diabetic Nephropathy?
Xiaodie Mu, Min Yang, Peiyao Ling, Aihua Wu, Hua Zhou, Jingting Jiang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 247. CrossRef - Research Progress on Natural Products’ Therapeutic Effects on Atrial Fibrillation by Regulating Ion Channels
Jinshan He, Sicong Li, Yumeng Ding, Yujia Tong, Xuebin Li, Simona Saponara
Cardiovascular Therapeutics.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Mechanisms of podocyte injury and implications for diabetic nephropathy
Federica Barutta, Stefania Bellini, Gabriella Gruden
Clinical Science.2022; 136(7): 493. CrossRef - A Rheostat of Ceramide and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate as a Determinant of Oxidative Stress-Mediated Kidney Injury
Norishi Ueda
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(7): 4010. CrossRef - Implications of Sphingolipid Metabolites in Kidney Diseases
Shamroop kumar Mallela, Sandra Merscher, Alessia Fornoni
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4244. CrossRef - Role of ceramides in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus and its complications
Nawajes Mandal, Richard Grambergs, Koushik Mondal, Sandip K. Basu, Faiza Tahia, Sam Dagogo-Jack
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2021; 35(2): 107734. CrossRef - Rotten to the Cortex: Ceramide-Mediated Lipotoxicity in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Rebekah J. Nicholson, Marcus G. Pezzolesi, Scott A. Summers
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing lifespan of budding yeast by pharmacological lowering of amino acid pools
Nathaniel L. Hepowit, Jessica K. A. Macedo, Lyndsay E. A. Young, Ke Liu, Ramon C. Sun, Jason A. MacGurn, Robert C. Dickson
Aging.2021; 13(6): 7846. CrossRef - New insights into renal lipid dysmetabolism in diabetic kidney disease
Alla Mitrofanova, George Burke, Sandra Merscher, Alessia Fornoni
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(5): 524. CrossRef - Excessively Enlarged Mitochondria in the Kidneys of Diabetic Nephropathy
Kiyoung Kim, Eun-Young Lee
Antioxidants.2021; 10(5): 741. CrossRef - Mechanistic insights into the role of serum-glucocorticoid kinase 1 in diabetic nephropathy: A systematic review
Saba Noor, Taj Mohammad, Gulam M. Ashraf, Joviana Farhat, Anwar L. Bilgrami, Mathew Suji Eapen, Sukhwinder Singh Sohal, Dharmendra Kumar Yadav, Md Imtaiyaz Hassan
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2021; 193: 562. CrossRef - The Updates of Podocyte Lipid Metabolism in Proteinuric Kidney Disease
Yu Sun, Sijia Cui, Yunfeng Hou, Fan Yi
Kidney Diseases.2021; 7(6): 438. CrossRef - Saturated fatty acids induce insulin resistance in podocytes through inhibition of IRS1 via activation of both IKKβ and mTORC1
Benoit Denhez, Marina Rousseau, Crysta Spino, David-Alexandre Dancosst, Marie-Ève Dumas, Andréanne Guay, Farah Lizotte, Pedro Geraldes
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Interplay of lipid metabolism and inflammation in podocyte injury
- Complications
- Presence of Carotid Plaque Is Associated with Rapid Renal Function Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Normal Renal Function
- Da Hea Seo, So Hun Kim, Joon Ho Song, Seongbin Hong, Young Ju Suh, Seong Hee Ahn, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Kwan Woo Lee, Young Seol Kim, Moonsuk Nam
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):840-853. Published online March 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0186
- 5,529 View
- 57 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Recent evidences indicate that early rapid renal function decline is closely associated with the development and progression of diabetic kidney disease. We have investigated the association between carotid atherosclerosis and rapid renal function decline in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and preserved renal function.
Methods In a prospective, multicenter cohort, a total of 967 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and preserved renal function were followed for 6 years with serial estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) measurements. Common carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and presence of carotid plaque were assessed at baseline. Rapid renal function decline was defined as an eGFR decline >3.3% per year.
