
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
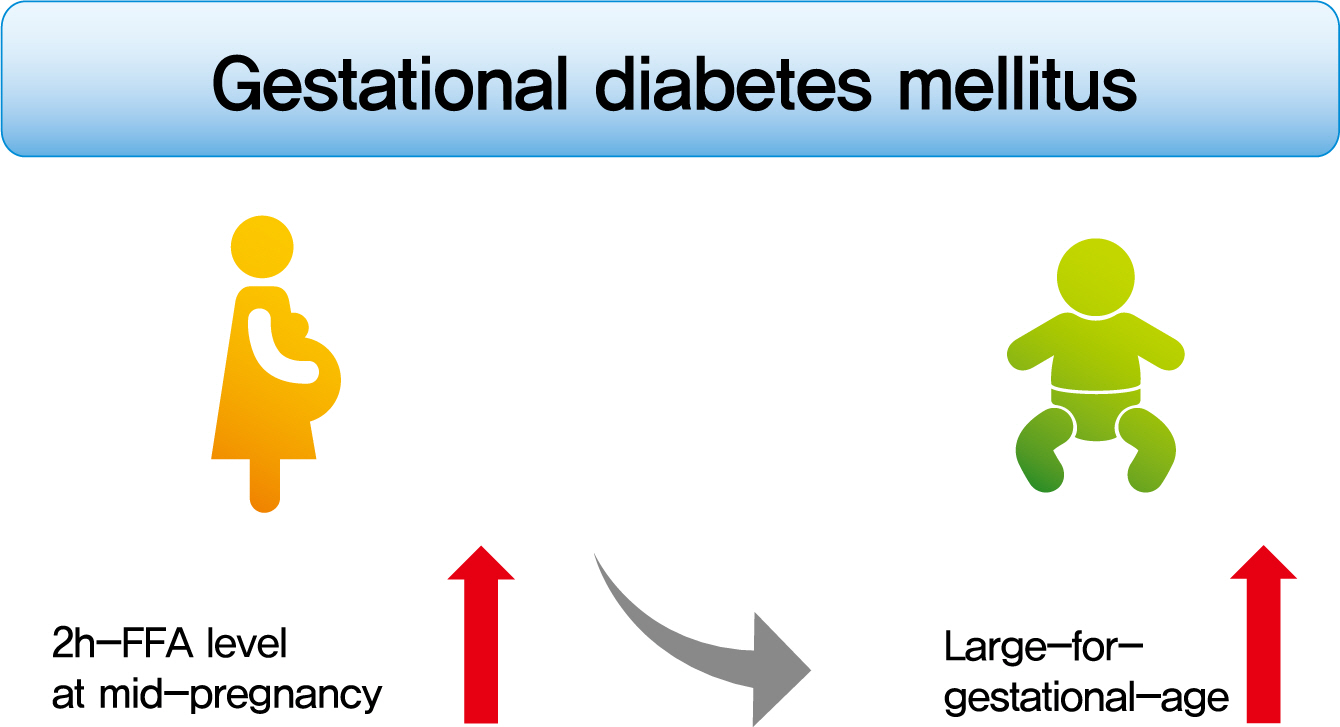
- Postprandial Free Fatty Acids at Mid-Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Large-for-Gestational-Age Newborns in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- So-Yeon Kim, Young Shin Song, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Wook Cho, Kyung-Soo Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):140-148. Published online August 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0023
- 5,080 View
- 160 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To investigate the association between free fatty acid (FFA) level at mid-pregnancy and large-for-gestational-age (LGA) newborns in women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
Methods
We enrolled 710 pregnant women diagnosed with GDM from February 2009 to October 2016. GDM was diagnosed by a ‘two-step’ approach with Carpenter and Coustan criteria. We measured plasma lipid profiles including fasting and 2-hour postprandial FFA (2h-FFA) levels at mid-pregnancy. LGA was defined if birthweights of newborns were above the 90th percentile for their gestational age.
