
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug/Regimen
- Cardiovascular Safety of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors as Add-on to Metformin Monotherapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ja Young Jeon, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):505-514. Published online October 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0057
- 7,937 View
- 344 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
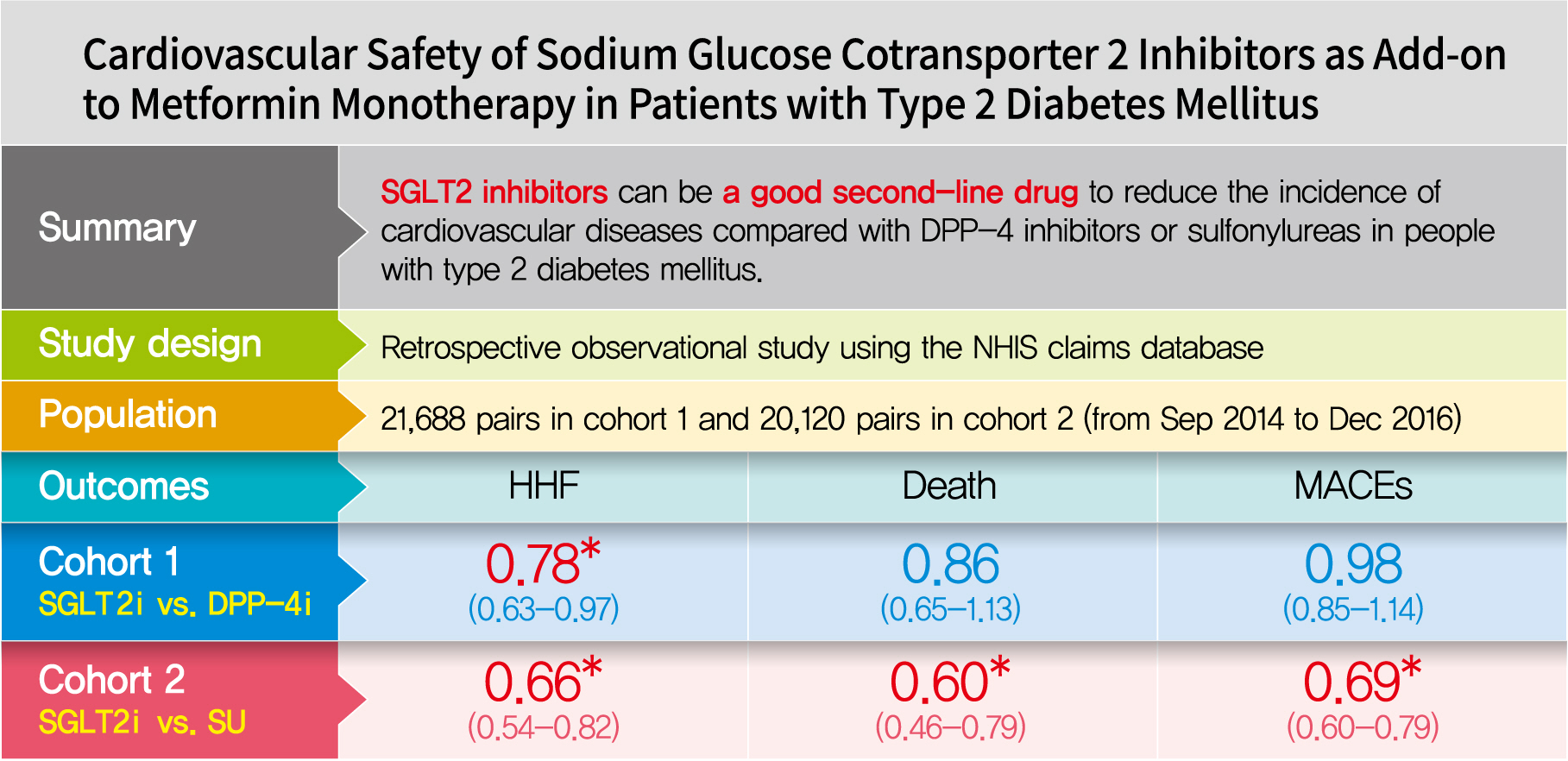
- Background
Using real-world data, cardiovascular safety was investigated in metformin users newly starting sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors compared with other glucose-lowering drugs in Korea.
