
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug/Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Self-Titration Algorithms of Insulin Glargine 300 units/mL in Individuals with Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (The Korean TITRATION Study): A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Jae Hyun Bae, Chang Ho Ahn, Ye Seul Yang, Sun Joon Moon, Soo Heon Kwak, Hye Seung Jung, Kyong Soo Park, Young Min Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):71-80. Published online June 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0274
- 7,974 View
- 434 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
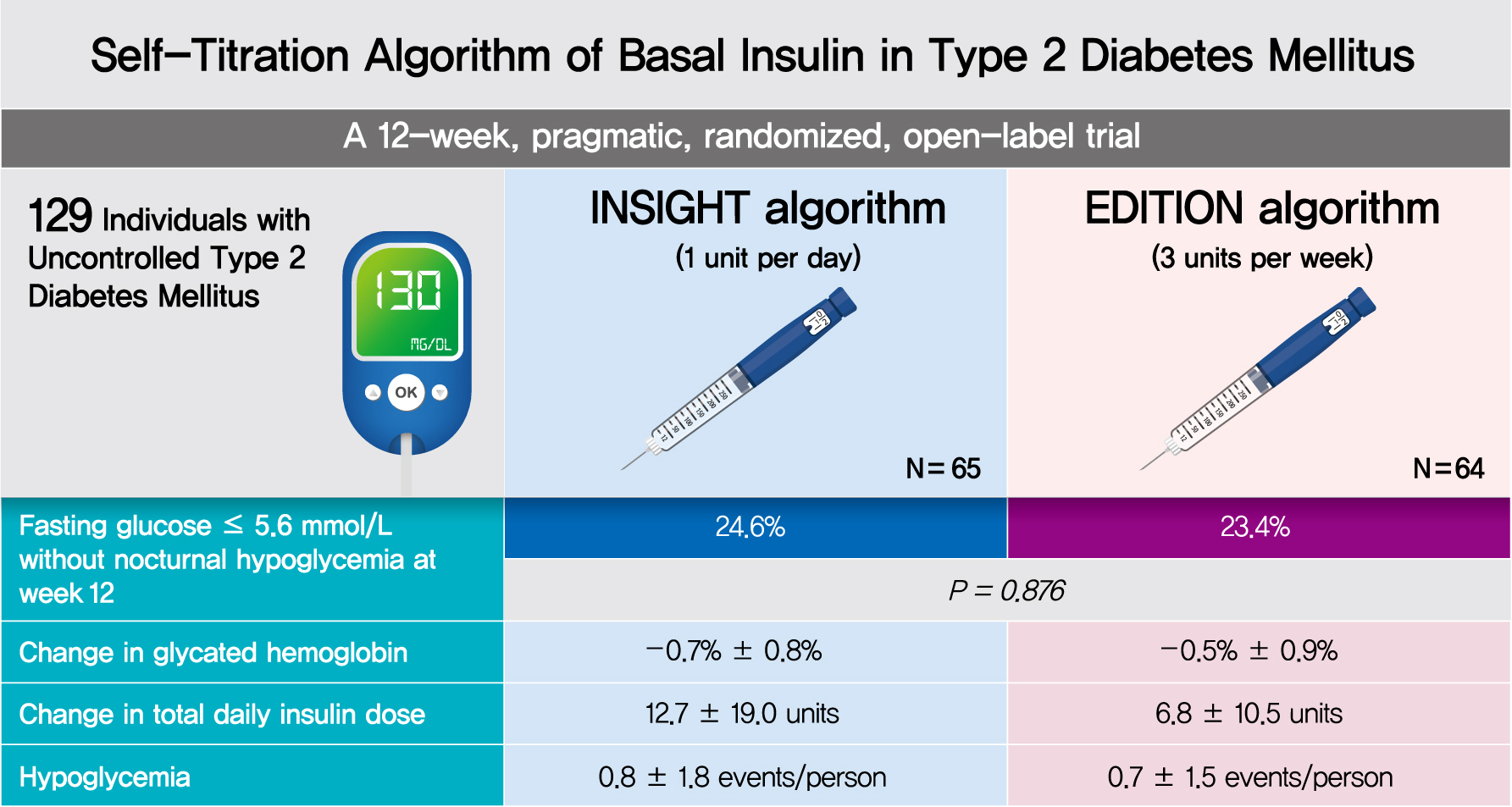
To compare the efficacy and safety of two insulin self-titration algorithms, Implementing New Strategies with Insulin Glargine for Hyperglycemia Treatment (INSIGHT) and EDITION, for insulin glargine 300 units/mL (Gla-300) in Korean individuals with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
In a 12-week, randomized, open-label trial, individuals with uncontrolled T2DM requiring basal insulin were randomized to either the INSIGHT (adjusted by 1 unit/day) or EDITION (adjusted by 3 units/week) algorithm to achieve a fasting self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) in the range of 4.4 to 5.6 mmol/L. The primary outcome was the proportion of individuals achieving a fasting SMBG ≤5.6 mmol/L without noct urnal hypoglycemia at week 12.