Results
Mean age of pregnant women in this study was 33.1 years. Mean pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI) was 22.4 kg/m2. The prevalence of LGA was 8.3% (n=59). Levels of 2h-FFA were higher in women who delivered LGA newborns than in those who delivered non-LGA newborns (416.7 μEq/L vs. 352.5 μEq/L, P=0.006). However, fasting FFA was not significantly different between the two groups. The prevalence of delivering LGA newborns was increased with increasing tertile of 2h-FFA (T1, 4.3%; T2, 9.8%; T3, 10.7%; P for trend <0.05). After adjustment for maternal age, pre-pregnancy BMI, and fasting plasma glucose, the highest tertile of 2h-FFA was 2.38 times (95% confidence interval, 1.11 to 5.13) more likely to have LGA newborns than the lowest tertile. However, there was no significant difference between groups according to fasting FFA tertiles.
Conclusion
In women with GDM, a high 2h-FFA level (but not fasting FFA) at mid-pregnancy is associated with an increasing risk of delivering LGA newborns. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in free fatty acid profiles in gestational diabetes mellitus
Haoyi Du, Danyang Li, Laura Monjowa Molive, Na Wu
Journal of Translational Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Modulation of gut microbiota and lipid metabolism in rats fed high-fat diets by Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids
Aijun Tong, Weihao Wu, Zhengxin Chen, Jiahui Wen, Ruibo Jia, Bin Liu, Hui Cao, Chao Zhao
Current Research in Food Science.2023; 6: 100427. CrossRef - Fetal Abdominal Obesity Detected at 24 to 28 Weeks of Gestation Persists until Delivery Despite Management of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:547-57)
Wonjin Kim, Soo Kyung Park, Yoo Lee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 970. CrossRef
- Advances in free fatty acid profiles in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Relationship of Insulin-like Growth Factor(IGF)-1, IGF-2, IGF Binding Protein(IGFBP)-3, and Mitochondrial DNA Amount in the Umbilical Cord Blood to Birth Weight.
- Yun Yong Lee, Do Joon Park, Chan Soo Shin, Kyong Soo Park, Hong Kyu Lee, Jong Kwan Jun, Boh Yun Yoon, Jih Yeun Song, Bong Sun Kang
- Korean Diabetes J. 1999;23(1):36-45. Published online January 1, 2001
- 942 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Reaven proposed a syndrome (syndrome X), consisting of glucose intolerance, hypertension, hyperinsulinemia, dyslipidemia, as a clinical entity. The fundamental metabolic defect of this syndrome was recognized as insulin resistance, but the pathophysiology of insulin resistance is not clarified as of yet. Recent evidence, suggests that non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) ancl lipid and cardiovascular abnormalities-syndrome X-are associated with intrauterine growth retar- dation (IUGR). Recently Shin reported that the amounts of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) in a given amount of genomic DNA were lower in NIDDM patients than in healthy controls, and the amount of mtDNA is negatively correlated with blood pressure ancl waist-hip ratio. Birth weight is known to be correlated with levels of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs). The purpose of this study was to identify the correlation of low birth weight with reduced mtDNA and syndrome X. We investigated the relationship of birth weight to IGFs and the amount of mtDNA METHODS: 72 singleton pregnancy babies and their mathers admitted in Seoul National University Hospital from March to May, 1997 were studied. After delivery, the cord blcxxl and maternal venous blood sampling was done. Using the imnnmoradiometric assay (IRMA) the IGF-l, IGF-2, IGFBP-3 was measured from cord and maternal plasma. Among them only 27 pairs samples were measured mtDNA amount with competitive PCR method in their buffy coat. Then statistical analysis was done within these paratneters. RESULTS: Birth weight is correlated significantly with cord plasma IGF-1 (r=0.32, p<0.01), IGFBP-3 (r=0.44, p<0.01), prepregnancy maternal body weight (r=0.45, p<0.01), maternal mtDNA amount (r=0.63, p<0.01). Cord blood mtDNA is correlated with maternal mtDNA amount (r=0.55, p<0,01). In multiple regression analysis, the maternal mtDNA was found to be the only independent factor related to birth weight (p<0.01). COMCLUSION: We have found the correlation between birth weight and maternal prepregnancy body weight and mtDNA amount. The clinical implications of this result remain yet to be deiermined.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