Methods
This was a retrospective observational study using the National Health Insurance Service claims database in Korea. The study period was from September 2014 to December 2016. The study included subjects who were newly prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors or other glucose-lowering drugs while on metformin monotherapy; cohort 1 was composed of new users of SGLT2 inhibitors versus dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors and cohort 2 included new users of SGLT2 inhibitors versus sulfonylureas. To balance the patient characteristics, propensity score matching was performed at a 1:1 ratio. Cardiovascular outcomes included hospitalization for heart failure (HHF), all-cause mortality, HHF plus all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and modified major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs).
Results
After propensity score matching, each cohort group was well balanced at baseline (21,688 pairs in cohort 1 and 20,120 pairs in cohort 2). As the second-line treatment, use of SGLT2 inhibitors was associated with a lower risk of HHF and HHF plus all-cause mortality compared with DPP-4 inhibitors. In addition, use of SGLT2 inhibitors versus sulfonylurea as add-on therapy to metformin was associated with decreased risks of HHF, all-cause mortality, HHF plus all-cause mortality, MI, stroke, and modified MACEs.
Conclusion
SGLT2 inhibitors can be a good second-line drug to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular diseases compared with DPP-4 inhibitors or sulfonylureas in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Heart Failure.2023; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - Advances in Research on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Targets and Therapeutic Agents
Jingqian Su, Yingsheng Luo, Shan Hu, Lu Tang, Songying Ouyang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(17): 13381. CrossRef - Cardioprotective effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors versus sulfonylureas in addition to metformin: A nationwide cohort study of patients with type 2 diabetes
Jui Wang, Hon-Yen Wu, Kuo-Liong Chien
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(3): 101299. CrossRef - Cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Ja Young Jeon, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(4): 614. CrossRef - The Impact of Novel Anti-Diabetic Medications on CV Outcomes: A New Therapeutic Horizon for Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Cardiac Patients
Israel Mazin, Fernando Chernomordik, Paul Fefer, Shlomi Matetzky, Roy Beigel
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(7): 1904. CrossRef - Effect of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter Inhibitors on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events and Hospitalization for Heart Failure in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Atrial Fibrillation
Chang Hee Kwon, Ye-Jee Kim, Min-Ju Kim, Myung-Jin Cha, Min Soo Cho, Gi-Byoung Nam, Kee-Joon Choi, Jun Kim
The American Journal of Cardiology.2022; 178: 35. CrossRef - Using real-world data for supporting regulatory decision making: Comparison of cardiovascular and safety outcomes of an empagliflozin randomized clinical trial versus real-world data
Ha Young Jang, In-Wha Kim, Jung Mi Oh
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular Safety of SGLT2 Inhibitors Compared to DPP4 Inhibitors and Sulfonylureas as the Second-Line of Therapy in T2DM Using Large, Real-World Clinical Data in Korea
Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 502. CrossRef - The effect of sodium‐glucose transport protein 2 inhibitors on mortality and heart failure in randomized trials versus observational studies
Jesper Krogh, Carsten Hjorthøj, Søren L. Kristensen, Christian Selmer, Steen B. Haugaard
Diabetic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcomes of patients with type 2 diabetes treated with SGLT-2 inhibitors versus DPP-4 inhibitors. An Italian real-world study in the context of other observational studies
Enrico Longato, Benedetta Maria Bonora, Barbara Di Camillo, Giovanni Sparacino, Lara Tramontan, Angelo Avogaro, Gian Paolo Fadini
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 179: 109024. CrossRef
- Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
- Others
- Novel Molecular Mechanisms in the Development of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
- Davide Povero, Ariel E. Feldstein
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(1):1-11. Published online February 19, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.1.1
- 5,821 View
- 55 Download
- 45 Web of Science
- 46 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the most common causes of chronic liver disease in adults and children worldwide. NAFLD has become a severe health issue and it can progress towards a more severe form of the disease, the non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). A combination of environmental factors, host genetics, and gut microbiota leads to excessive accumulation of lipids in the liver (steatosis), which may result in lipotoxicity and trigger hepatocyte cell death, liver inflammation, fibrosis, and pathological angiogenesis. NASH can further progress towards liver cirrhosis and cancer. Over the last few years, cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) have been identified as effective cell-to-cell messengers that transfer several bioactive molecules in target cells, modulating the pathogenesis and progression of NASH. In this review, we focused on recently highlighted aspects of molecular pathogenesis of NASH, mediated by EVs via their bioactive components. The studies included in this review summarize the state of art regarding the role of EVs during the progression of NASH and bring novel insight about the potential use of EVs for diagnosis and therapeutic strategies for patients with this disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Walnut fruit diaphragm ethanol extract ameliorates damage due to Triton WR‐1339‐induced hyperlipidemia in rats
Esra Palabiyik, Ayse Nurseli Sulumer, Handan Uguz, Bahri Avci, Seda Askin, Hakan Askin
European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Extracellular Vesicles and Their Correlation with Inflammatory Factors in an Experimental Model of Steatotic Liver Disease Associated with Metabolic Dysfunction
Melina Belén Keingeski, Larisse Longo, Vitória Brum da Silva Nunes, Fabrício Figueiró, Danieli Rosane Dallemole, Adriana Raffin Pohlmann, Thalia Michele Vier Schmitz, Patrícia Luciana da Costa Lopez, Mário Reis Álvares-da-Silva, Carolina Uribe-Cruz
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - β-sitosterol attenuates high- fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis in rats by modulating lipid metabolism, inflammation and ER stress pathway
Omayma AR Abo-Zaid, Fatma SM Moawed, Effet Soliman Ismail, Mostafa A. Farrag
BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Phospholipid metabolism in the liver – Implications for phosphatidylserine in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Marziyeh Anari, Magdalene K. Montgomery
Biochemical Pharmacology.2023; 213: 115621. CrossRef - Exosome GLUT1 derived from hepatocyte identifies the risk of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis
Wenyan Zhang, Jing Zhang, Honglin Shi, Fang Liu, Haibin Yu, Hongbo Shi
Hepatology International.2023; 17(5): 1170. CrossRef - Role of extracellular vesicles in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Wei Jiang, Youhui Xu, Jou-Chen Chen, Yi-Hung Lee, Yushin Hu, Chang-Hai Liu, Enqiang Chen, Hong Tang, Hua Zhang, Dongbo Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Angiopoietin-2 levels correlates with disease activity in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Melania Manco, Nadia Panera, Annalisa Crudele, Maria Rita Braghini, Marzia Bianchi, Donatella Comparcola, Rita De Vito, Giuseppe Maggiore, Anna Alisi
Pediatric Research.2022; 91(7): 1781. CrossRef - The Neglected Role of Bile Duct Epithelial Cells in NASH
Massimiliano Cadamuro, Alberto Lasagni, Samantha Sarcognato, Maria Guido, Roberto Fabris, Mario Strazzabosco, Alastair J. Strain, Paolo Simioni, Erica Villa, Luca Fabris
Seminars in Liver Disease.2022; 42(01): 034. CrossRef - Relationship between prevalence and risk of osteoporosis or osteoporotic fracture with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Binjing Pan, Jing Cai, Pingping Zhao, Jingfang Liu, Songbo Fu, Gaojing Jing, Qianglong Niu, Qiong Li