Results Over a median follow-up of 6 years, 158 participants (16.3%) developed rapid renal function decline. While there was no difference in CIMT, the presence of carotid plaque in rapid decliners was significantly higher than in non-decliners (23.2% vs. 12.2%,
P <0.001). In multivariable logistic regression analysis, presence of carotid plaque was an independent predictor of rapid renal function decline (odds ratio, 2.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.48 to 3.68;P <0.0001) after adjustment for established risk factors. The model including the carotid plaque had better performance for discrimination of rapid renal function decline than the model without carotid plaque (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve 0.772 vs. 0.744,P =0.016).Conclusion Close monitoring of renal function and early intensive management may be beneficial in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and carotid plaques.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of diabetes distress on glycemic control and diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hye-Sun Park, Yongin Cho, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, Young Ju Suh, Suk Chon, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Kwan Woo Lee, So Hun Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation analysis of carotid plaque in young patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio and neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio
Huijun Wen, Hai Yu
Vascular.2023; 31(1): 90. CrossRef - Diabetic vascular diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies
Yiwen Li, Yanfei Liu, Shiwei Liu, Mengqi Gao, Wenting Wang, Keji Chen, Luqi Huang, Yue Liu
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Carotid intima-media thickness and atherosclerotic plaques are associated with renal function decline: a 14-year longitudinal population-based study
Miriam Goepfert, Till Ittermann, Marcus Dörr, Nele Friedrich, Henry Völzke, Thomas Dabers, Stephan B Felix, Ulf Schminke, Sylvia Stracke, Sabrina von Rheinbaben
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation.2023; 38(11): 2598. CrossRef - Blood pressure and vascular determinants of glomerular filtration rate decline in diabetic kidney disease
Luca Truscello, Dina Nobre, Vehashini Sabaratnam, Olivier Bonny, Grégoire Wuerzner, Michel Burnier, Fadi Fakhouri, Menno Pruijm, Anne Zanchi
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Explainable Artificial Intelligence Paves the Way in Precision Diagnostics and Biomarker Discovery for the Subclass of Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetics
Fatma Hilal Yagin, Seyma Yasar, Yasin Gormez, Burak Yagin, Abdulvahap Pinar, Abedalrhman Alkhateeb, Luca Paolo Ardigò
Metabolites.2023; 13(12): 1204. CrossRef - Evaluation of Subclinical Vascular Disease in Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Tool for Personalization of Management of a High-Risk Population
Christodoula Kourtidou, Vasileios Rafailidis, Garyfallia Varouktsi, Efthimios Kanakis, Vassilios Liakopoulos, Timoleon-Achilleas Vyzantiadis, Maria Stangou, Smaragdi Marinaki, Konstantinos Tziomalos
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(7): 1139. CrossRef - Prevalence and Predictors of Renal Disease in a National Representative Sample of the Romanian Adult Population: Data from the SEPHAR IV Survey
Călin Pop, Oana Florentina Gheorghe Fronea, Ioana Antonia Branea, Lucian Mihai Itu, Roxana Darabont, Irinel Parepa, Theodora Benedek, Maria Dorobantu
Diagnostics.2022; 12(12): 3199. CrossRef - Clinical features of and risk factors for normoalbuminuric diabetic kidney disease in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a retrospective cross-sectional study
Qi Dai, Nan Chen, Ling Zeng, Xin-Jie Lin, Feng-Xiu Jiang, Xiong-Jie Zhuang, Ze-Yuan Lu
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Predictive Value of Carotid Ultrasonography With Cardiovascular Risk Factors—A “SPIDER” Promoting Atherosclerosis
Hongwei Li, Xiaolin Xu, Baoming Luo, Yuling Zhang
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Update on pathogenesis and diagnosis flow of normoalbuminuric diabetes with renal insufficiency
Le Deng, Wenjie Li, Gaosi Xu