Results
Of 129 individuals (age, 64.1±9.5 years; 66 [51.2%] women), 65 and 64 were randomized to the INSIGHT and EDITION algorithms, respectively. The primary outcome of achievement was comparable between the two groups (24.6% vs. 23.4%, P=0.876). Compared with the EDITION group, the INSIGHT group had a greater reduction in 7-point SMBG but a similar decrease in fasting plasma glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin. The increment of total daily insulin dose was significantly higher in the INSIGHT group than in the EDITION group (between-group difference: 5.8±2.7 units/day, P=0.033). However, body weight was significantly increased only in the EDITION group (0.6±2.4 kg, P=0.038). There was no difference in the occurrence of hypoglycemia between the two groups. Patient satisfaction was significantly increased in the INSIGHT group (P=0.014).
Conclusion
The self-titration of Gla-300 using the INSIGHT algorithm was effective and safe compared with that using the EDITION algorithm in Korean individuals with uncontrolled T2DM (ClinicalTrials.gov number: NCT03406663). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Basal insulin titration algorithms in patients with type 2 diabetes: the simplest is the best (?)
V.I. Katerenchuk
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(1): 72. CrossRef - Issues of insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes and ways to solve them
V.I. Katerenchuk, A.V. Katerenchuk
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(3): 240. CrossRef - Time for Using Machine Learning for Dose Guidance in Titration of People With Type 2 Diabetes? A Systematic Review of Basal Insulin Dose Guidance
Camilla Heisel Nyholm Thomsen, Stine Hangaard, Thomas Kronborg, Peter Vestergaard, Ole Hejlesen, Morten Hasselstrøm Jensen
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2022; : 193229682211459. CrossRef
- Basal insulin titration algorithms in patients with type 2 diabetes: the simplest is the best (?)
- Clinical Diabetes and Therapeutics
- Hospital-Based Korean Diabetes Prevention Study: A Prospective, Multi-Center, Randomized, Open-Label Controlled Study
- Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Jeong-Taek Woo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(1):49-58. Published online November 2, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0033
- 5,307 View
- 131 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) continues to increase, and the disease burden is the highest of any medical condition in Korea. However, large-scale clinical studies have not yet conducted to establish the basis for diabetes prevention in Korea.
Methods The hospital-based Korean Diabetes Prevention Study (H-KDPS) is a prospective, multi-center, randomized, open-label controlled study conducted at university hospitals for the purpose of gathering data to help in efforts to prevent type 2 DM. Ten university hospitals are participating, and 744 subjects will be recruited. The subjects are randomly assigned to the standard care group, lifestyle modification group, or metformin group, and their clinical course will be observed for 36 months.
Results All intervention methodologies were developed, validated, and approved by Korean Diabetes Association (KDA) multi-disciplinary team members. The standard control group will engage in individual education based on the current KDA guidelines, and the lifestyle modification group will participate in a professionally guided healthcare intervention aiming for ≥5% weight loss. The metformin group will begin dosing at 250 mg/day, increasing to a maximum of 1,000 mg/day. The primary endpoint of this study is the cumulative incidence of DM during the 3 years after randomization.