Osteoporosis International.2022; 33(11): 2275. CrossRef - Ethanol Extract of Pinus koraiensis Leaves Mitigates High Fructose-Induced Hepatic Triglyceride Accumulation and Hypertriglyceridemia
Min-Ho Lee, Sunyeong Park, Yinzhu Xu, Jung-Eun Kim, Hengmin Han, Jae-Hyeon Lee, Jean Kyung Paik, Hyo-Jeong Lee
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(13): 6745. CrossRef - TWIST2 and the PPAR signaling pathway are important in the progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Yanmei Zhang, Xiaoxiao Ge, Yongqing Li, Bingyang Zhang, Peijun Wang, Mingju Hao, Peng Gao, Yueyi Zhao, Tao Sun, Sumei Lu, Wanshan Ma
Lipids in Health and Disease.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Allopurinol ameliorates high fructose diet induced hepatic steatosis in diabetic rats through modulation of lipid metabolism, inflammation, and ER stress pathway
In-Jin Cho, Da-Hee Oh, Jin Yoo, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho-Yeon Chung, Soung Won Jeong, Ju-Young Moon, Sang-Ho Lee, Sung-Jig Lim, In-Kyung Jeong
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Tabebuia rosea (Bertol.) DC. ethanol extract attenuates body weight gain by activation of molecular mediators associated with browning
Elsa Cecilia Pagaza-Straffon, Carla Elena Mezo-González, David Armando Chavaro-Pérez, Jorge Cornejo-Garrido, Laurence A. Marchat, Claudia G. Benítez-Cardoza, Maricruz Anaya-Reyes, Cynthia Ordaz-Pichardo
Journal of Functional Foods.2021; 86: 104740. CrossRef - Effects of Oral Vitamin C Supplementation on Liver Health and Associated Parameters in Patients With Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Zhangya He, Xiaomin Li, Hexiang Yang, Pei Wu, Shanshan Wang, Dan Cao, Xiaoxiao Guo, Zhangrui Xu, Jiayi Gao, Wanyu Zhang, Xiaoqin Luo
Frontiers in Nutrition.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Hepatic lipid droplet homeostasis and fatty liver disease
Fabian Seebacher, Anja Zeigerer, Nora Kory, Natalie Krahmer
Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology.2020; 108: 72. CrossRef - Orotic acid-treated hepatocellular carcinoma cells resist steatosis by modification of fatty acid metabolism
Johanna Matilainen, Anne-Mari Mustonen, Kirsi Rilla, Reijo Käkelä, Sanna P. Sihvo, Petteri Nieminen
Lipids in Health and Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Liver fibrogenesis: un update on established and emerging basic concepts
Erica Novo, Claudia Bocca, Beatrice Foglia, Francesca Protopapa, Marina Maggiora, Maurizio Parola, Stefania Cannito
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics.2020; 689: 108445. CrossRef - Relative contribution of fat diet and physical inactivity to the development of metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fat liver disease in Wistar rats
Antonio Bovolini, Juliana Garcia, Maria Amparo Andrade, José Alberto Duarte
Physiology & Behavior.2020; 225: 113040. CrossRef - Novel hepatoprotective role of Leonurine hydrochloride against experimental non-alcoholic steatohepatitis mediated via AMPK/SREBP1 signaling pathway
Li Zhang, Hui-Xia Li, Wu-Si Pan, Farhan Ullah Khan, Cheng Qian, Feng-Rong Qi-Li, Xiaojun Xu
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2019; 110: 571. CrossRef - Association Between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Future Deterioration of Metabolic Health: A Cohort Study
You‐Cheol Hwang, Hong‐Yup Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park
Obesity.2019; 27(8): 1360. CrossRef - Tumorigenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic potential of exosomes in liver cancer
Hongbo Wang, Zaiming Lu, Xiangxuan Zhao
Journal of Hematology & Oncology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Elastography in the Diagnosis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Elena N. Shirokova, Chavdar S. Pavlov, Anna D. Karaseva, Aliya M. Alieva, Alla V. Sedova, Vladimir T. Ivashkin
Annals of the Russian academy of medical sciences.2019; 74(1): 5. CrossRef - Curcumin Recovers Intracellular Lipid Droplet Formation Through Increasing Perilipin 5 Gene Expression in Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells In Vitro
Xiao-qun Han, San-qing Xu, Jian-guo Lin