European Journal of Medical Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of serum fibroblast growth factor 21 with kidney function in a population-based Chinese cohort
Rui Zhang, Yufeng Li, Xianghai Zhou, Fang Zhang, Meng Li, Simin Zhang, Xiuying Zhang, Xin Wen, Linong Ji
Medicine.2021; 100(50): e28238. CrossRef - Letter: Presence of Carotid Plaque Is Associated with Rapid Renal Function Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Normal Renal Function (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:840–53)
Min-Ji Kim, Jae-Han Jeon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 201. CrossRef - Response: Presence of Carotid Plaque Is Associated with Rapid Renal Function Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Normal Renal Function (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:840–53)
Da Hea Seo, So Hun Kim, Moonsuk Nam
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 205. CrossRef - Serum Levels of Adipocyte Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Are Associated with Rapid Renal Function Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Preserved Renal Function
Da Hea Seo, Moonsuk Nam, Mihye Jung, Young Ju Suh, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, So Hun Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 875. CrossRef - Proteinuria Is Associated with Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis in Non-Albuminuric Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jaehyun Bae, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(1): 136. CrossRef
- Impact of diabetes distress on glycemic control and diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Complications
- Effect of Empagliflozin, a Selective Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor, on Kidney and Peripheral Nerves in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Kyung Ae Lee, Heung Yong Jin, Na Young Lee, Yu Ji Kim, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(4):338-342. Published online April 25, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0095
- 3,989 View
- 64 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader The effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on peripheral nerves and kidneys in diabetes mellitus (DM) remains unexplored. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the effect of empagliflozin in diabetic rats. DM in rats was induced by streptozotocin injection, and diabetic rats were treated with empagliflozin 3 or 10 mg/kg. Following 24-week treatment, response thresholds to four different stimuli were tested and found to be lower in diabetic rats than in normal rats. Empagliflozin significantly prevented hypersensitivity (
P <0.05) and the loss of skin intraepidermal nerve fibers, and mesangial matrix expansion in diabetic rats. Results of this study demonstrate the potential therapeutic effects of empagliflozin for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and nephropathy.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Review of Recent Pharmacological Advances in the Management of Diabetes-Associated Peripheral Neuropathy
Osman Syed, Predrag Jancic, Nebojsa Nick Knezevic
Pharmaceuticals.2023; 16(6): 801. CrossRef - Renal intrinsic cells remodeling in diabetic kidney disease and the regulatory effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors
Wenwen Guo, Han Li, Yixuan Li, Wen Kong
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 165: 115025. CrossRef - A systematic review on renal effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in rodent models of diabetic nephropathy
Aqsa Ashfaq, Myriam Meineck, Andrea Pautz, Ebru Arioglu-Inan, Julia Weinmann-Menke, Martin C. Michel
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2023; 249: 108503. CrossRef - The impact of canagliflozin on the risk of neuropathy events: A post-hoc exploratory analysis of the CREDENCE trial
Jinlan Liao, Amy Kang, Chao Xia, Tamara Young, Gian Luca Di Tanna, Clare Arnott, Carol Pollock, Arun V. Krishnan, Rajiv Agarwal, George Bakris, David M. Charytan, Dick de Zeeuw, Hiddo J.L. Heerspink, Adeera Levin, Bruce Neal, David C. Wheeler, Hong Zhang,
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(4): 101331. CrossRef - Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor Protects Against Diabetic Neuropathy and Nephropathy in Modestly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes: Follow-Up Study