Conclusion The H-KDPS study is the first large-scale clinical study to establish evidence-based interventions for the prevention of type 2 DM in Koreans. The evidence gathered by this study will be useful for enhancing the health of Koreans and improving the stability of the Korean healthcare system (Trial registration: CRIS KCT0002260, NCT02981121).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estimating insulin sensitivity and β-cell function from the oral glucose tolerance test: validation of a new insulin sensitivity and secretion (ISS) model
Joon Ha, Stephanie T. Chung, Max Springer, Joon Young Kim, Phil Chen, Aaryan Chhabra, Melanie G. Cree, Cecilia Diniz Behn, Anne E. Sumner, Silva A. Arslanian, Arthur S. Sherman
American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 326(4): E454. CrossRef - Development and Adaptability of Smartphone-based Dietary Coaching Program for Patients Undergoing Diabetes and Prediabetes with Continuous Glucose Monitoring Device
Myoung Soo Kim, Jung Mi Ryu, Minkyeong Kang, Jiwon Park, Yeh Chan Ahn, Yang Seok Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(1): 36. CrossRef - Improving Machine Learning Diabetes Prediction Models for the Utmost Clinical Effectiveness
Juyoung Shin, Joonyub Lee, Taehoon Ko, Kanghyuck Lee, Yera Choi, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(11): 1899. CrossRef - Impaired fasting glucose levels in overweight or obese subjects for screening of type 2 diabetes in Korea
Jin-Hee Lee, Suk Chon, Seon-Ah Cha, Sun-Young Lim, Kook-Rye Kim, Jae-Seung Yun, Sang Youl Rhee, Kun-Ho Yoon, Yu-Bae Ahn, Jeong-Taek Woo, Seung-Hyun Ko
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2021; 36(2): 382. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Based Diabetes Prediction System Using a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort
Sang Youl Rhee, Ji Min Sung, Sunhee Kim, In-Jeong Cho, Sang-Eun Lee, Hyuk-Jae Chang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 515. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Kyu Yeon Hur, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Soo-Kyung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Jong Ha Baek, Junghyun Noh, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Ye Seul Yang, Jang Won Son, Jong Han Choi, Kee Ho Song, Nam Hoon Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jin Wha Kim,
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 461. CrossRef - Short-Term Effects of the Internet-Based Korea Diabetes Prevention Study: 6-Month Results of a Community-Based Randomized Controlled Trial
Jin-Hee Lee, Sun-Young Lim, Seon-Ah Cha, Chan-Jung Han, Ah Reum Jung, Kook-Rye Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 960. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Seung-Hyun Ko
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 244. CrossRef - Optimal fasting plasma glucose and haemoglobin A1c levels for screening of prediabetes and diabetes according to 2‐hour plasma glucose in a high‐risk population: The Korean Diabetes Prevention Study
Seon‐Ah Cha, Suk Chon, Jae‐Seung Yun, Sang Youl Rhee, Sun‐Young Lim, Kun‐Ho Yoon, Yu‐Bae Ahn, Seung‐Hyun Ko, Jeong‐Taek Woo, Jin‐Hee Lee
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - How was the Diabetes Metabolism Journal added to MEDLINE?