Current Medical Science.2019; 39(5): 766. CrossRef - Lipid mediators of liver injury in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Suthat Liangpunsakul, Naga Chalasani
American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology.2019; 316(1): G75. CrossRef - Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues
Maurizio Parola, Massimo Pinzani
Molecular Aspects of Medicine.2019; 65: 37. CrossRef - Ostreolysin induces browning of adipocytes and ameliorates hepatic steatosis
Lili Nimri, Katerina Staikin, Irena Peri, Einav Yehuda‐Shnaidman, Betty Schwartz
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2018; 33(12): 1990. CrossRef - miRNAs in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Chang-Hai Liu, Javier Ampuero, Antonio Gil-Gómez, Rocío Montero-Vallejo, Ángela Rojas, Rocío Muñoz-Hernández, Rocío Gallego-Durán, Manuel Romero-Gómez
Journal of Hepatology.2018; 69(6): 1335. CrossRef - Efficient scalable production of therapeutic microvesicles derived from human mesenchymal stem cells
Jae Min Cha, Eun Kyoung Shin, Ji Hee Sung, Gyeong Joon Moon, Eun Hee Kim, Yeon Hee Cho, Hyung Dal Park, Hojae Bae, Jinseok Kim, Oh Young Bang
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in the Structure of the Liver during Obesity (Literature Review)
V. I. Prymachenko
Ukraïnsʹkij žurnal medicini, bìologìï ta sportu.2018; 4(2): 45. CrossRef - Recent Insights into the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Juan Pablo Arab, Marco Arrese, Michael Trauner
Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease.2018; 13(1): 321. CrossRef - Apoptosis and non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases
Tatsuo Kanda, Shunichi Matsuoka, Motomi Yamazaki, Toshikatsu Shibata, Kazushige Nirei, Hiroshi Takahashi, Tomohiro Kaneko, Mariko Fujisawa, Teruhisa Higuchi, Hitomi Nakamura, Naoki Matsumoto, Hiroaki Yamagami, Masahiro Ogawa, Hiroo Imazu, Kazumichi Kuroda
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2018; 24(25): 2661. CrossRef - Immunotherapy with oral administration of humanized anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody: a novel gut-immune system-based therapy for metaflammation and NASH
Y Ilan, K Shailubhai, A Sanyal
Clinical and Experimental Immunology.2018; 193(3): 275. CrossRef - Long-term exposure to high-sucrose diet down-regulates hepatic endoplasmic reticulum-stress adaptive pathways and potentiates de novo lipogenesis in weaned male mice
Karla Frida Torres Flister, Bruno Araújo Serra Pinto, Lucas Martins França, Caio Fernando Ferreira Coêlho, Pâmela Costa dos Santos, Caroline Castro Vale, Daniela Kajihara, Victor Debbas, Francisco Rafael Martins Laurindo, Antonio Marcus de Andrade Paes
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2018; 62: 155. CrossRef - Blood-based novel biomarkers for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Yun Qiu, Sufan Wang, Ting Wan, Mingtong Ye, Rui Jiang, Lei Pei, Lili Yang
Biomarkers in Medicine.2018; 12(5): 501. CrossRef - The effect of cannabinoid receptor 1 blockade on hepatic free fatty acid profile in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Bojan Jorgačević, Danijela Vučević, Ivana Đuričić, Slađana Šobajić, Dušan Mladenović, Milena Vesković, Rada Ješić Vukićević, Tatjana Radosavljević
Chemistry and Physics of Lipids.2017; 204: 85. CrossRef - Ezetimibe ameliorates steatohepatitis via AMP activated protein kinase-TFEB-mediated activation of autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition
Soo Hyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, Dai Hoon Han, Milim Lee, Irene Kim, Bohkyung Kim, Kook Hwan Kim, Young-Mi Song, Jeong Eun Yoo, Hye Jin Wang, Soo Han Bae, Yong-Ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Myung-Shik Lee
Autophagy.2017; 13(10): 1767. CrossRef - Obesity is more closely related with hepatic steatosis and fibrosis measured by transient elastography than metabolic health status
Ji Hye Huh, Kwang Joon Kim, Seung Up Kim, Seung Hwan Han, Kwang-Hyub Han, Bong-Soo Cha, Choon Hee Chung, Byung-Wan Lee
Metabolism.2017; 66: 23. CrossRef - Significant liver fibrosis assessed using liver transient elastography is independently associated with low bone mineral density in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Gyuri Kim, Kwang Joon Kim, Yumie Rhee, Sung-Kil Lim, Salvatore Petta