Fukashi Ishibashi, Aiko Kosaka, Mitra Tavakoli
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Protective effect of empagliflozin on gentamicin-induced acute renal injury via regulation of SIRT1/NF-κB signaling pathway
Sandy R. Botros, Asmaa I. Matouk, Aliaa Anter, Mohamed M.A. Khalifa, Gehan H. Heeba
Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology.2022; 94: 103907. CrossRef - Empagliflozin mitigates type 2 diabetes-associated peripheral neuropathy: a glucose-independent effect through AMPK signaling
Noha F. Abdelkader, Marawan A. Elbaset, Passant E. Moustafa, Sherehan M. Ibrahim
Archives of Pharmacal Research.2022; 45(7): 475. CrossRef - Pathogenesis and Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Seon Mee Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(4): 222. CrossRef - Empagliflozin and neohesperidin protect against methotrexate-induced renal toxicity via suppression of oxidative stress and inflammation in male rats
Adel T. Osman, Souty M.Z. Sharkawi, Mohamed I.A. Hassan, Amira M. Abo-youssef, Ramadan A.M. Hemeida
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2021; 155: 112406. CrossRef - Effect of exenatide on peripheral nerve excitability in type 2 diabetes
Tushar Issar, Natalie C.G. Kwai, Ann M. Poynten, Ria Arnold, Kerry-Lee Milner, Arun V. Krishnan
Clinical Neurophysiology.2021; 132(10): 2532. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Empagliflozin With Vitamin D Supplementation in Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Sanjana Mehta, Parminder Nain, Bimal K Agrawal, Rajinder P Singh, Jaspreet Kaur, Sabyasachi Maity, Aniruddha Bhattarcharjee, Jagannadha Peela, Shreya Nauhria, Samal Nauhria
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting oxidative stress, proinflammatory cytokines, apoptosis and toll like receptor 4 by empagliflozin to ameliorate bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis
Ahmed M. Kabel, Remon S. Estfanous, Majed M. Alrobaian
Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology.2020; 273: 103316. CrossRef - Empagliflozin reduces high glucose-induced oxidative stress and miR-21-dependent TRAF3IP2 induction and RECK suppression, and inhibits human renal proximal tubular epithelial cell migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Nitin A. Das, Andrea J. Carpenter, Anthony Belenchia, Annayya R. Aroor, Makoto Noda, Ulrich Siebenlist, Bysani Chandrasekar, Vincent G. DeMarco
Cellular Signalling.2020; 68: 109506. CrossRef - Differential Effects of Empagliflozin on Microvascular Complications in Murine Models of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Stephanie A. Eid, Phillipe D. O’Brien, Lucy M. Hinder, John M. Hayes, Faye E. Mendelson, Hongyu Zhang, Lixia Zeng, Katharina Kretzler, Samanthi Narayanan, Steven F. Abcouwer, Frank C. Brosius, Subramaniam Pennathur, Masha G. Savelieff, Eva L. Feldman
Biology.2020; 9(11): 347. CrossRef - Pre-treatment with Empagliflozin ameliorates Cisplatin induced acute kidney injury by suppressing apoptosis
Maaly A. Abd Elmaaboud, Ahmed M. Kabel, Mohamed Elrashidy
Journal of Applied Biomedicine.2019; 17(1): 90. CrossRef - Effects of ticagrelor, empagliflozin and tamoxifen against experimentally-induced vascular reactivity defects in rats in vivo and in vitro
Yasmin Moustafa Ahmed, Basim Anwar Shehata Messiha, Mahmoud El-Sayed El-Daly, Ali Ahmed Abo-Saif
Pharmacological Reports.2019; 71(6): 1034. CrossRef - SGLT2 inhibition with empagliflozin attenuates myocardial oxidative stress and fibrosis in diabetic mice heart
Chenguang Li, Jie Zhang, Mei Xue, Xiaoyu Li, Fei Han, Xiangyang Liu, Linxin Xu, Yunhong Lu, Ying Cheng, Ting Li, Xiaochen Yu, Bei Sun, Liming Chen
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Empagliflozin Contributes to Polyuria via Regulation of Sodium Transporters and Water Channels in Diabetic Rat Kidneys
Sungjin Chung, Soojeong Kim, Mina Son, Minyoung Kim, Eun Sil Koh, Seok Joon Shin, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ho-Shik Kim
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- A Review of Recent Pharmacological Advances in the Management of Diabetes-Associated Peripheral Neuropathy

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