Hye Jin Yoo
Science Editing.2020; 7(2): 201. CrossRef - Commercial Postural Devices: A Review
Nicole Kah Mun Yoong, Jordan Perring, Ralph Jasper Mobbs
Sensors.2019; 19(23): 5128. CrossRef - Changes in Metabolic Profile Over Time: Impact on the Risk of Diabetes
Yunjung Cho, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 407. CrossRef - Metformin for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in persons at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Kasper S Madsen, Yuan Chi, Maria-Inti Metzendorf, Bernd Richter, Bianca Hemmingsen
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Estimating insulin sensitivity and β-cell function from the oral glucose tolerance test: validation of a new insulin sensitivity and secretion (ISS) model
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Diabetes Prevention in Australia: 10 Years Results and Experience
- James A. Dunbar
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(3):160-167. Published online February 2, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.3.160
- 4,871 View
- 69 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of lifestyle modification for the prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus but it was achieved at higher cost than can be sustained in routine health services. The first clinical trial to report was the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study. This paper describes how Australia worked with Finnish colleagues to adapt the findings of that study to achieve a statewide diabetes prevention program. Small evaluative, effectiveness trials have been conducted in a number of countries to see if the results of the clinical trials can be replicated in routine health services. The Australian evaluative trial, Greater Green Triangle Diabetes Prevention Program is described in detail to demonstrate the ingredients for success in moving a program from one country to another. Few countries have managed to scale up from evaluative trials to statewide or national programs. The Australian experience is described in detail including lessons learned about what reduced the effectiveness, particularly the need for policy makers in government, people from the implementing organisation and researchers to work together from the start of the evaluative trial and throughout the first 5 years of a national program.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Miscarriage, stillbirth and the risk of diabetes in women: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Qiqi You, Qingqing Jiang, Irakoze Shani, Yiling Lou, Shen Huang, Shiqi Wang, Shiyi Cao
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 195: 110224. CrossRef - A multiple case study of pre-diabetes care undertaken by general practice in Aotearoa/New Zealand: de-incentivised and de-prioritised work
Christine Barthow, Jeremy Krebs, Eileen McKinlay
BMC Primary Care.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Implementation of a diabetes prevention programme in a multi-ethnic community in primary care in England: An evaluation using constructs from the RE-AIM Framework
Helen Dallosso, Kamlesh Khunti, Laura J. Gray, Kerry Hulley, Mel Ghaly, Naina Patel, Joe Kai, Navneet Aujla, Melanie J. Davies, Tom Yates
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(4): 309. CrossRef - A critical realist exploration of factors influencing engagement in diabetes prevention programs in rural settings
Britney McMullen, Kerith Duncanson, David Schmidt, Clare Collins, Lesley MacDonald-Wicks
Australian Journal of Primary Health.2023; 29(5): 510. CrossRef - Characteristics of participants in the first fully online National Diabetes Prevention Programme: A quantitative survey
Clair Haseldine, Gráinne O'Donoghue, Patricia M Kearney, Fiona Riordan, Margaret Humphreys, Liz Kirby, Sheena McHugh
HRB Open Research.2023; 6: 61. CrossRef - Delivering the Diabetes Remission Clinical Trial (DiRECT) in primary care: Experiences of healthcare professionals
Lucia Rehackova, Roy Taylor, Mike Lean, Alison Barnes, Louise McCombie, George Thom, Naomi Brosnahan, Wilma S. Leslie, Falko F. Sniehotta
Diabetic Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - It is time for a more targeted approach to prediabetes in primary care in Aotearoa New Zealand
Christine Barthow, Sue Pullon, Eileen McKinlay, Jeremy Krebs, Stokes Tim
Journal of Primary Health Care.2022; 14(4): 372. CrossRef - Implementing a national diabetes prevention programme in England: lessons learned
Jonathan Stokes, Judith Gellatly, Peter Bower, Rachel Meacock, Sarah Cotterill, Matt Sutton, Paul Wilson
BMC Health Services Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - How do we identify people at high risk of Type 2 diabetes and help prevent the condition from developing?
J. Fagg, J. Valabhji
Diabetic Medicine.2019; 36(3): 316. CrossRef - Associations between physical activity and cataract treated surgically in patients with diabetes: findings from the 45 and Up Study
Changfan Wu, Xiaotong Han, Xixi Yan, Xianwen Shang, Lei Zhang, Mingguang He
British Journal of Ophthalmology.2019; 103(8): 1099. CrossRef - Usefulness of a Novel Mobile Diabetes Prevention Program Delivery Platform With Human Coaching: 65-Week Observational Follow-Up
Andreas Michaelides, Jennifer Major, Edmund Pienkosz Jr, Meghan Wood, Youngin Kim, Tatiana Toro-Ramos
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2018; 6(5): e93. CrossRef
- Miscarriage, stillbirth and the risk of diabetes in women: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Clinical Care/Education
- Insulin Initiation in Insulin-Naïve Korean Type 2 Diabetic Patients Inadequately Controlled on Oral Antidiabetic Drugs in Real-World Practice: The Modality of Insulin Treatment Evaluation Study
- Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, Yong Ki Kim, Kun Ho Yoon, Ho Young Son, Sung Woo Park, Yeon Ah Sung, Hong Sun Baek
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(6):481-488. Published online November 25, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.6.481
- 3,978 View
- 69 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The Modality of Insulin Treatment Evaluation (MOTIV) study was performed to provide real-world data concerning insulin initiation in Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients with inadequate glycemic control with oral hypoglycemic agents (OHAs).