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(7): e0182202. CrossRef - Increased risk for development of coronary artery calcification in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and systemic inflammation
Jihyun Kim, Da Young Lee, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Susanne Kaser
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(7): e0180118. CrossRef - Ameliorative effects of Compound K and ginsenoside Rh1 on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats
Xu-Jia Chen, Wen-Jing Liu, Meng-Liang Wen, Hong Liang, Shao-Mei Wu, Yun-Zhen Zhu, Jiang-Yuan Zhao, Xiang-Qian Dong, Ming-Gang Li, Li Bian, Cheng-Gang Zou, Lan-Qing Ma
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Loss of miR-141/200c ameliorates hepatic steatosis and inflammation by reprogramming multiple signaling pathways in NASH
Melanie Tran, Sang-Min Lee, Dong-Ju Shin, Li Wang
JCI Insight.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Galectin-3 and IL-33/ST2 axis roles and interplay in diet-induced steatohepatitis
Nada Pejnovic, Ilija Jeftic, Nemanja Jovicic, Nebojsa Arsenijevic, Miodrag L Lukic
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2016; 22(44): 9706. CrossRef - Hepatocyte mitochondrial DNA released in microparticles and toll‐like receptor 9 activation: A link between lipotoxicity and inflammation during nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Maria Eugenia Inzaugarat, Alexander Wree, Ariel E. Feldstein
Hepatology.2016; 64(2): 669. CrossRef - Metabolic aspects of adult patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Ludovico Abenavoli, Natasa Milic, Laura Di Renzo, Tomislav Preveden, Milica Medić-Stojanoska, Antonino De Lorenzo
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2016; 22(31): 7006. CrossRef - Pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Recent solutions, unresolved issues, and future research directions
Maria Grazia Clemente, Claudia Mandato, Marco Poeta, Pietro Vajro
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2016; 22(36): 8078. CrossRef - Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Health: The Potential Beneficial Effects of a Medium Chain Triglyceride Diet in Obese Individuals
Sabri Rial, Antony Karelis, Karl-F. Bergeron, Catherine Mounier
Nutrients.2016; 8(5): 281. CrossRef
- Walnut fruit diaphragm ethanol extract ameliorates damage due to Triton WR‐1339‐induced hyperlipidemia in rats
- Cause-of-Death Trends for Diabetes Mellitus over 10 Years.
- Su Kyung Park, Mi Kyoung Park, Ji Hye Suk, Mi Kyung Kim, Yong Ki Kim, In Ju Kim, Yang Ho Kang, Kwang Jae Lee, Hyun Seung Lee, Chang Won Lee, Bo Hyun Kim, Kyung Il Lee, Mi Kyoung Kim, Duk Kyu Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(1):65-72. Published online February 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.1.65
- 2,637 View
- 39 Download
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Recently, diabetic mortality is lower than ever before, likely due to dramatic improvements in diabetes care. This study set to analyze changes in the cause of death in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in the past 10 years. METHODS: All subjects were T2DM patients over the age of 30 whose death certificates were issued at six hospitals in the Busan metropolitan area from 2000 to 2004. The patients were excluded if they had been clinically diagnosed with significant tuberculosis, liver, thyroid, renal, connective tissue diseases and cancers, prior to T2DM diagnosis. We classified the cause of death into several groups by KCD-4. The results were compared with published data on the period from 1990 to 1994. RESULTS: The study comprised 680 patients, of which 374 (55.0%) were male. The average age of death was 66.3 +/- 10.7 years. The most common cause of death was cardiovascular disease (30.6%), followed by infectious disease (25.3%), cancer (21.9%), congestive heart failure (7.1%), renal disease (4.7%), liver disease (2.7%), and T2DM itself (1.9%). In the study from the earlier period, the most common cause of death was also cardiovascular disease (37.6%), followed by infectious disease (24.2%), T2DM (6.0%), liver disease (5.4%), cancer (4.7%), and renal disease (3.3%). CONCLUSION: Over both study periods, the first and second cause of death in T2DM were cardiovascular disease and infectious disease, respectively. However, death by cerebral infarction among cardiovascular disease patients was significantly lower in the latter period, while death by malignancy was markedly increased. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Socio-Economic Cost of Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Using National Health Insurance Claim Data, 2017
Heesun Kim, Eun-Jung Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(9): 1601. CrossRef - Arterial stiffness is an independent predictor for risk of mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the REBOUND study
Jeong Mi Kim, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, Jong Ho Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Soon Hee Lee, Chang Won Lee, Min Chul Kim, Jun Hyeob Ahn, Jinmi Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Mentors, The Social Support and Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Yu Jeong Park
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2019; 20(2): 112. CrossRef - How to build nomogram for type 2 diabetes using a naïve Bayesian classifier technique
Jae-Cheol Park, Jea-Young Lee
Journal of Applied Statistics.2018; 45(16): 2999. CrossRef - Impact of change in job status on mortality for newly onset type II diabetes patients: 7 years follow-up using cohort data of National Health Insurance, Korea
Donggyo Shin, Ji Man Kim, Tinyami Erick Tandi, Eun-Cheol Park
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2016; 10(1): S1. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Poor Glycemic Control among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2010-2012)
Jinhyun Park, Seungji Lim, Eunshil Yim, Youngdae Kim, Woojin Chung
Health Policy and Management.2016; 26(2): 125. CrossRef - Mortality and causes of death in a national sample of type 2 diabetic patients in Korea from 2002 to 2013
Yu Mi Kang, Ye-Jee Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee, Chang Hee Jung
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of Cell Phone Application for Blood Glucose Self-Monitoring Based on ISO/IEEE 11073 and HL7 CCD
Hyun Sang Park, Hune Cho, Hwa Sun Kim
Healthcare Informatics Research.2015; 21(2): 83. CrossRef - Cost-Utility Analysis of Screening Strategies for Diabetic Retinopathy in Korea
Sang-Won Kim, Gil-Won Kang
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2015; 30(12): 1723. CrossRef - Quality characteristics of brown rice boiled with medicinal herbs extract for diabetes prevention
Kyung-Mi Yang, Jung-Ran Park, Su-Jung Hwang
Korean Journal of Food Preservation.2014; 21(1): 55. CrossRef - Does Diabetes Mellitus Influence Standardized Uptake Values of Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography in Colorectal Cancer?
Da Yeon Oh, Ji Won Kim, Seong-Joon Koh, Mingoo Kim, Ji Hoon Park, Su Yeon Cho, Byeong Gwan Kim, Kook Lae Lee, Jong Pil Im
Intestinal Research.2014; 12(2): 146. CrossRef - The Relationship between Metformin and Cancer in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Hyun Hee Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Ji Sung Yoon, Hyoung Woo Lee, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(2): 125. CrossRef - Relationship between Milk and Calcium Intake and Lipid Metabolism in Female Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
JaeHee Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang, Ki Nam Kim, Young-Ju Choi, Namsoo Chang, Kap-Bum Huh
Yonsei Medical Journal.2013; 54(3): 626. CrossRef - Comorbidity Study on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Data Mining
Hye Soon Kim, A Mi Shin, Mi Kyung Kim, Yoon Nyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2012; 27(2): 197. CrossRef - Glucose, Blood Pressure, and Lipid Control in Korean Adults with Diagnosed Diabetes
Sun-Joo Boo
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(4): 406. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Eating Habits and Food Intake in Women with Gestational Diabetes according to Early Postpartum Glucose Tolerance Status
You Jeong Hwang, Bo Kyung Park, Sunmin Park, Sung-Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(4): 354. CrossRef - Diabetes and Cancer: Is Diabetes Causally Related to Cancer?