Methods This multicenter, non-interventional, prospective, observational study enrolled T2DM patients with inadequate glycemic control (glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] ≥7.0%) who had been on OHAs for ≥3 months and were already decided to introduce basal insulin by their physician prior to the start of the study. All treatment decisions were at the physician's discretion to reflect real-world practice.
Results A total of 9,196 patients were enrolled, and 8,636 patients were included in the analysis (mean duration of diabetes, 8.9 years; mean HbA1c, 9.2%). Basal insulin plus one OHA was the most frequently (51.0%) used regimen. After 6 months of basal insulin treatment, HbA1c decreased to 7.4% and 44.5% of patients reached HbA1c <7%. Body weight increased from 65.2 kg to 65.5 kg, which was not significant. Meanwhile, there was significant increase in the mean daily insulin dose from 16.9 IU at baseline to 24.5 IU at month 6 (
P <0.001). Overall, 17.6% of patients experienced at least one hypoglycemic event.Conclusion In a real-world setting, the initiation of basal insulin is an effective and well-tolerated treatment option in Korean patients with T2DM who are failing to meet targets with OHA therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Real-World Outcomes of Individualized Targeted Therapy with Insulin Glargine 300 Units/mL in Insulin-Naïve Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes: TOBE Study
Eun-Gyoung Hong, Kyung-Wan Min, Jung Soo Lim, Kyu-Jeung Ahn, Chul Woo Ahn, Jae-Myung Yu, Hye Soon Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Won Kim, Dong Han Kim, Hak Chul Jang
Advances in Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Evidence and Practice-Based Guidelines on the Utility of Basal
Insulin Combined Oral Therapy (Metformin and Glimepiride) in the
Current Era
Abhishek Shrivastava, Jothydev Kesavadev, Viswanathan Mohan, Banshi Saboo, Dina Shrestha, Anuj Maheshwari, Brij Mohan Makkar, Kirtikumar D. Modi, Ashok Kumar Das
Current Diabetes Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Where to Initiate Basal Insulin Therapy: Inpatient or Outpatient Department? Real-World Observation in China
Minyuan Chen, Puhong Zhang, Yang Zhao, Nadila Duolikun, Linong Ji
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 3375. CrossRef - Therapeutic Effect of Quadruple Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Who Have Insulin Limitations
Won Sang Yoo, Do Hee Kim, Hee Jin Kim, Hyun Kyung Chung
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2019; 20(2): 117. CrossRef - Use of Insulin Glargine 100 U/mL for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in East Asians: A Review
Takahisa Hirose, Ching-Chu Chen, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Jacek Kiljański
Diabetes Therapy.2019; 10(3): 805. CrossRef - Nationwide Trends in Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Cancer Risk Among Patients With Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Receiving Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors
Minyoung Lee, Jiyu Sun, Minkyung Han, Yongin Cho, Ji-Yeon Lee, Chung Mo Nam, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes Care.2019; 42(11): 2057. CrossRef - Insulin therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2017
Byung-Wan Lee, Jin Hwa Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Kyung Mook Choi
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 967. CrossRef - Insulin Therapy for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2017
Byung-Wan Lee, Jin Hwa Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 367. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Vildagliptin in Clinical Practice: Pooled Analysis of Three Korean Observational Studies (the VICTORY Study)
Sunghwan Suh, Sun Ok Song, Jae Hyeon Kim, Hyungjin Cho, Woo Je Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Diabetes Research.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Comparison of Antidiabetic Regimens in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Uncontrolled by Combination Therapy of Sulfonylurea and Metformin: Results of the MOHAS Disease Registry in Korea
Sung Hee Choi, Tae Jung Oh, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(3): 170. CrossRef - Instauration d’une insulinothérapie chez le patient diabétique de type 2 en médecine générale : Comparaison de l’étude belge InsuStar avec quelques études françaises et internationales
A.-J. Scheen
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques.2016; 10(4): 334. CrossRef
- Real-World Outcomes of Individualized Targeted Therapy with Insulin Glargine 300 Units/mL in Insulin-Naïve Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes: TOBE Study

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