Sunghwan Suh, Kwang-Won Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(3): 193. CrossRef - The Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Colorectal Cancer
Byeong Do Yi, Young Pil Bae, Bong Gun Kim, Jong Wha Park, Dong Hyun Kim, Ja Young Park, Seong Ho Choi, Hee Seung Park, Jae Seung Lee, Chang Won Lee, Sang Soo Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Moon Ki Choi, In Joo Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2011; 26(2): 126. CrossRef - The Hypoglycemic Effect of Complex of Chinese Traditional Herbs (CTH) and Macelignan in Type 2 Diabetic Animal Model
Journal of Life Science.2010; 20(7): 1113. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Coronary Artery Calcification and Serum Apolipoprotein A-1 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Hyun Ae Seo, Yeon Kyung Choi, Jae Han Jeon, Jung Eun Lee, Ji Yun Jeong, Seong Su Moon, In Kyu Lee, Bo Wan Kim, Jung Guk Kim
Korean Diabetes Journal.2009; 33(6): 485. CrossRef - Epidemiologic Characteristics of Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: Current Status of Diabetic Patients Using Korean Health Insurance Database
Ie Byung Park, Sei Hyun Baik
Korean Diabetes Journal.2009; 33(5): 357. CrossRef - Cause-of-Death Trends for Diabetes Mellitus over 10 Years (Korean Diabetes J 33(1):65-72, 2009)
Hae Jin Kim
Korean Diabetes Journal.2009; 33(2): 164. CrossRef
- The Socio-Economic Cost of Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Using National Health Insurance Claim Data, 2017
- Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS) Expression in the Hypoxic Injury to Pancreatic Beta (MIN6) Cells.
- Seung Hyun Ko, Seung Bum Kim, Kyung Ryul Ryu, Ji Won Kim, Yu Bai Ahn, Sung Dae Moon, Sung Rae Kim, Jung Min Lee, Hyuk Snag Kwon, Kun Ho Yoon, Ki Ho Song
- Korean Diabetes J. 2006;30(5):336-346. Published online September 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2006.30.5.336
- 2,183 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Islet transplantation is an alternative potential strategy to cure type 1 diabetes mellitus. However, two or more donors are usually needed for one recipient because a substantial part of the graft becomes nonfunctional due to several factors including hypoxia. Though hypoxic exposure of pancreatic beta cells has been reported to induce apoptotic cell death, the molecular processes involved in hypoxia-induced cell death are poorly understood. In type I diabetes, Nitric Oxide (NO) is known as an important cytokine, involved in the pathogenesis of beta cell dysfunction. Pancreatic beta cells are sensitive to the induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) when stimulated by TNF-a or IL-1beta. But contribution of iNOS in response to hypoxia is not yet fully understood. METHODS: Mouse insulinoma cells (MIN6) were incubated in an anaerobic chamber (75% N2/15% CO2/5% H2) for up to 12 hours. Cell viability was measured after AO/PI staining. Caspase-3 activation was also determined using Western blot analysis. Nitric Oxide (NO) release into culture medium was measured using a Griess reagent. The expression of iNOS and PDX-1 mRNA and iNOS protein was examined using real time PCR and Western blot analysis. RESULTS: Marked cell death was observed within 6 hours after hypoxic exposure of MIN6 cells (control, < 5%; 2 hr, 11.0+/-7.6%; 6 hr, 46.2+/-12.8%, P < 0.05). Immunoreactivity to activated caspase-3 was observed at 2, 4 and 6 hrs. NO production was increased in a time dependent manner. Expression of iNOS mRNA and protein was significantly increased at 4 and 6 hour after hypoxia. iNOS expression was confirmed by immunostaining. Of note, Pdx-1 mRNA expression was markedly attenuated by hypoxic treatment. Pretreatment with a selective iNOS inhibitor, 1400 W, significantly prevented beta cell death induced by hypoxic injury. CONCLUSION: Our data suggest that iNOS-NO play an important role in hypoxic injury to MIN6 cells. Therefore, iNOS-NO might be a potential therapeutic target for improving engraftment of the transplanted islets and suppression of iNOS would be helpful for prevention of beta cells damage to hypoxic injury.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





